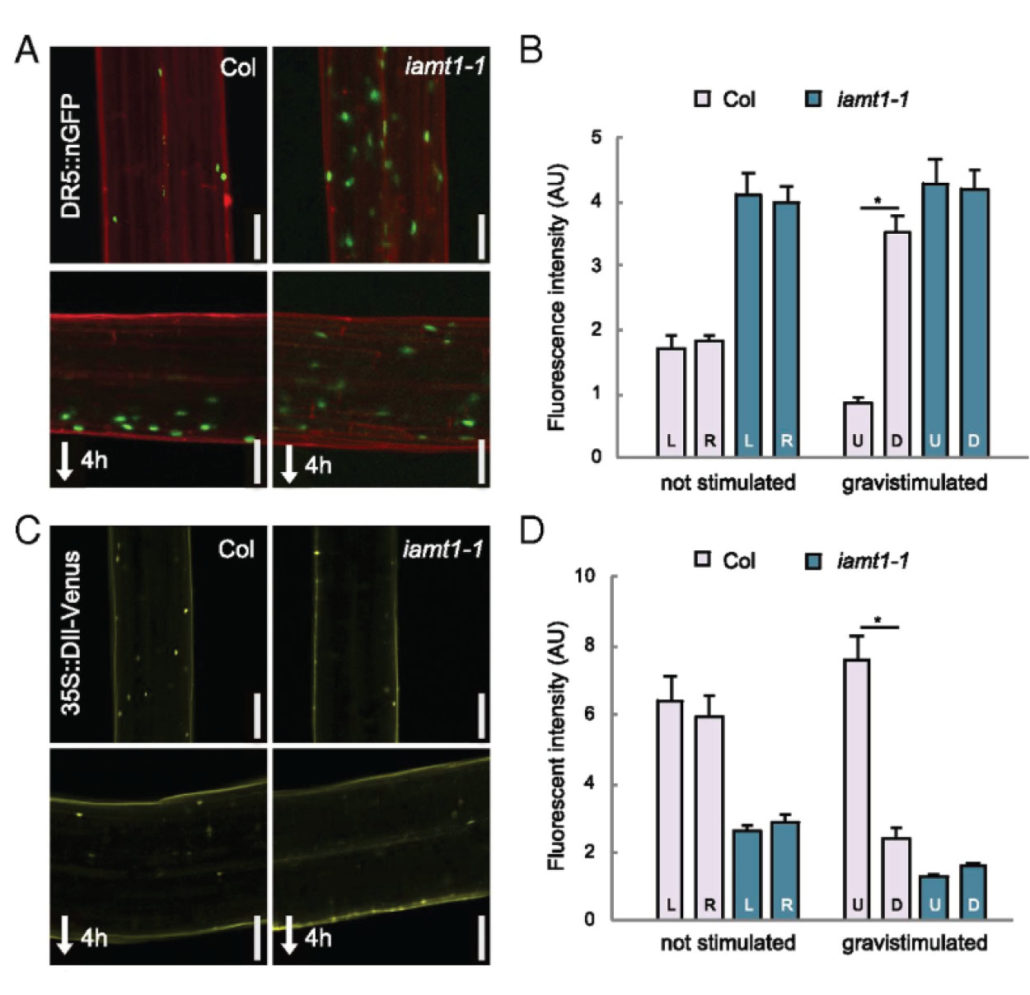
Auxin methylation is required for differential growth in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to navigate and adjust their growth according to the environmental clues, such as light or gravity. Asymmetric distribution of auxin is necessary for organ bending. Abbas and colleagues show that conversion of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) into methyl-IAA (Me-IAA) is important for asymmetric…
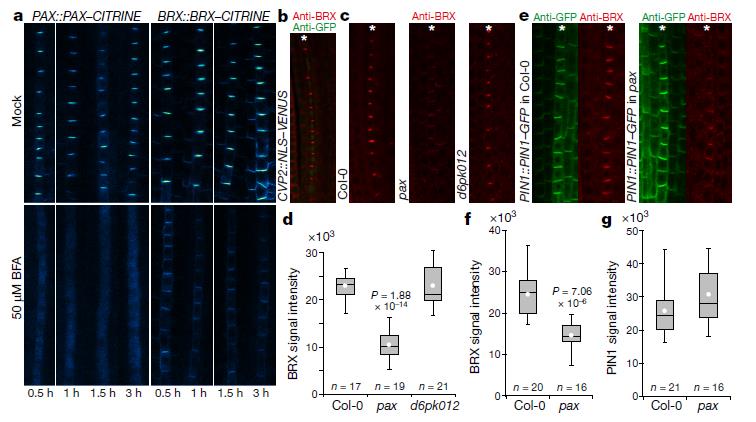
A molecular rheostat adjusts auxin flux to promote root protophloem differentiation ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plant development, auxin serves as a concentration-dependent signal that regulates cell differentiation, elongation and proliferation. The distribution of auxin is carried out by auxin efflux carriers such as PIN-FORMED (PIN) proteins and the specific accumulation of auxin directs organ differentiation…
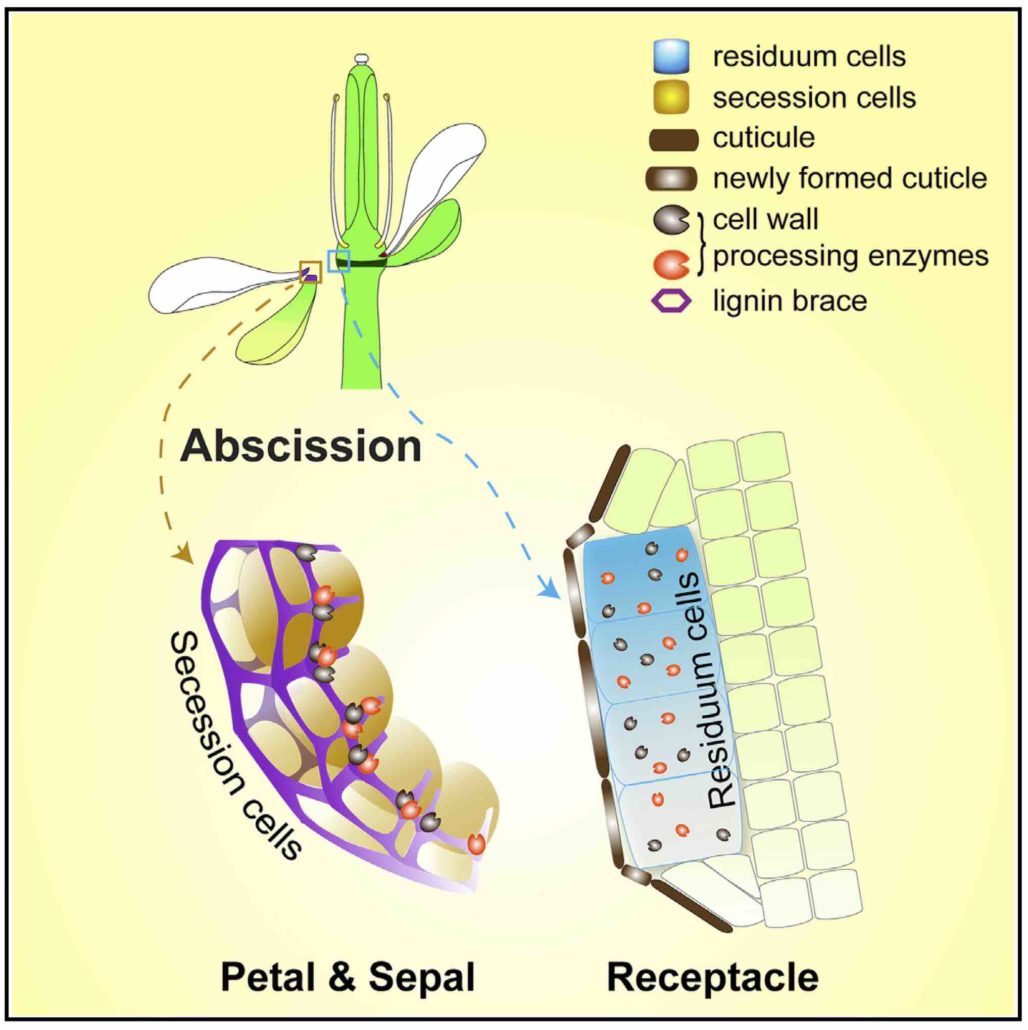
Discarding unwanted organs is a highly regulated process in plants (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants frequently, seasonally, discard unwanted organs (termed abscission), which include dead leaves, flowers and ripe fruit. Abscission requires tight control to avoid exposure to biotic and abiotic factors, which can lead to tissue damage or infection. Due to the presence of the cell wall, plant cells…
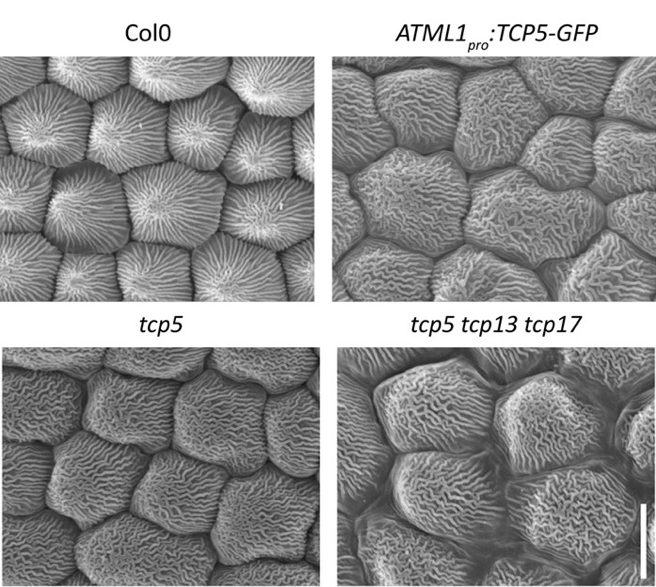
Novel functions of TCP5 in petal development and ethylene biosynthesis (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe flower is one of the most important organs of a plant as it provides fruits and seeds. Due to its economic value, flowers are studied extensively to understand its developmental process. Based on the popular ABC model of flower development, floral organ development is mostly regulated through the…
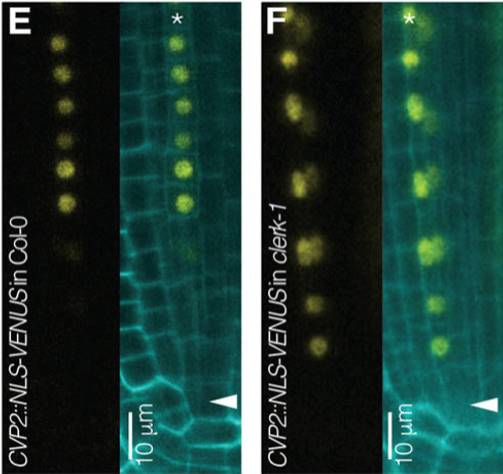
CLERK is a novel receptor kinase required for sensing of root-active CLE peptides in Arabidopsis (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklySmall secreted peptides including CLEs have been identified as contributing to plant development. CLE26 and CLE45 have been shown to regulate protophloem differentiation in the root tip. Anne et al. used a combination of genetic screening and transcriptomics to identify factors downstream of these peptides.…

ONE GENE: DIFFERENT mRNAs, DIFFERENT TISSUES, DIFFERENT FUNCTIONS IN DEVELOPMENT
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellNapoli et al. show that mRNA splicing variants have tissue- and developmental stage-specific activity in flower development https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00840.
By Roberta Ghelli and Patrizia Brunetti
Background: Plants that are self-pollinating contain both male (stamen) and female (pistil)…
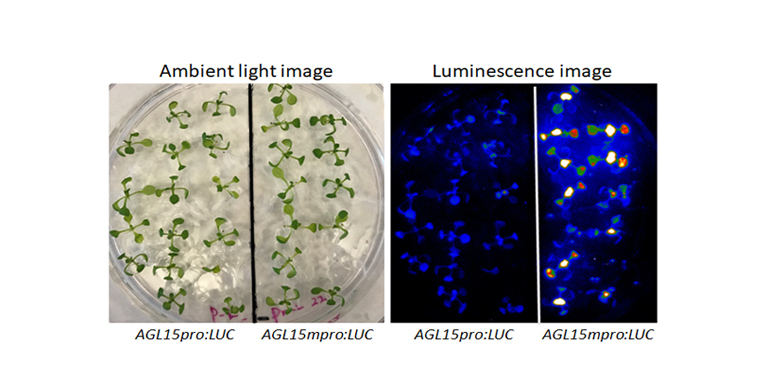
Switching off Seed Maturation Genes in Seedlings
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellChen et al identify AGL15 as a direct target of HSI2-dependent transcriptional repression in Arabidopsis seedlings https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00655.
By Naichong Chen and Randy Allen
Background: The developmental transition from seeds to seedlings is a critical step in the plant life cycle.…
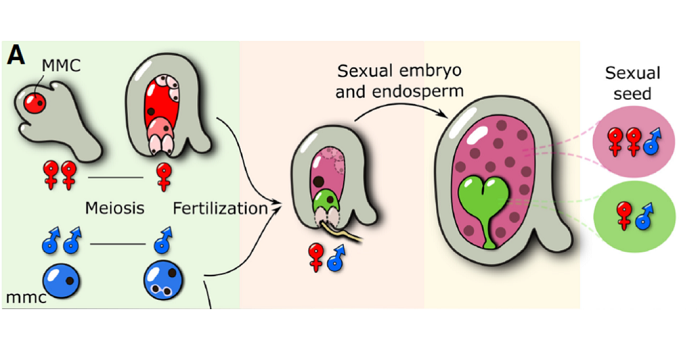
Review: Auxin: a molecular trigger of seed development (Genes Devel.) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeeds are hugely important, providing the opportunity for reproductive dormancy in seed-bearing plants and as a nutrient-dense food source for animals. Seed development involves the formation of three genetically distinct tissues, the embryo, seed coat and endosperm. Although normally dependent on fertilization…
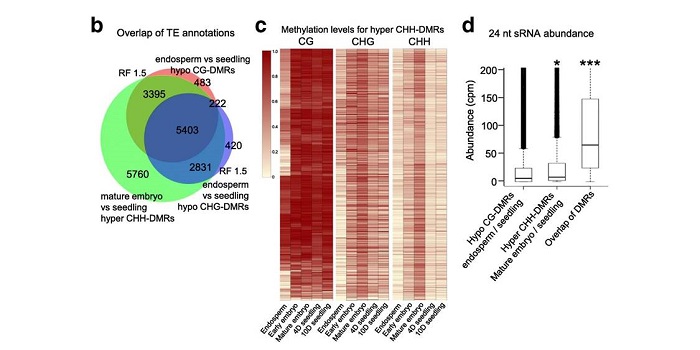
DNA methylation dynamics during early plant life
Plant Science Research WeeklyDNA methylation is extensively reprogrammed in the early embryo and germlines of mammals, whereas flowering plants do not show such extensive resetting except in the endosperm. Active DNA demethylation in the central cell and reduced activity of DNA methyltransferases leads to global hypomethylation…

