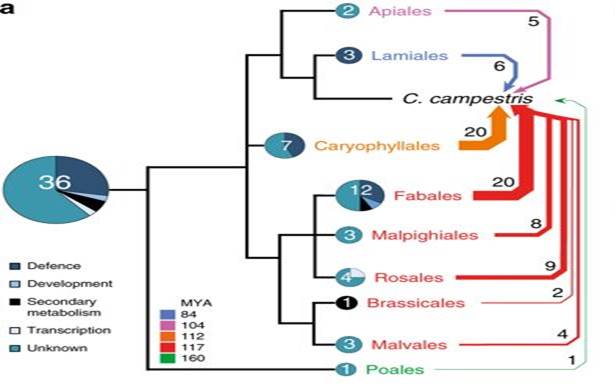
Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEven without knowing a lot about parasitic plants, you can probably guess some of the insights that come from the first parasitic plant genomic sequence. Because parasitic plants get their nutrients from another organism (functionally, they become heterotrophic), you might expect they would gradually…
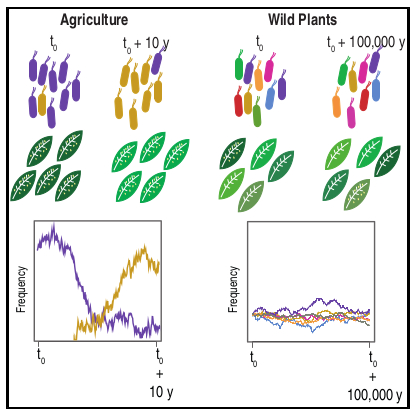
Arabidopsis thaliana-associated Pseudomonas diversity and evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere is not much available information regarding the evolutionary aspects of one of the most studied pathosystem in plant biology: Arabidopsis thaliana and Pseudomonas. Karazov et al. performed various surveys in Arabidopsis wild populations, for the detection and characterization of their associated…

The demise of the largest and oldest African baobabs ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPatrut et al. report that 8 of the 13 oldest and 5 of the 6 largest African Baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) trees, known for their enormous size and great longevity, have died (or at least their largest and/or oldest parts/stems have collapsed and died). Included in the dead are Panke, the oldest Baobab…
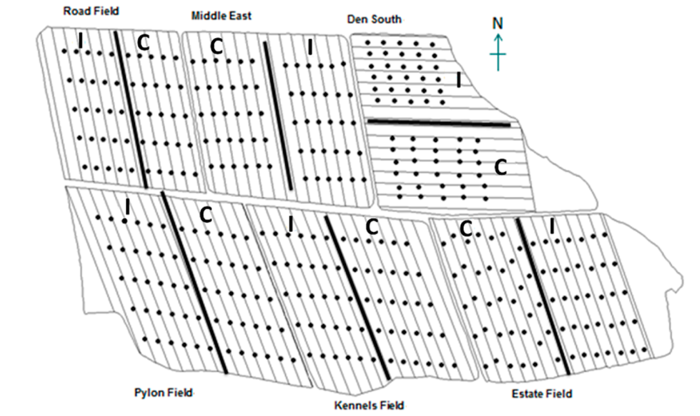
Impact of Conventional and Integrated Management Systems on the Water-Soluble Vitamin Content in Potatoes, Field Beans, and Cereals ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchJ. Agric. Food Chem. Agriculture in the EU is shifting towards a more sustainable use of resources and preservation of the biodiversity. This process requires a careful assessment of the balance between economic and environmental demands. To achieve this goal, the James Hutton Institute set up a long-term…
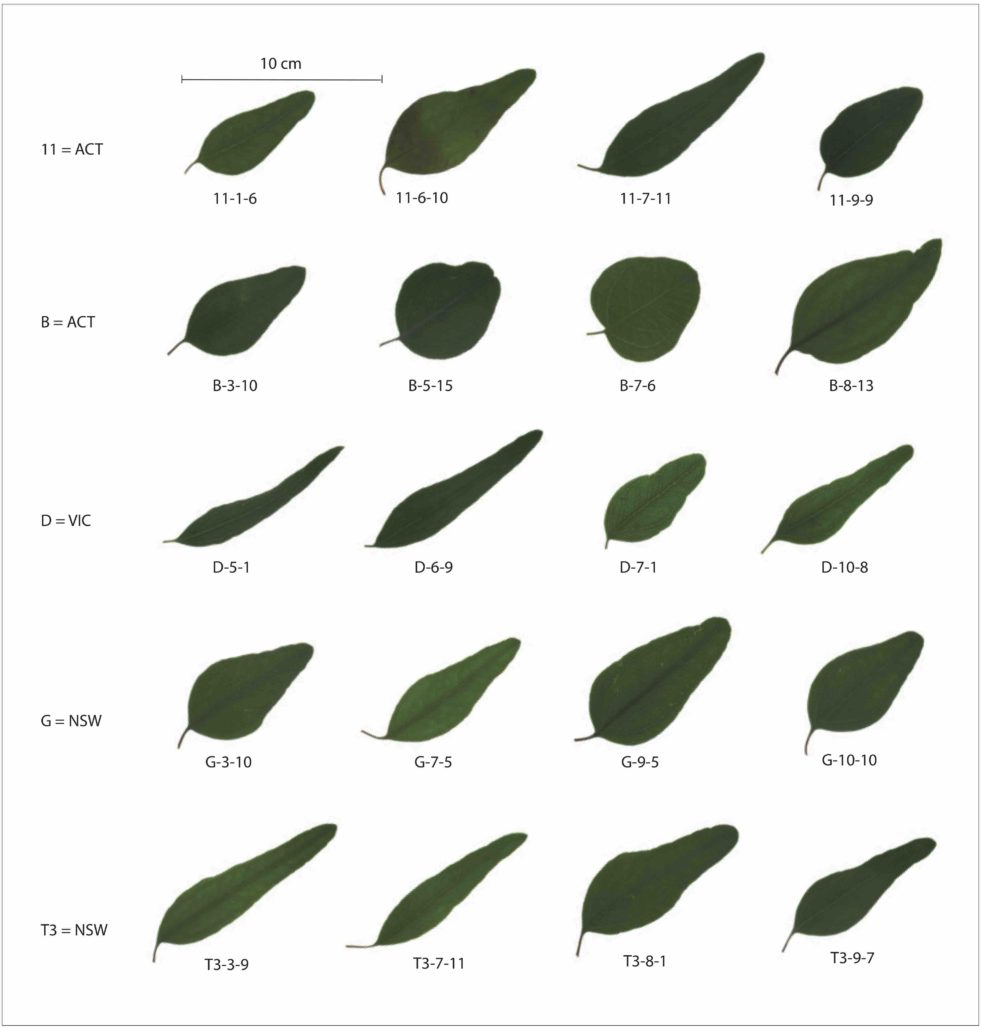

Strategic seed sourcing will enable species to better adapt to changing environments (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyYellow box, Eucalyptus melliodora, is an iconic Australian tree and foundation species of a critically endangered woodland community that is the target for restoration efforts. This community is currently severely fragmented, and less that 5 % of its original distribution remains. Models of climate prediction…
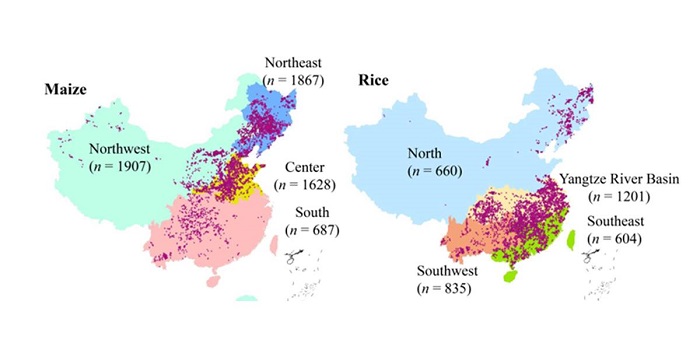
Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers ($) (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyImproving crop productivity of rural areas while addressing pollution problems is a challenge that not only depends on scientific studies and technology but also requires an effective dialog with the smallholder farming communities. This month, Nature published the results of a ten-year Chinese agricultural…
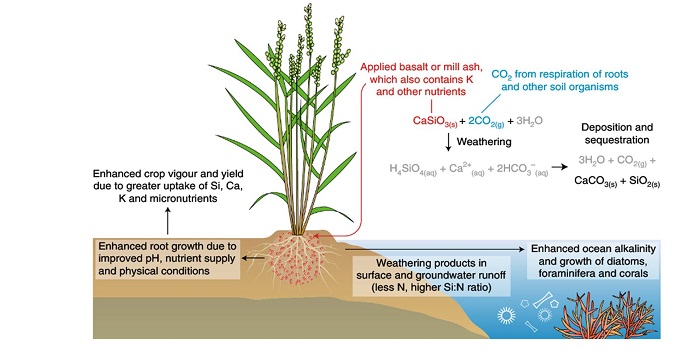
Perspective: Farming with crops and rocks to address global climate, food and soil security (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRising atmospheric CO2 levels are causing wide-ranging climate abnormalities. Beerling et al. discuss ways to capture CO2 in soils through augmenting soils with crushed basalt, or silicate-rich wastes such as sugarcane mill ash. As the added rock weathers, it reacts with gaseous CO2 to release cations…
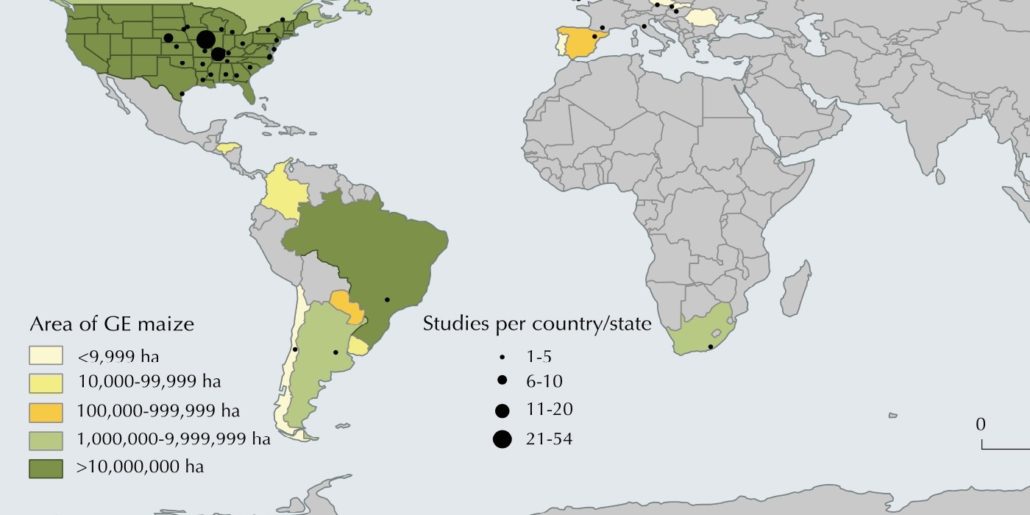
Impact of genetically engineered maize on agronomic, environmental and toxicological traits (Sci. Rep.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe question of the relative risks and benefits of genetically engineered (GE) maize is still in the middle of a heated debate, despite the widespread cultivation of GE crops (12% of the global crop-land) and long standing commercialization (since 1996). Pellegrino et al. report a meta-analysis of…

Review. Rhizobia: From saprophytes to endosymbionts (Nat. Rev. Microbiol.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogOne of the best characterized plant-bacteria interactions is that between legumes and rhizobia. This review by Poole et al. explores rhizobia in their non-plant associated state (as saprophytes that derive energy and nutrients from organic matter in the soil), through the complex signals that lead to…

