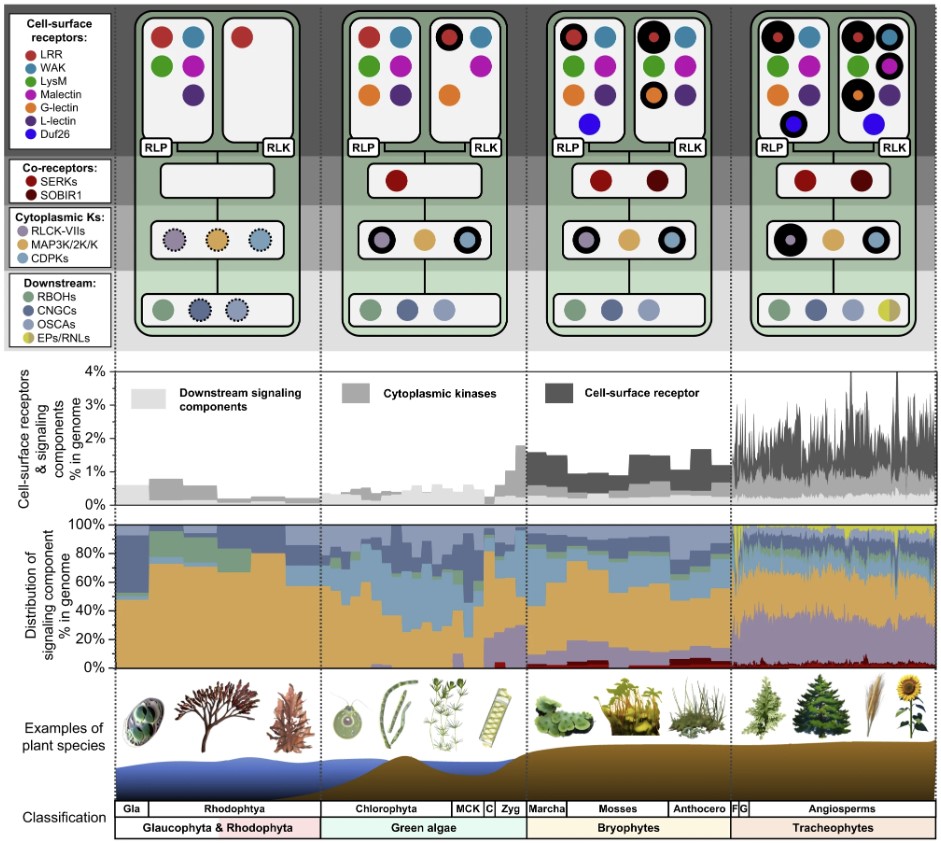
Patterns of evolution: Dissecting the history of pattern recognition receptors from development to immunity
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants use a suite of cell-surface receptors as signal transducers in both development and immunity. In this study, Ngou et al. utilized computational and functional approaches to examine the evolutionary origin of a subclass of plant cell-surface receptors called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs),…

Interactions of plant RETINOBLASTOMA RELATED PROTEINS
Plant Science Research WeeklyRETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED (RBR) is the plant homolog of the metazoan Retinoblastoma protein (pRB) tumor suppressor and is a conserved cell cycle regulator. RBR has been linked to several multicellularity-related processes, such as controlled cell proliferation, stem cell regulation, and asymmetric cell…

Special issue on Grasses (Science)
Plant Science Research Weekly“Grassy biomes—from the steppes of Mongolia to the savannas of Tanzania— are predicted to be the ecosystems hardest hit by the ongoing climate and land use crises,” begins a Perspective by Strömberg and Staver in the August 4, 2022 Science special issue on Grasses that raises awareness of the…
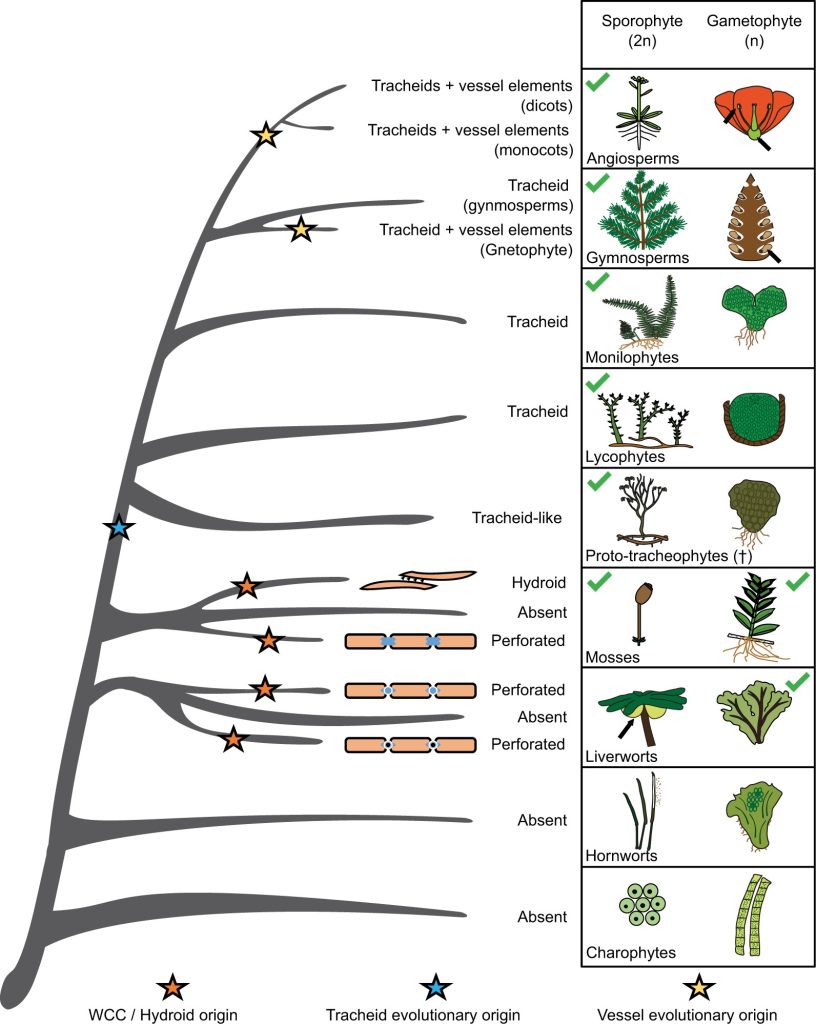
Review: Deep origin and gradual evolution of transporting tissues: Perspectives from across the land plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe development of vascular plants (tracheophytes) was a major innovation during the evolution of land plants. The classic view is that the evolution of transporting tissues is distinct to tracheophytes, but Woudenberg and Renema et al. discuss an alternative hypothesis where this was a gradual process…
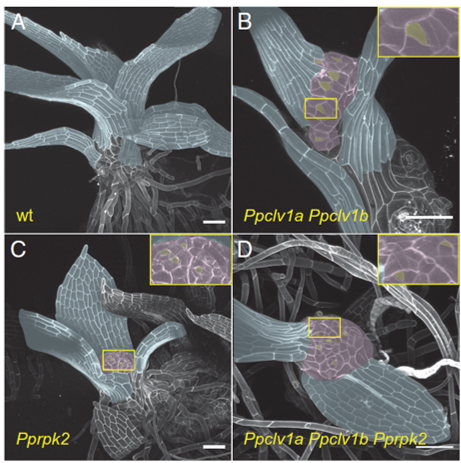
Cytokinin–CLAVATA cross-talk is an ancient mechanism regulating shoot meristem homeostasis in land plants (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe shoot apical meristem (SAM) maintains a small pool of pluripotent stem cells, which are the source of all above-ground plant tissues. In Arabidopsis thaliana, CLAVATA3 (CLV3), CLAVATA1(CLV1) and RECEPTOR-LIKE PROTEIN KINASE2 (RPK2) repress WUSCHEL (WUS) expression. WUS induces CLV3, forming a local…

A conserved superlocus regulates above- and belowground root initiation (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe vascular plant body composed of root and shoot is specified during embryogenesis, but most flowering plants can also develop additional root systems post-embryonically: lateral roots, as a response to wounding, or shoot-borne roots (“adventitious” roots, literally meaning “in the wrong place”).…
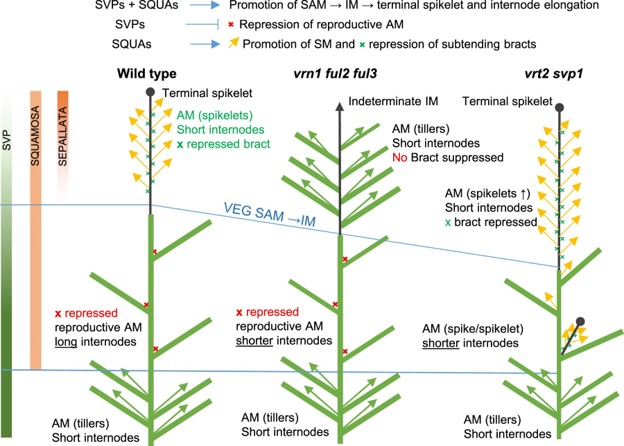
An essential role of MADS-box proteins during wheat spike development (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWheat yields depend on the morphology of the inflorescence known as the spike, which harbors multiple lateral spikelets. To control and manipulate wheat productivity, it is necessary to understand the molecular and genetic mechanisms behind the development of inflorescence architecture. Wheat spike development…
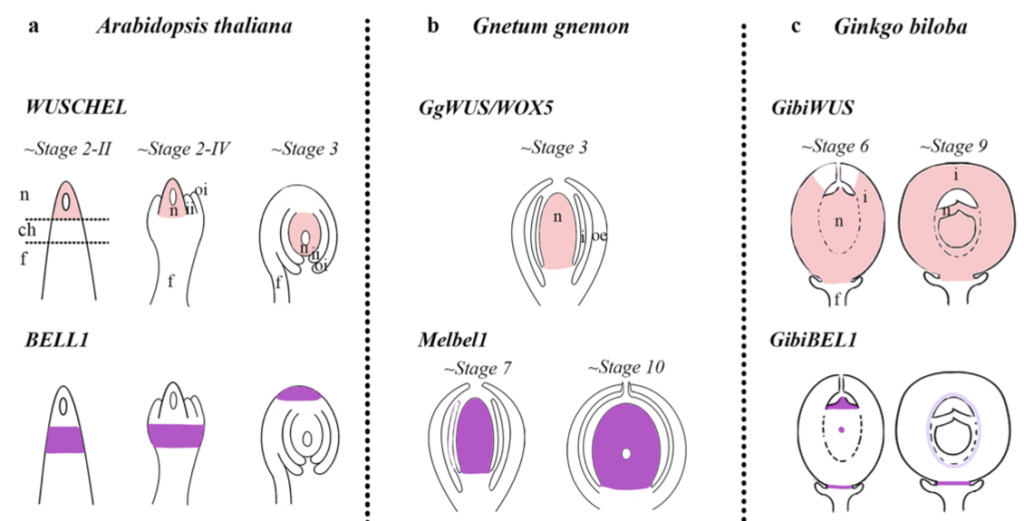
Expression analyses in Ginkgo biloba provide new insights into the evolution and development of the seed (Sci. Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed production was a decisive adaptation that appeared during plant evolution. Not in vain! The most diverse plant lineage today is that of the so-called seed plants, a group that includes gymnosperms and angiosperms. Therefore, it is not surprising that understanding seed origin and evolution has been…
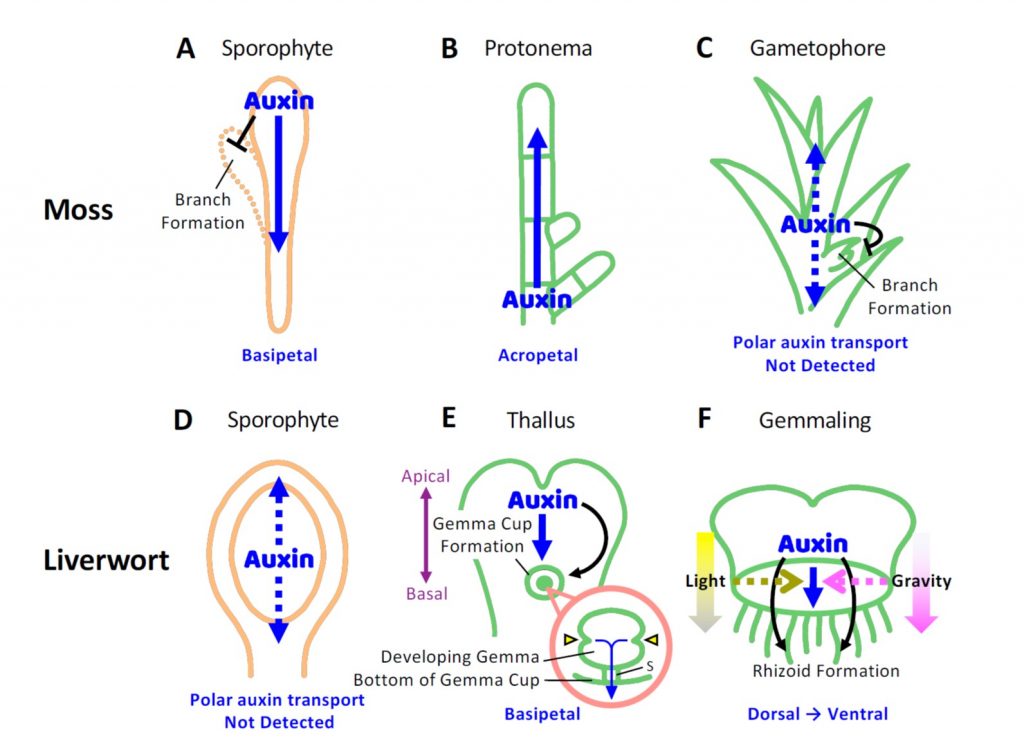
Review: Bryophytes as model systems for studying evolutionary cell and developmental biology (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe development of Arabidopsis as a model system greatly advanced the field of plant cell biology by bringing in molecular approaches, so much of our conceptual foundation rests on studies from angiosperms. More recently, model bryophytes, particularly Marchantia polymorpha (liverworts) and Physcomitrium…

