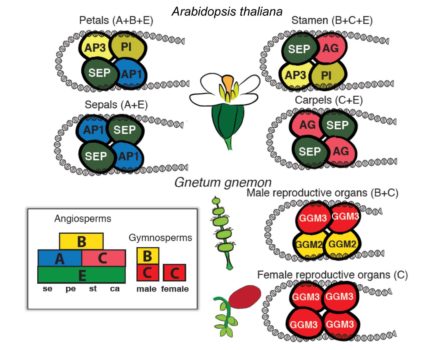
The origin of floral identity quartets
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Where do flowers come from? Their sudden appearance and rapid radiation was described as an “abominable mystery” by Charles Darwin. Ruelens et al. examine the genetic toolkit that underpins reproductive organ formation in gymnosperms to uncover the origins of flowers (which they pragmatically describe…

Review: Dark signaling in plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants use light as a source of energy and information; however, they are also sensitive and respond to light/dark diurnal cycling, with many processes happening during the dark phase of the diurnal cycle. In this review, Seluzicki et al. emphasize the importance of studying and understanding what…

CATchUP: A web database providing information on spatiotemporal specific gene expression
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNakamura et al. have created a searchable database, CATchUP (http://plantomics.mind.meiji.ac.jp/CATchUP) that allows the user to explore the spatiotemporal expression of genes across eight plant species (monocots and dicots) using data from publically available databases of large-scale RNA-Seq data.…
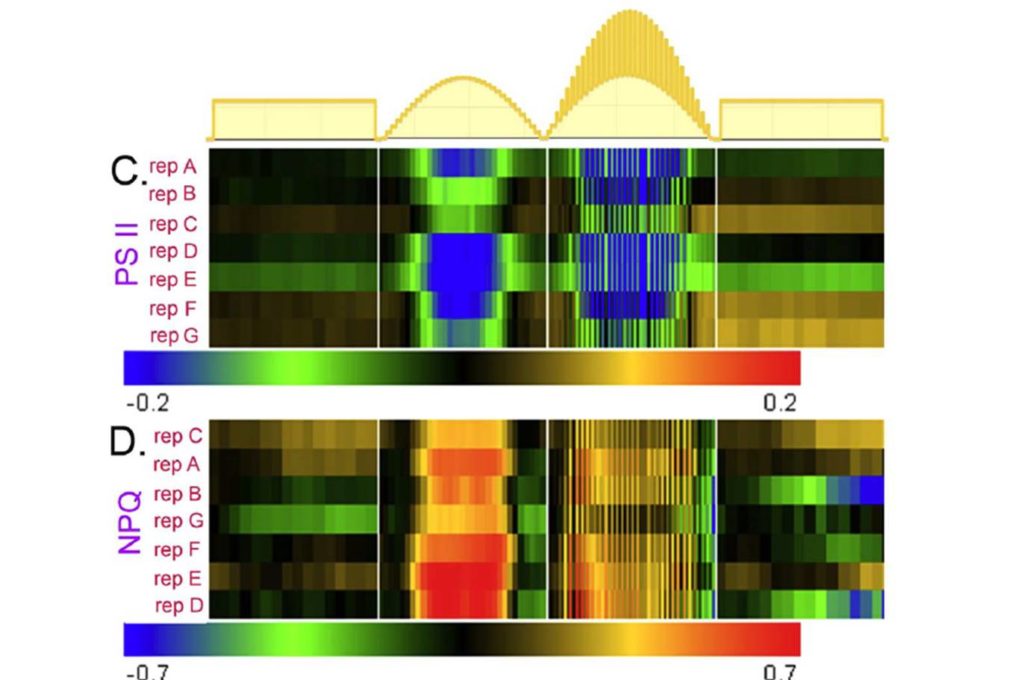
A shadow detector for photosynthesis efficiency ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchEfficient photosynthesis demands that plants have the capacity to capture photons when they are scarce, but at the same time not suffer damage from capturing more light energy than they are able to assimilate. To accomplish this, leaves need to be able to differentiate between a steady light level and…
Opinion: ATG8 expansion as a driver of selective diversification of autophagy? ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAutophagy is a process of selective membrane trafficking that delivers cargo to the vacuole or plasma membrane for recycling or secretion. ATG8 is a small ubiquitin-like protein that is required for formation of the double-membrane enclosed autophagy vesicle, the autophagosome. The ATG8 gene family has…

Review: Modeling stomatal conductance
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe transpiration rate of water though stomata, known as stomatal conductance or gs is one of the most critical and regulated of plant physiological processes. Buckley reviews recent progress on the development of comprehensive models of stomatal conductance, including the effect of soil moisture and…

Effect of selective logging on recovery of stored carbon in Amazonian forests
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe Amazon rainforest stores 30% of land-based ecosystem carbon. How are carbon stores affected by selective tree removal and subsequent regrowth? Stored carbon continues to be lost for several years after logging due to damage-associated mortality of surviving trees. Piponoit et al. use data from more…

Unexpected effect of “public good” mutants in a pathogen population
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchDisease-causing organisms attack as a population of diverse individuals. Is it possible to reduce the virulence of this population by introducing less-virulent individuals? Some studies have shown such an effect; as an example, application of low-virulence strains of Aspergillus flavus can protect…
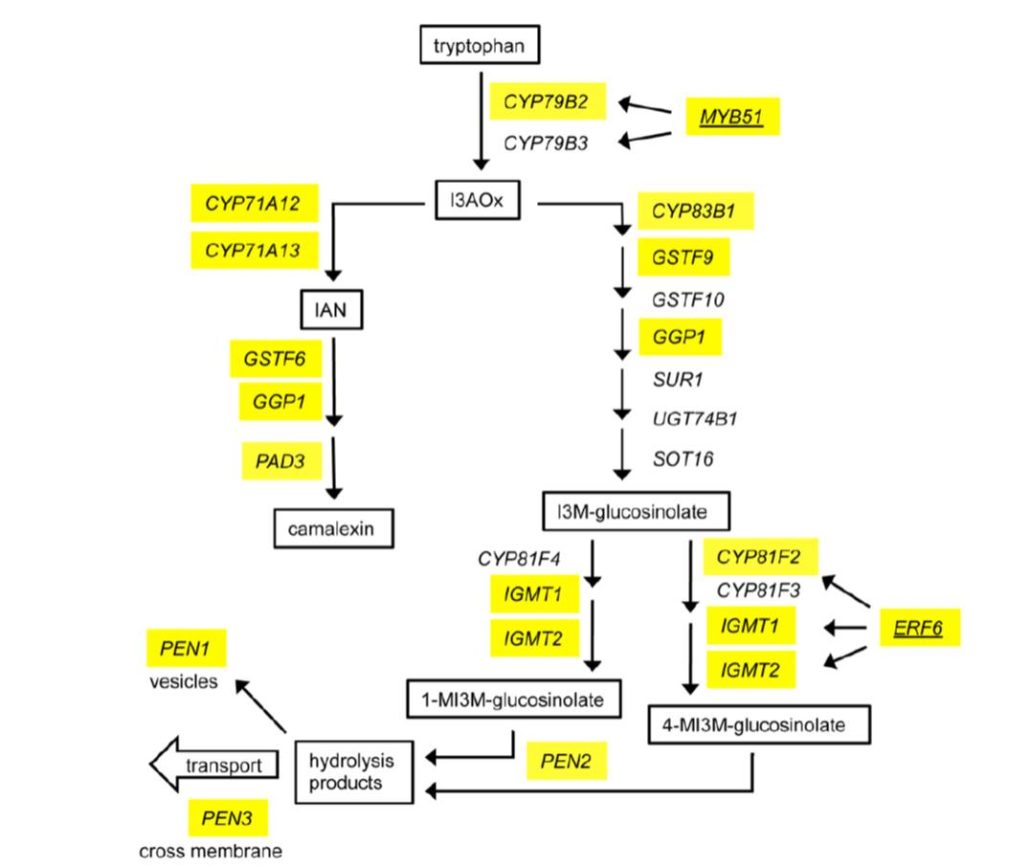
Transcriptional response to microbial pattern conferred by three WRKY transcription factors ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants perceive microbial pathogens though cell-surface receptors that recognize conserved microbial patterns such as flagellin. Previous studies have identified the WRKY family of transcription factors as contributors to Microbial-Associated Molecular Pattern (MAMP)-Triggered Immunity (MTI). Birkenbihl…

