Calling from distance: attraction of soil bacteria by plant root volatiles (ISME J.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant interactions with beneficial microbes are good strategies to survive biotic and abiotic challenging conditions, but the mechanisms that plants use to recruit these interactions, specially belowground, remain scarcely known. Schulz-Bohm et al. designed an olfactometer system to analyze the long…
Drastic genome reduction in an herbivore’s pectinolytic symbiont
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCell. In a very interesting report, Salem et al., showed evidence of an alternative mechanism supporting how the degradation of pectin, a very hard to metabolize component of the cell wall, has directed the evolution of herbivory in insects and arthropods. Recent reports have indicated that horizontally…
Hidden shift of the ionome of plants exposed to elevated CO2 depletes minerals at the base of human nutrition
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogeLife. Free air CO2 enrichment (FACE) has been used to surround plants with an elevated concentration of CO2 (eCO2) during growth, and has consistently conferred an increase in carbon assimilation and plant productivity. However, the effect of eCO2 on nutrient status of the plant is unclear due to…
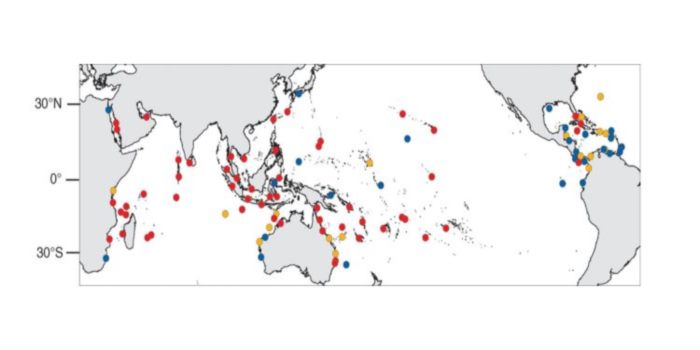
Spatial and temporal patterns of mass bleaching of corals in the Anthropocene
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogScience. As our ecosystems are changing rapidly, more studies are needed to document them. One of these important events is “coral bleaching”, a phenomenon that occurs due to environmental stress and when coral hosts lose their algal symbionts or zooxanthellae (Symbiodinium spp.), showing the white…
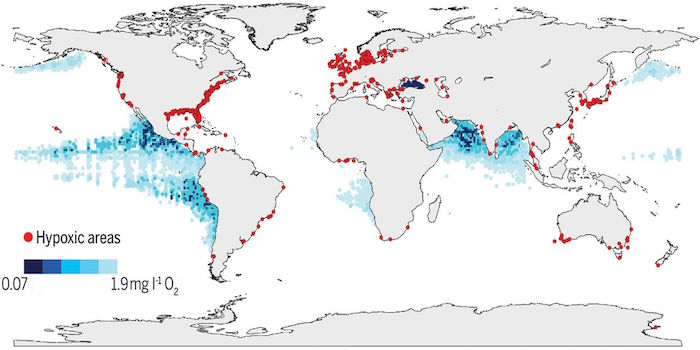
Review: Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogScience. Oxygen levels have been declining in oceans since the middle of the 20th century, largely because of global warming phenomena and human-driven nutrient enrichment of coastal regions. These effects have enhanced microbial oxygen intake, altering the cycles of nutrients and carbon, and lowering…
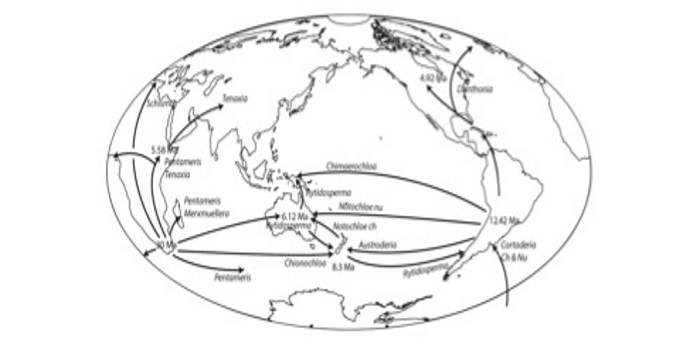
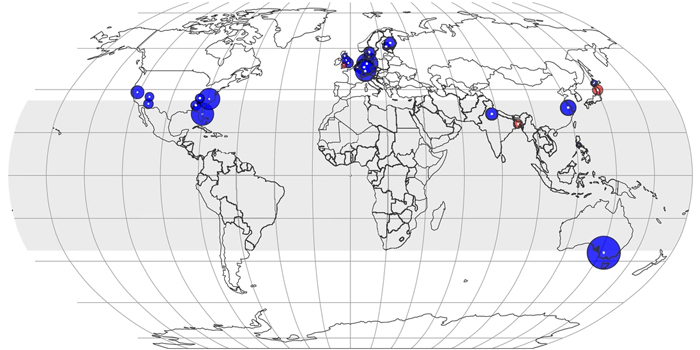
Review. Grasses: The original Vikings ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe Vikings were notorious raiders for centuries, pillaging and looting the shores throughout the northern hemisphere. Through their successful raids, the Vikings established colonies that grew into states and countries, among these Normandy, England, Sicily, and Russia. The success of the Vikings is…
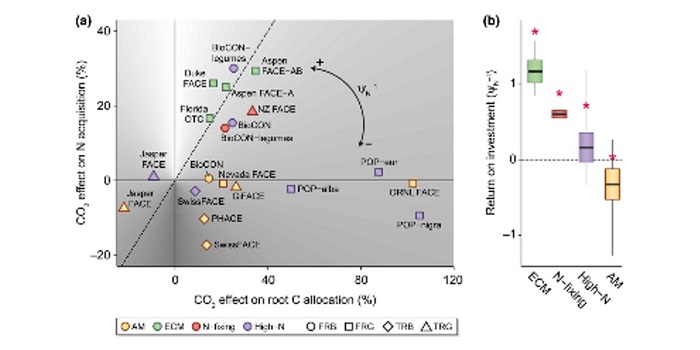
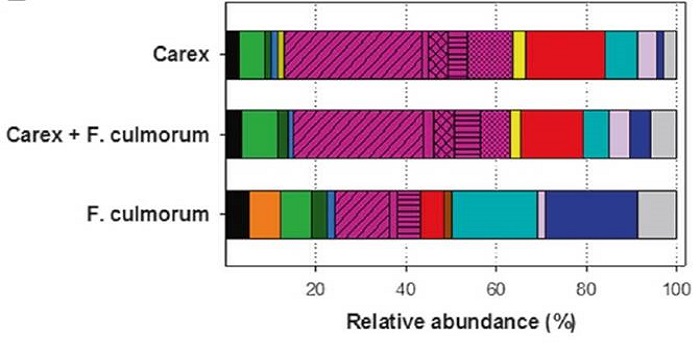
Ecosystem responses to elevated CO2 are governed by plant-soil interactions and the cost of nitrogen acquisition
Blog, Careers, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHow does the cost of nitrogen acquisition affect how an ecosystem responds to elevated CO2? Terrer et al. have addressed this question in a comprehensive review of findings from elevated CO2 experiments, using a plant economics framework. The authors describe ecosystem responses, particularly those of…

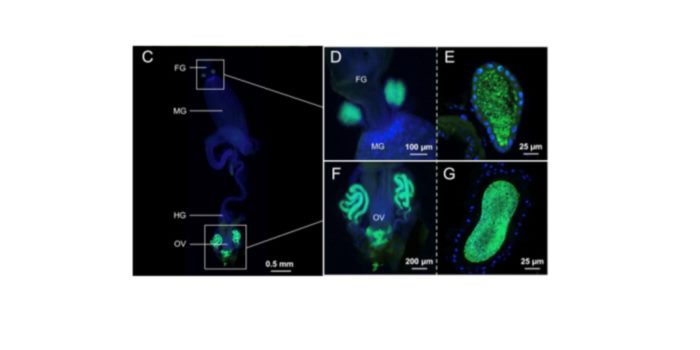
A root hair-seeking endophytic microbe from an unusual volcanic swamp corn enhances phosphate uptake
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIn plants the location of microbes to specific cell types, including endophytes, is still scarcely described in contrast with the situation in the animal kingdom. Shehata et al. describe a bacterial endophyte (Strain 3F11, possibly Enterobacter asburiae) from Zea nicaraguensis, a wild corn growing at…
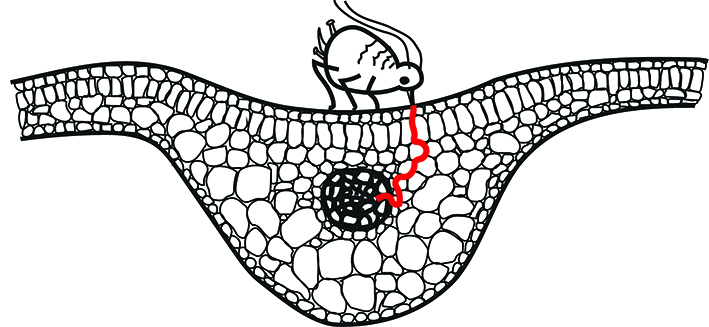
A Plant Protein That Foils Aphid Feeding
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKloth et al. probe aphid feeding behavior. The Plant Cell 2017 doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00424
By Karen Kloth
Background: Aphids are phloem-feeding insects. They penetrate plants with a piercing-sucking mouth. Once they reach a tube where the plant transports its sugar-rich phloem sap, they can take…

