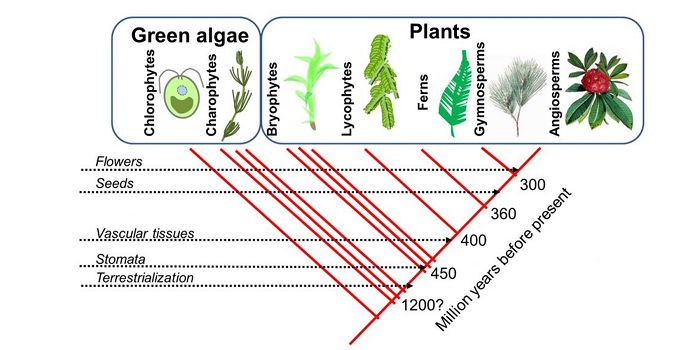
From LUCA to Lily: 12 perspectives for teaching about plants
Blog, Education, Resources, Resources, Undergraduate0 Comments
/
The other day I was talking to a friend about the need to demystify plants, so that teachers feel as confident in their teaching of plant biology as they do about animal biology. I wonder if sometimes we teach plants too much in isolation, so it’s not always clear how plants relate to other organisms…
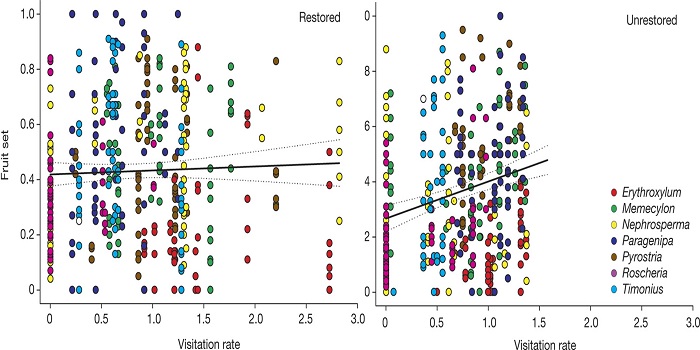
Ecosystem restoration strengthens pollination network resilience and function ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHow does ecosystem restoration affect ecosystem services such as pollination? Kaiser-Bunbury et al. analysed 64 plant-pollinator networks across four restored and four unrestored communities. Restoration involved the removal of all exotic plants (nearly 40,000 individuals). After restoration, over a…

Two clustered NLR genes with opposing functions in rice blast resistance and yield ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe indigenous Chinese rice variety Gumei 4 (GM4) shows durable and specific resistance to the rice blast fungal pathogen Manaporthe oryzae. Deng et al. mapped and sequenced the resistance locus Pigm, and found that it contains a cluster of 13 NLR (nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat) genes, three…
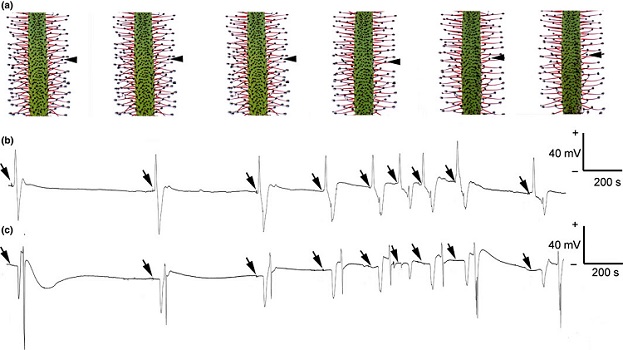
Electrical and hormonal signals of prey capture in sundew ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWithout eyes, mouths or noses, how do carnivorous plants know that they’ve captured prey? Previous studies in various carnivorous species have shown that electrical signals as well as the jasmonate defense hormones contribute to prey detection. Krausko et al. examined these signals in leaves of the…

How can genomics help neglected crops fight disease?
Blog, Research, Research BlogGuest post by Kelsey Wood (@klsywd) a PhD student researching the genetics and genomics of plant-pathogen interactions at the University of California, Davis.
I recently attended a Plant Pathology symposium on “Genomics Strategies for Developing Sustainable Disease Resistance for Neglected Crops…
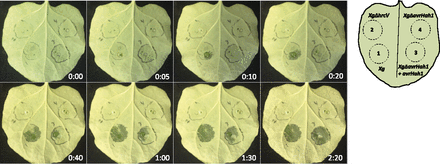
A pectase lyase that is an indirect target of a Xanthomonas TAL effector promotes susceptibility
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchOne of the many ways that Xanthomonas bacteria manipulate their host plants is by the production of transcription activator-like (TAL) effectors, which the bacterium introduces into the host cell where they alter gene expression in the host nucleus. Schwartz et al. investigated the targets of the TAL…
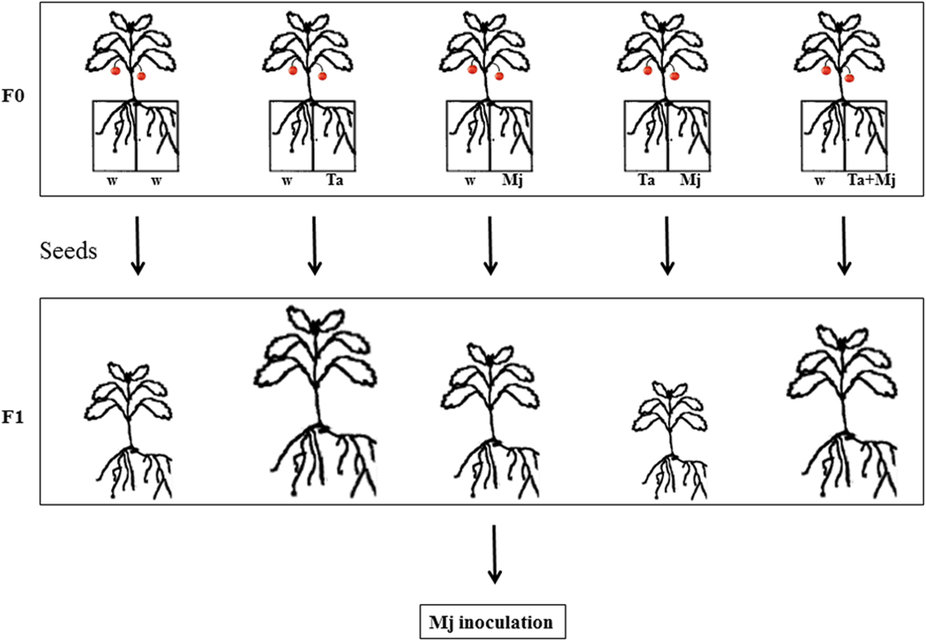
Transgenerational biocontrol against root-knot nematode following priming by biocontrol fungus
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRoot-knot nematodes including Meloidogyne javanica are major agricultural pests. Previous studies have shown that biocontrol agents including species of the fungal genus Trichoderma interfere with root-knot nematode pathogenicity, directly through effects on the nematode, and indirectly through a stimulation…
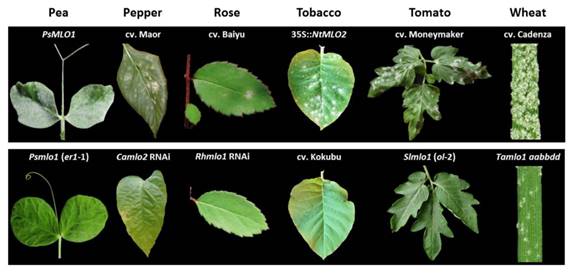
Review: mlo-based resistance: An apparently universal “weapon” to defeat powdery mildew disease ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPowdery mildew disease is a broad term that encompasses more than 650 species of powdery mildew fungi that affect about 10,000 plant species, with serious economic consequences. In the 1930s/40s, broad-spectrum resistance to powdery mildew was found in barley with a loss-of-function of the Mildew resistance…

Review: The sexual advantage of looking, smelling and tasting good, the metabolic network that produces signals for pollinators ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe interaction between angiosperms and their pollinators provides an excellent system to study co-evolution, and underpins the evolution of the biosynthesis of numerous interesting and useful specialized metabolites, from pigments to fragrances. Borghi et al. review the metabolic pathways that produce…

