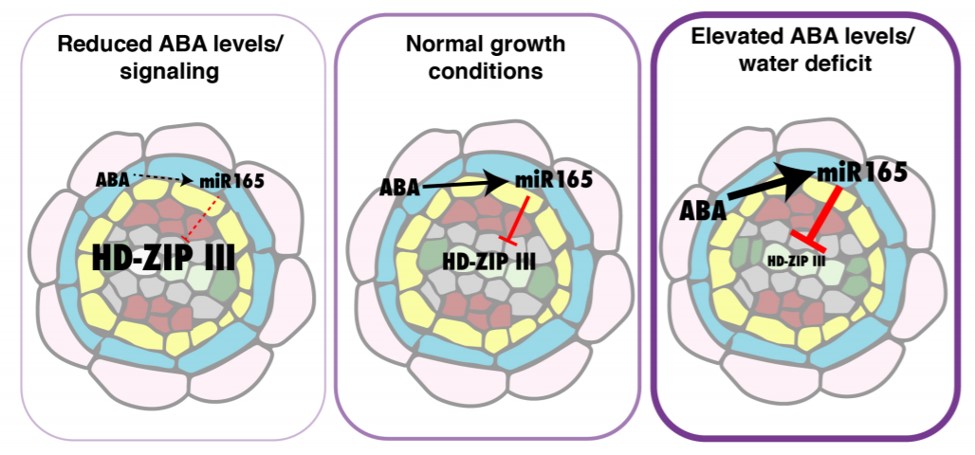
Root xylem formation and vascular acclimation to water deficit involves endodermal ABA signaling via miR166 ($) (Development)
Abiotic stress influences plant development, with the phytohormone ABA playing an important role. Ramachandran et al. have demonstrated ABA mediated activation of microRNA 166, which regulates expression levels of the HD-ZIP III transcriptional factor family. Exogenously supplied ABA alters xylem patterning…
Lipids and Auxin Signaling in Plant Salt Responses
Wang et al. highlight the importance of lipid protein interactions in spatiotemporal regulation of auxin signalling. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00528
By Peipei Wang and Qun Zhang
Background: Salt stress inhibits plant growth and development, leading to many physiological reactions.…
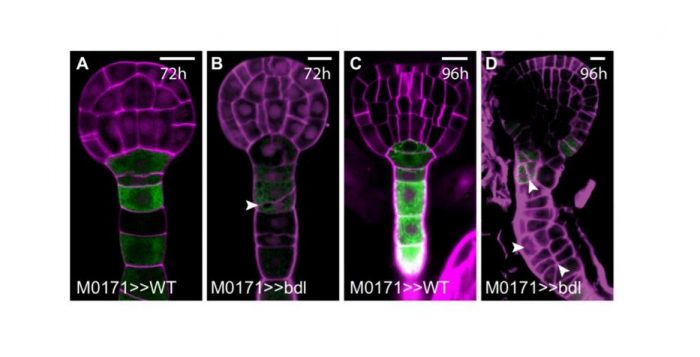
A Transcriptional Module Regulates Embryo and Suspensor Development
Radoeva et al. investigate a transcription module that controls aspects of embryogenesis in plants. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00518.
Background: After the start of embryo development in plants, which is marked by fertilization of the egg cell, the resulting zygote divides asymmetrically…
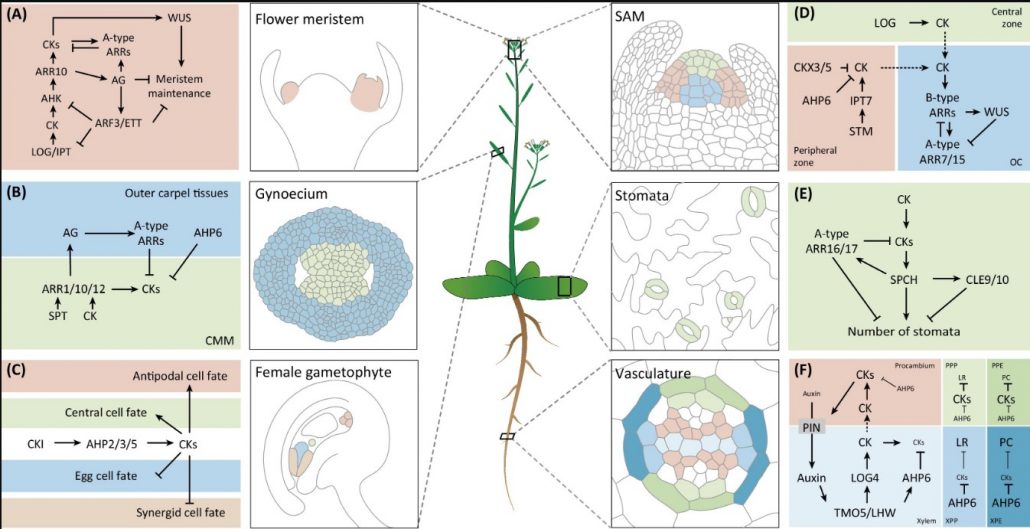
Review: Cytokinin – A developing story (Trends Plant Sci) ($)
With its diverse chemical structures, the phytohormone cytokinin is significant from embryogenesis to the maturation of plants. In this review, Wybouw and De Rybel highlight in detail cytokinin signaling in multiple plant developmental process including shoot, flower, stomata, root and vascular development.…
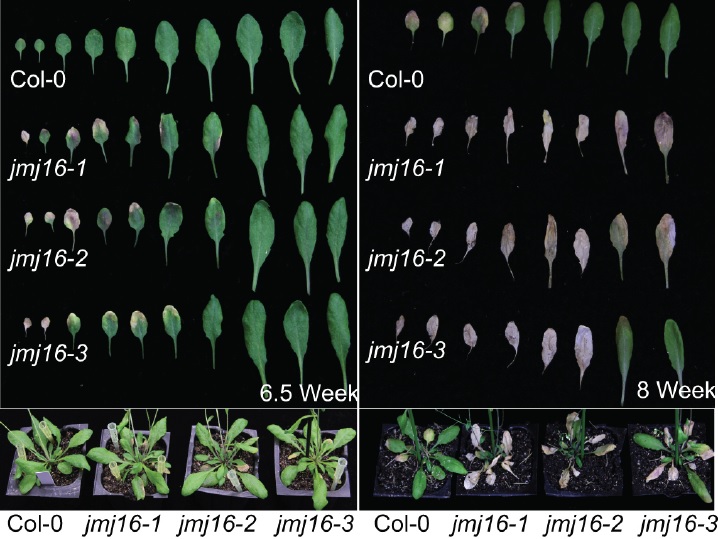

Leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana is regulated by a histone H3K4 demethylase (Plant Cell)
Leaf senescence is the final stage of leaf development where the organ turns yellow and programmed cell death occurs. While it is generally understood that the regulation of senescence associated genes (SAGs) is dependent on the trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 (H3K4me3), the exact mechanism…
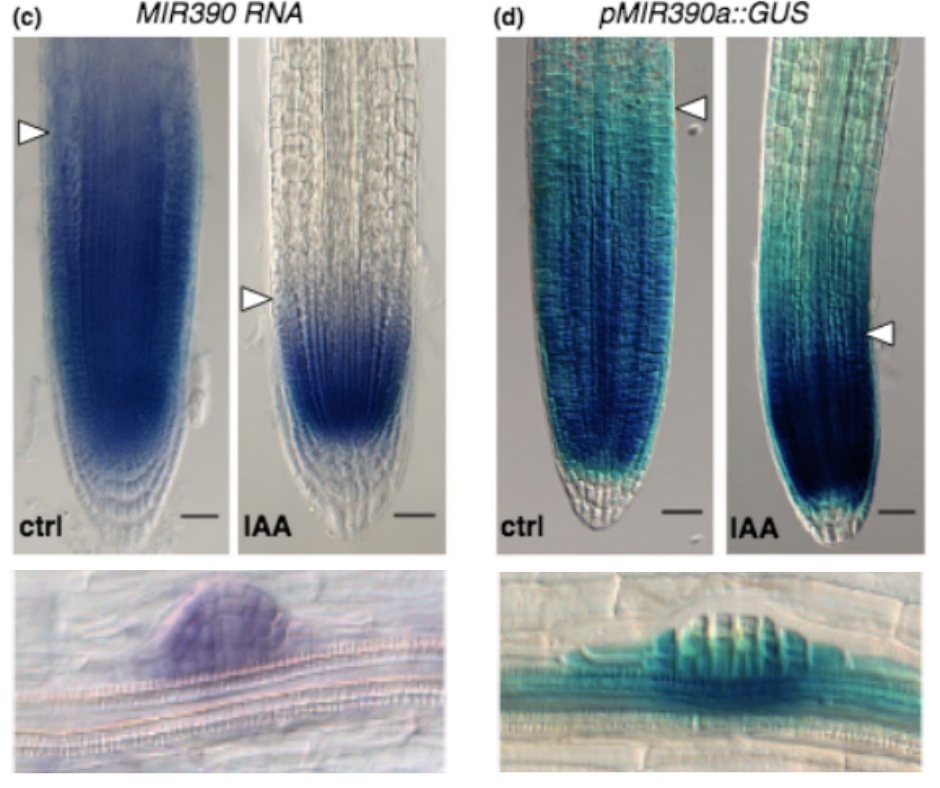
ARF5/MONOPTEROS directly regulates miR390 expression in the Arabidopsis thaliana primary root meristem (Plant Direct)
Previous studies have indicated that auxin controls gene expression via regulatory transcriptional networks, mediated by a family of DNA-binding auxin response factors (ARFs) that bind to auxin response DNA elements (AuxREs) in the promoters of genes. In this study, Dastidar et al. investigated the…

Seed size is regulated by siRNAs from Arabidopsis maternal tissue in a spatial-temporal manner ($)(PNAS)
Studying seed development is important for understanding plant evolution and engineering food production. Previous discoveries have shown that maternal small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which induce RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) through NRPD1-mediated pathway, regulate seed development in Arabidopsis.…
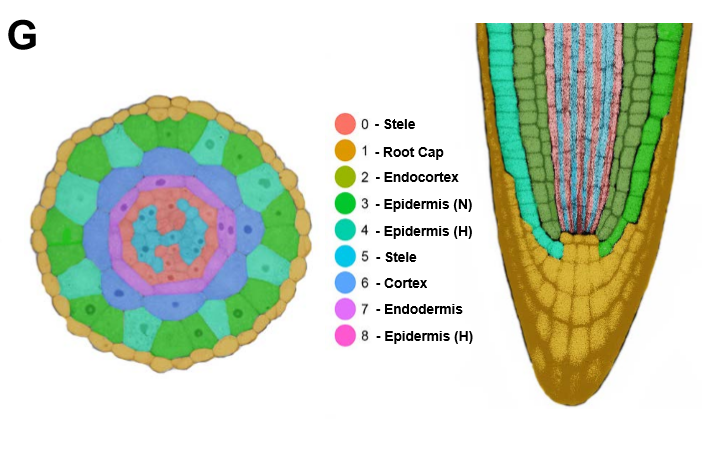
Single-cell RNA sequencing resolves molecular relationships among individual plant cells (Plant Physiol)
Single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has transformed our understanding of gene expression within and amongst individual cells. These techniques have been applied extensively to animal cell populations to discover the development of specific cell lines and identify rare cell types but are not commonly…
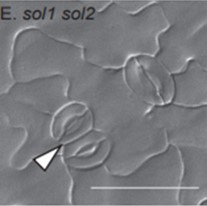
SOL1 and SOL2 regulate fate transition and cell division in stomatal lineage ($) (Development)
Stomata and pavement cell development in the leaves occur through programmed asymmetric cell division. In this paper the authors demonstrated the role of two CHC domain proteins, SOL1 and SOL2 that were identified previously by the same group to be downstream targets of a bHLH transcriptional factor…

