
Update: Leaf hydraulic architecture and stomatal conductance: a functional perspective
Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
By Fulton E. Rockwell, and N. Michele Holbrook
The structure of leaf vasculature viewed over a broad phylogenetic scale from lycophytes to eudicots correlates with stomatal conductance (gs), providing the basis for the hypothesis that increasing vein density drove the evolution of high fluxes in angiosperms.…
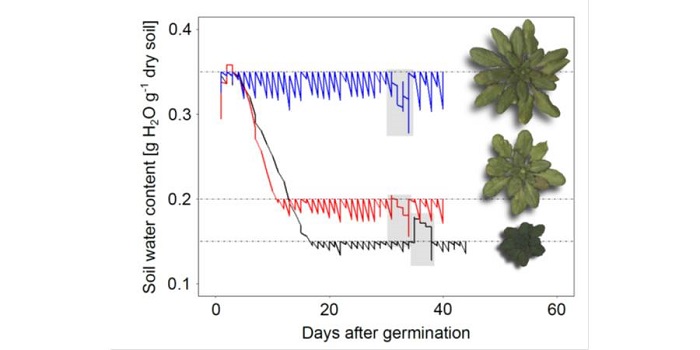
Phenotyping Water Deficit Acclimation Responses
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogWater deficit (WD) is one of the main environmental stress factors affecting crops and global food security. Acclimation to WD, however, enables plants to maintain growth under unfavorable environmental conditions. To shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying WD acclimation, Rymaszewski et al.…
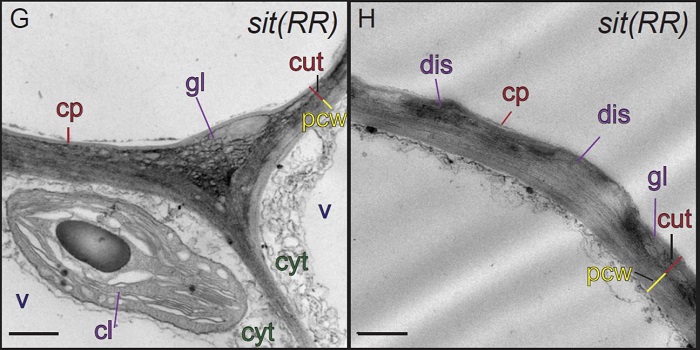
ABA is Required for Cuticle Formation Independent of Water Stress
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchThe waxy cuticle, a key barrier to desiccation and pathogen entry, is a dynamic structure, the composition, area, permeability and thickness of which can change in response to environmental conditions. For example, water deficit in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) triggers an increase in the accumulation…
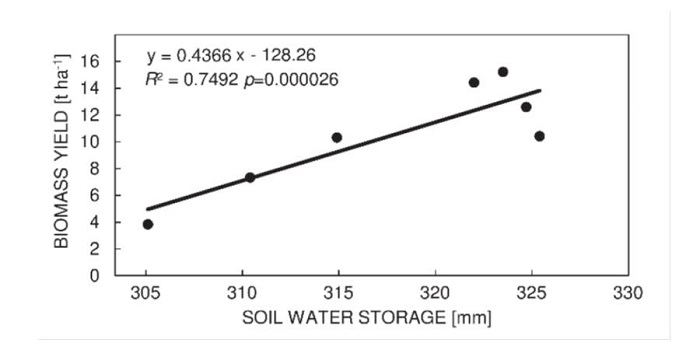
For drought tolerance, is water use efficiency (WUE) no longer a recommended selection criteria for energy crops?
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPodlaski et al. conducted experiments with energy crops like miscanthus, prairie cordgrass, willow, etc, and report that water use efficiency (WUE) is no longer a valid trait for selecting energy crops for drought tolerance. They could not find any significant relationship between WUE and biomass …
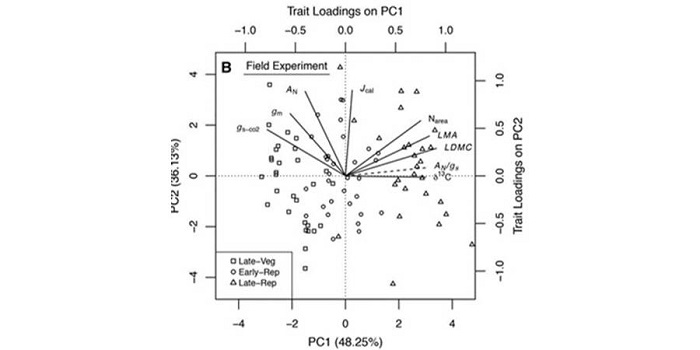
Variable mesophyll conductance among soybean cultivars sets a tradeoff between photosynthesis and water-use-efficiency
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAn experimental study by Tomeo and Rosenthal with soybean cultivars demonstrated that there exists genotypic differences in mesophyll conductance (gm), and that the potential exploitation of this trait may increase crop productivity. It was found that there exists a proper coordination mechanism…
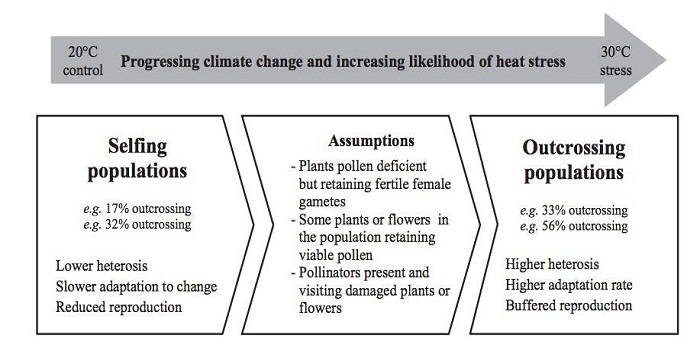
Elevated temperature drives a shift from selfing to outcrossing in the insect-pollinated legume, faba bean (Vicia faba)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe effects of climate change on agriculture to human health have been well discussed in both scientific and public domains. In plants, changes in climate might affect interactions between the plants and their insect pollinators due to variable availability of pollinators in severe weather conditions,…
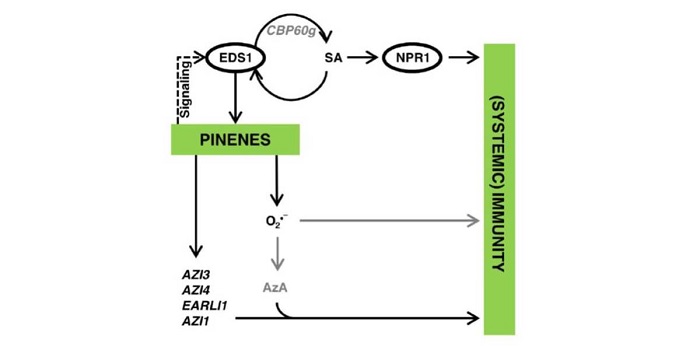
Monoterpenes support systemic acquired resistance within and between plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPathogen perception leads to local and systemic immune responses including systemic acquired resistance (SAR). The nature of the mobile signals and their movements remain uncertain. Riedlmeier et al. demonstrated that certain monoterpenes including α- and β-pinene accumulate in SAR-inducing conditions…
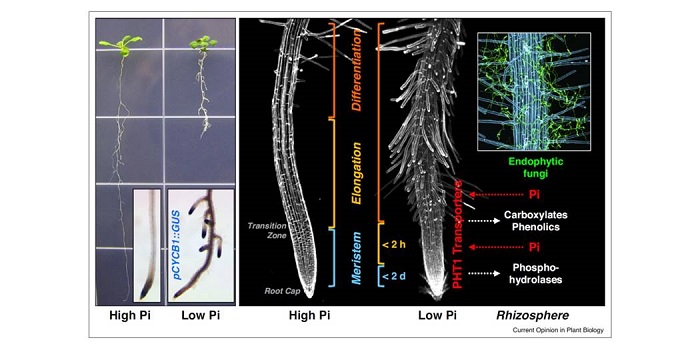
Review: Phosphate scouting by root tips ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPhosphate is both really important (think of its abundance in DNA, RNA, ATP, and membrane lipids), and really difficult to assimilate due to its insolubility and immobility in soil. Phosphate is frequently limiting for growth, meaning that it is widely applied as fertilizer, but global supplies of phosphate…
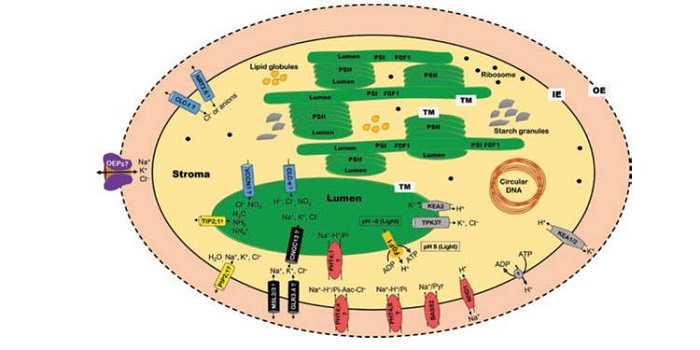
Review: Chloroplast function and ion regulation in plants growing on saline soils: lessons from halophytes ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSalinity is a growing problem for food production. Progress has been made in understanding how plants tolerate salinity, mostly focused on strategies for tolerance at the plasma membrane and cytosol. Bose et al. review studies that focus on how the chloroplast is affected by salinity. The authors review…

