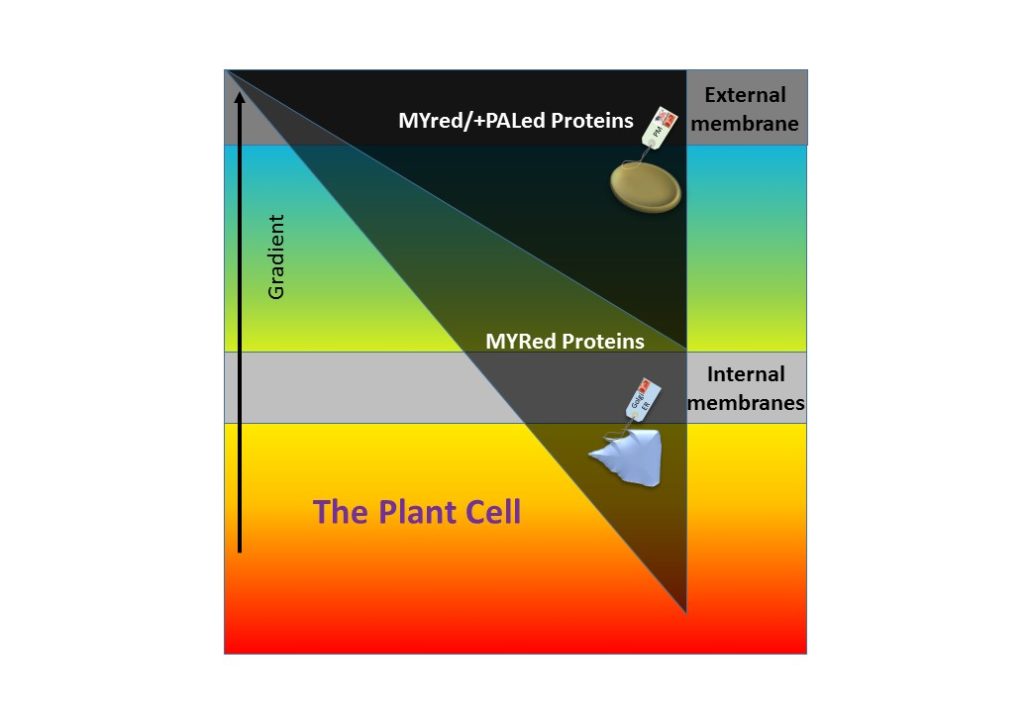
Lipid Anchor: Postal Code for Proteins on the Road to Membranes
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMajeran et al. investigate how plant cells target proteins to membrane compartments https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00523
By Wojciech Majeran, Thierry Meinnel & Carmela Giglione
Background: Living cells are encased in an oily barrier, the plasma membrane, made up of a double layer of lipids…
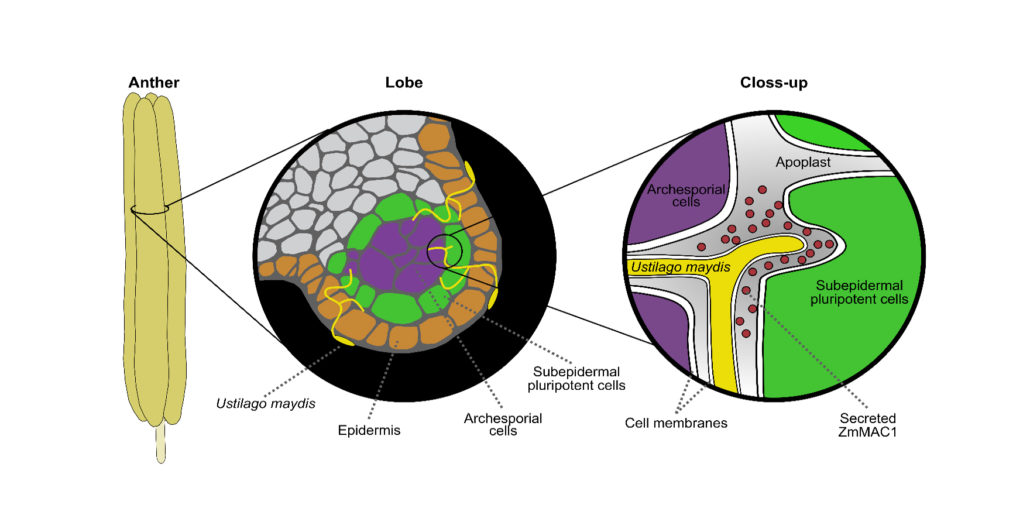
PLANT PROTEIN MEETS HOMER´S TROJAN HORSE
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBy Karina van der Linde and Virginia Walbot
Background: In contrast to animals in which meiotically competent cells develop in embryos, plants switch from vegetative to reproductive growth only during flowering. In maize, the most productive cereal crop, the tassel contains male flowers in which…

Bacteria exploit autophagy for proteasome degradation and enhanced virulence in plants (Plant Cell)
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyAutophagy has been defined as non-specific self-eating to obtain material that will be used for key processes within the cell. Even through authophagy has been demonstrated to be very important, its role during plant-bacteria interactions is not well known. Üstün et al. examined interactions between…
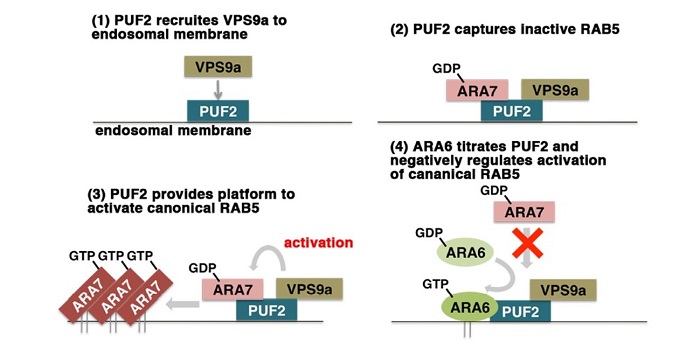
Integration of two RAB5 groups during endosomal transport in plants (OA) (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRAB proteins are membrane-anchored proteins that coordinate and regulate vesicle trafficking. Plants contain two group of RAB5 proteins, canonical (ARA7, RHA1) and plant-specific (ARA6), which share a common activator, VPS9A (Vacuolar Protein Sorting 9A). Ito et al. used an activated (GTP-bound) version…
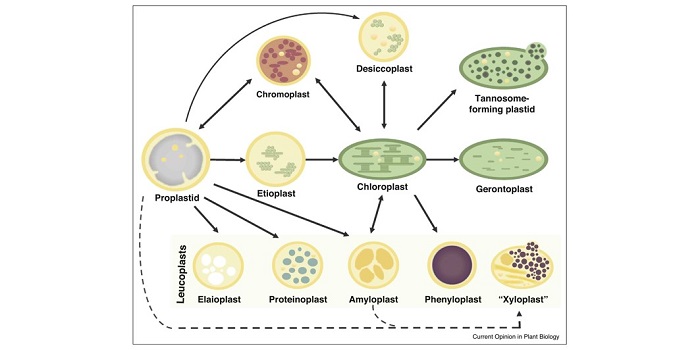
Review: A newly proposed plastid: the xyloplast (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn its simplest definition, a plastid is an organelle that manufactures and stores essential chemical compounds used by its host cell. Numerous plastids exist beyond the familiar chloroplast. Chromoplasts synthesise and store carotenoid pigments, and provide their hosts with district yellow, orange or…

The fungal MAP kinase Pmk1 controls intracellular spread of rice blast fungus in rice cells (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMagnaporthe oryzae is a devastating fungal pathogen that routinely threatens rice crop yields. Rice blast infection occurs when fungal hyphae penetrate into and proliferate within living plant cells, moving intracellulary from cell-to-cell through plasmodesmatal junctions. In a recent article published…
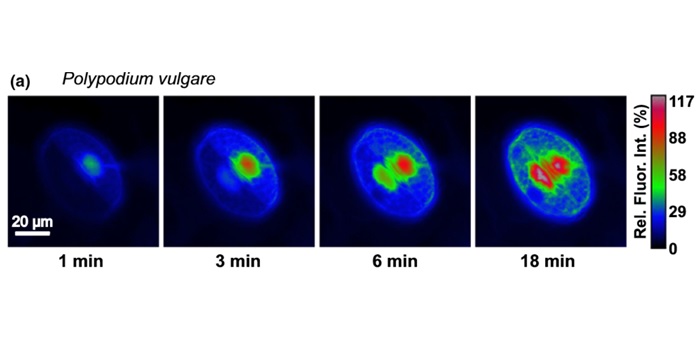
Guard cells in fern stomata are connected by plasmodesmata, but control cytosolic Ca2+ levels autonomously (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPotassium (K+) and calcium (Ca2+) ions are important for stomatal function in seed plants, however little is known about the contributions of these ions in the stomata of bryophytes and early-branching vascular plants. Voss et al. focus on how fern stomata regulate ion transport. Injection of K+ into…
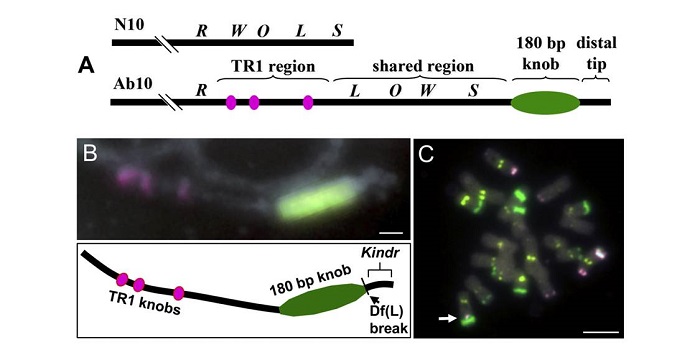
A Kinesin-14 motor activates neocentromeres to promote meiotic drive in maize
Plant Science Research WeeklyMeiotic drive is essentially a subversion of meiosis such that particular regions or alleles are preferentially favored for transmission to the progeny. Abnormal chromosome 10 (Ab10) is a classic example of meiotic drive in maize that converts heterochromatic chromosomal knobs into motile ‘neocentromeres’.…
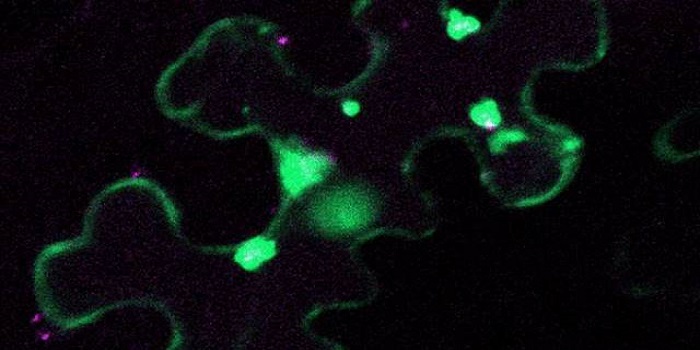
From The Scientist: Image of the day, Pseudomonas autophagy
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News
An image from a paper published in Plant Cell is featured as The Scientists "Image of the Day"
Image of the Day: Pseudomonas Autophagy
Researchers identify antibacterial functions of cell death in Arabidopsis when the plant is infected with Pseudomonas.
By The Scientist Staff | March 30, 2018
A…

