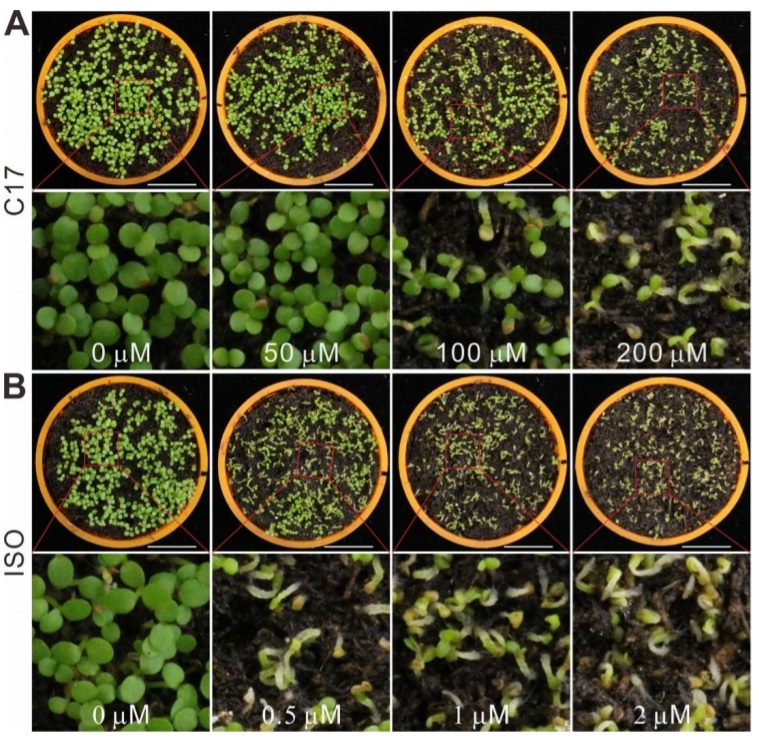
Generating novel, dual herbicide-resistant crops using CRISPR-mediated gene editing (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere is an ever-growing need for novel herbicides as more weeds are becoming resistant to commonly used herbicides. In a recent report from Hu et al., the authors identified that a previously described cellulose biosynthesis-inhibiting chemical, C17, possesses an herbicidal quality. The authors showed…

Review: CRISPR/Cas genome editing and precision plant breeding in agriculture (Annu Rev Plant Biol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo fulfill global food demand in the near future, plant researchers keep pursuing simpler and faster crop breeding strategies. CRISPR/Cas systems have been developed as a powerful tool for plant genome editing. In this review, Chen et al. highlight in detail advances in CRISPR/Cas9 and its variants and…
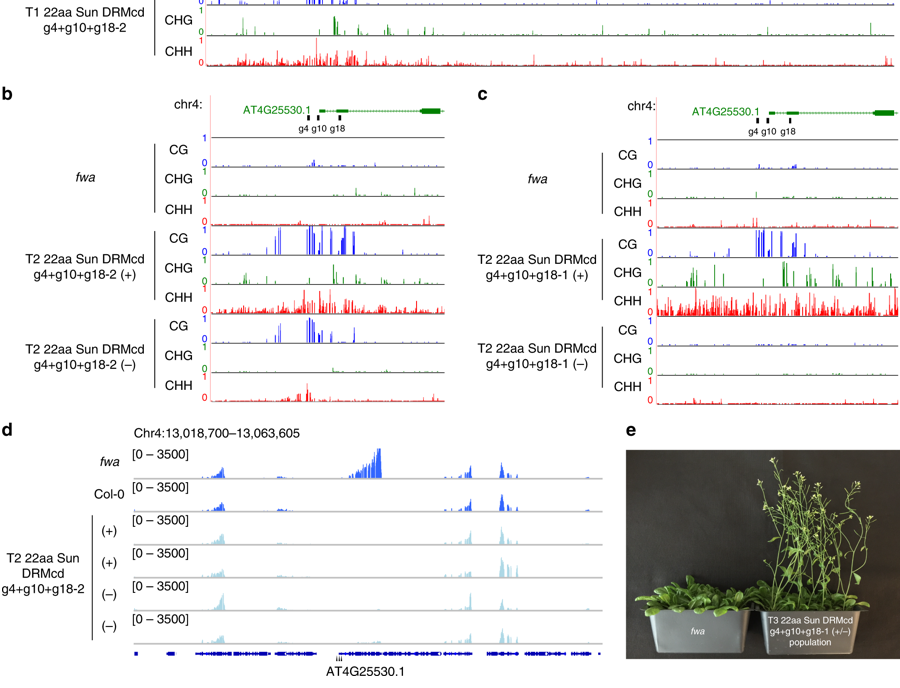
Site-specific manipulation of Arabidopsis loci using CRISPR-Cas9 SunTag systems (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklySteve Jacobsen’s group has been developing a broad range of synthetic biology tools to interrogate DNA-methylation in plants (see Gallego-Bartolomé et al., 2018, and Gallego-Bartolomé et al., 2019). Among them, they use the CRISPR-Cas9 SunTag system, in which the dCas9 protein is fused to SunTag,…
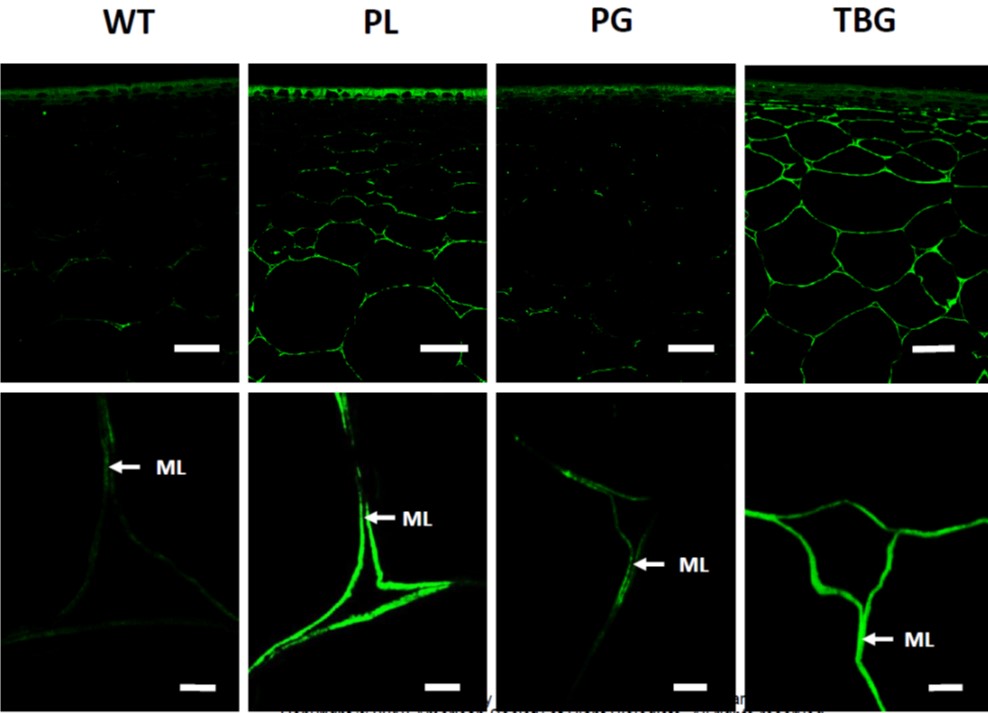
CRISPR Mutants Shed Light on Pectin’s Role in Tomato Fruit Softening
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideTomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruits undergo pronounced softening during ripening. Softening is important for flavor development and overall palatability, but also impacts fruit storage, transportability, and shelf life. Shelf life is a particularly important quality trait of tomato fruits affected by…
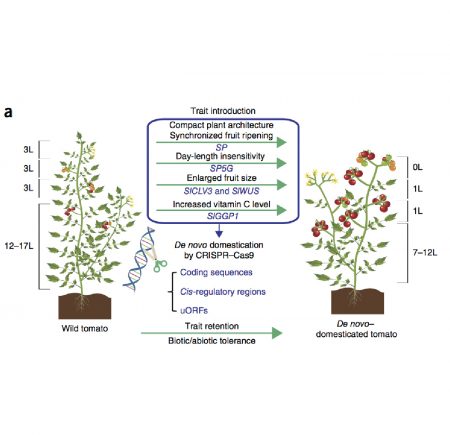
Domestication of wild tomato is accelerated by genome editing (Nature Biotech. - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWild tomato, Solanum pimpinellifolium, exhibits remarkable tolerance to salt stress and bacterial spot disease. Domestication of S.pimpinellifolium requires adjustment of day-length sensitivity, plant compactness, fruit size and the fruit could benefit from increased vitamin C content. Li et al. used…
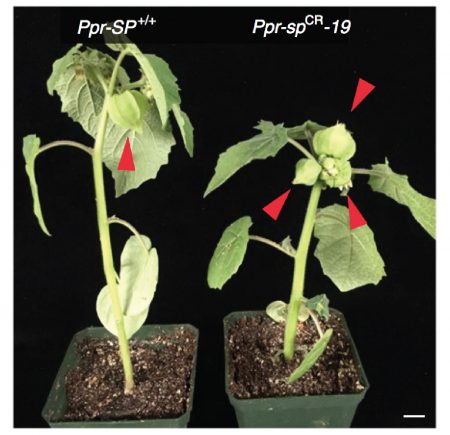

Rapid improvement of domestication traits in an orphan crop by genome editing (Nature Plants - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrphan crops, like groundcherry (Physalis pruinosa), are regionally important but are not grown on large commercial scale as they never went through a breeding cycle. Precision gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR/Cas9, can alter the most important agronomic traits in relatively short time. Lemmon…
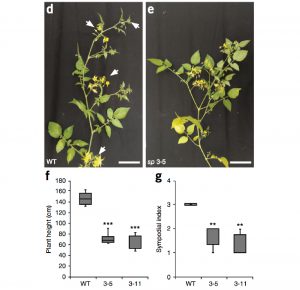
De novo domestication of wild tomato using genome editing (Nature Biotech - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBreeding of crops typically focuses on yield increase, and is accompanied with the loss the genetic diversity, reduced nutritional value as well as susceptibility to environmental stress. As many domestication traits exhibit simple Mendelian inheritance patterns, Zsögön et al. targeted known domestication…
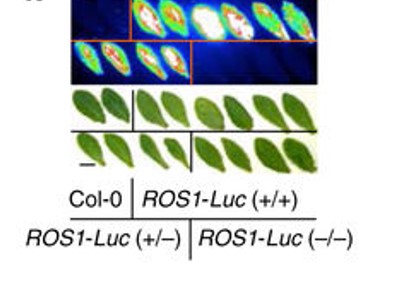
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene targeting in Arabidopsis using sequential transformation (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenome modification is a powerful tool, yet precise genome engineering in plants remains challenging. Miki et al. report on the sequential transformation method for gene targeting in Arabidopsis. The parental plants expressing CRISPR/Cas9 under the egg cell- and early embryo-specific DD45 promoter were…
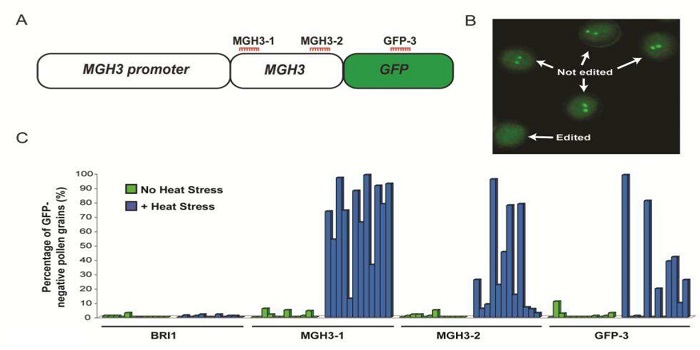
Increased efficiency of targeted mutagenesis by CRISPR/Cas9 in plants using heat stress ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCRISPR/Cas9 genome editing has rapidly become a powerful tool in modern plant science research. However, issues of low editing efficiencies and off-target mutations remain. LeBlanc et al. hypothesised that subjecting plants to high temperature stress, mimicking the optimal operating temperature of…

