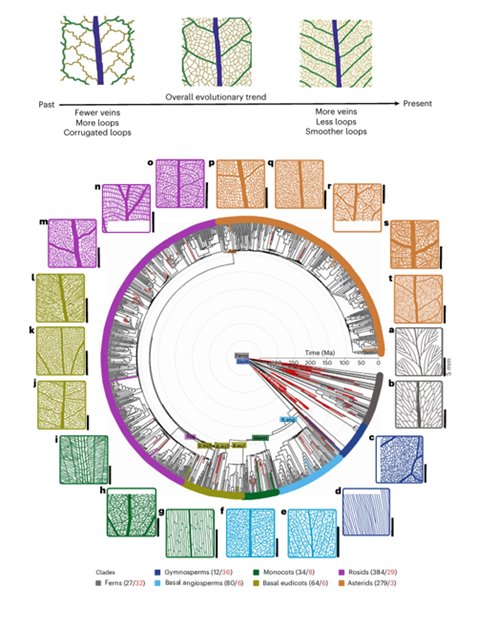
The shape of adaptation: Evolution of venation patterns in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyLeaf venation patterns display remarkable diversity across both living and fossil plant lineages, yet key questions remain about when and how these architectural differences emerged and what functional roles they serve. In their recent review, Mantos et al. explored the evolutionary history of venation…
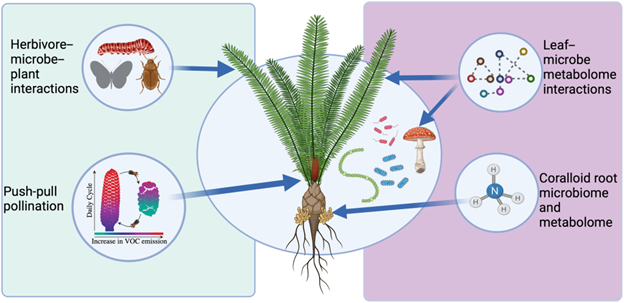
Review: Cycads, chemicals, and coevolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyCycads are an ancient lineage of gymnosperms with fascinating ecological interactions. In a recent review, Salzman et al. examine the various adaptations of cycads, from attracting pollinators to repelling parasites, focusing on the roles of their wide array of specialized metabolites. A somewhat unique…
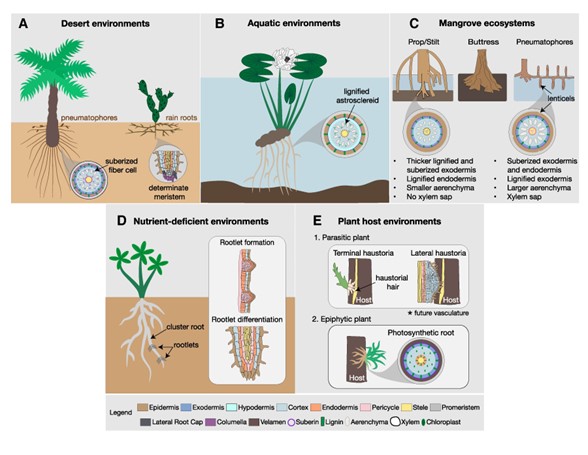
When form fits function: the value of root diversity to survival
Plant Science Research WeeklyFor a plant, form is function. Despite the diversity of forms that exist in nature, plant root diversity is notoriously understudied compared to their aerial counterpart. This review by Ramachandran and Ramirez et al. aims to revitalize the field of root form-function research by accentuating the vast…
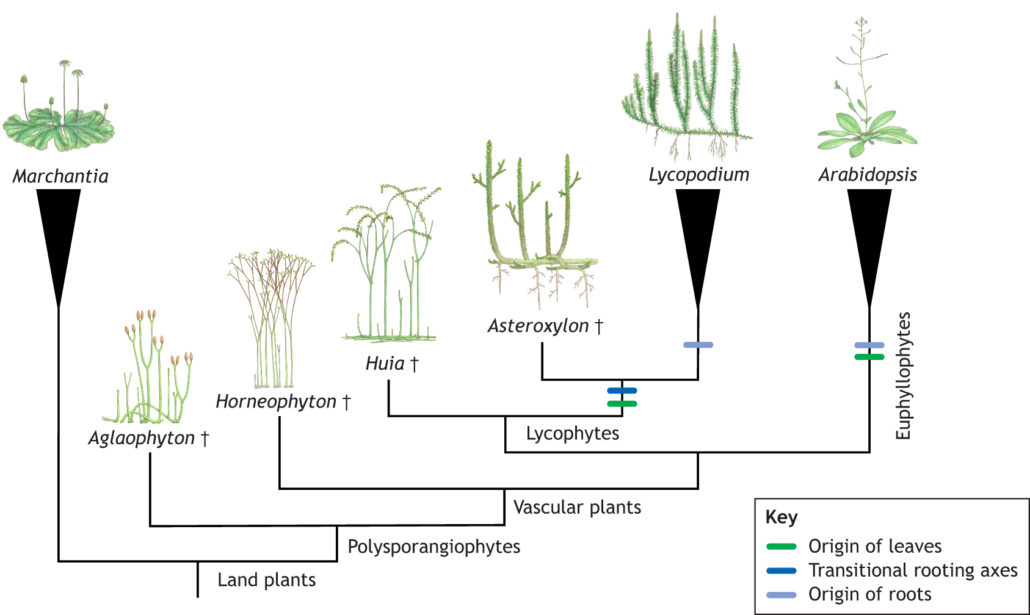
Spotlight: The role of fossils for reconstructing the evolution of plant development
Plant Science Research WeeklyI suspect if we asked someone to describe a fossil we’d hear a lot about dinosaur bones. Certainly, science museums are full of fossilized animal remains, which have greatly informed our understanding of animal evolution. Plant fossils similarly are rich sources of information about plant evolution…
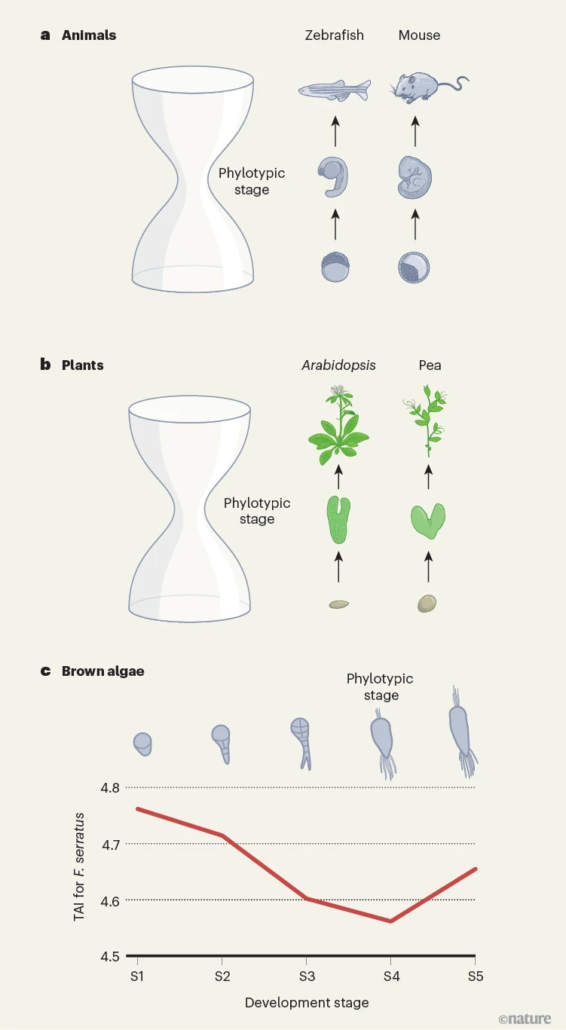
The ”hourglass” model of embryogenesis extends to brown algae
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe hourglass model of embryogenesis was proposed in the 1990s, and extended to green plants and fungi in the 2010s. During animal embryogenesis, the very earliest stages (post fertilization) are morphologically quite different from each other, and the later stages are quite different, but in the middle…

Comparative transcriptomics in ferns provide a framework for their unique evolutionary path
Plant Science Research WeeklyFerns are important and diverse land plants but are also known for their exceptionally large genomes. A new study by Ali et al. presents an extensive analysis of fern genomics through RNA-sequencing of 22 representative fern species. The study identified 18 whole-genome duplications across different…
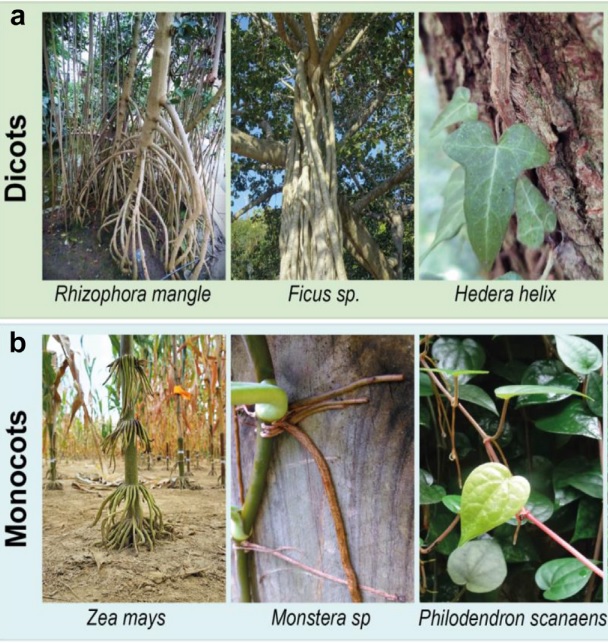
Review: Stem-borne roots as a framework to study trans-organogenesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants develop new organs and tissues throughout their lifespan as they grow new leaves, roots and reproductive structures. Many of these tissues arise from similar tissues, such as lateral roots arising from primary roots, and the mechanisms guiding their formation are well understood. But what about…

Convergent evolution of plant prickles
Plant Science Research WeeklyContrary to common belief, roses do not have thorns: instead, they have prickles. Thorns (as in hawthorns) are modified stems, spines (as in cactus spines) are modified leaves, and prickles (as in roses) are modified epidermal tissues. Prickles occur in a wide range of plants. Satterlee et al. set out…
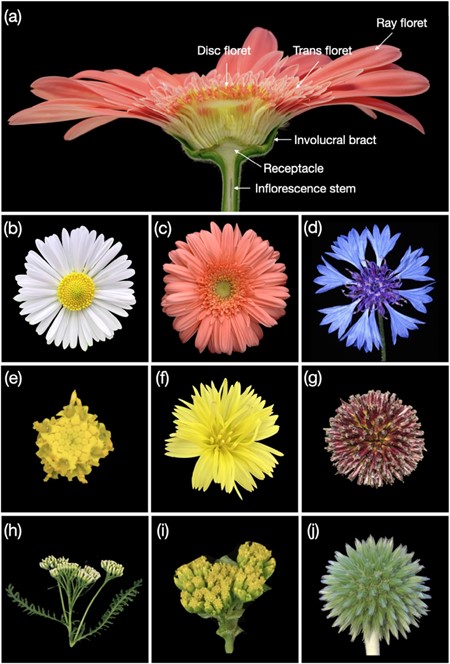

Review: Development and evolution of the Asteraceae inflorescence
Plant Science Research WeeklyAsteraceae, also known as Compositae or the daisy family, is one of the largest plant families and comprises 10% of all flowering plants. Members of this family are found in habitats worldwide. The unique inflorescence, called a capitulum, is a key innovation of the family and contributes to its success.…

