An Emerging Paradigm? RxLR Cleavage Before Effector Secretion
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In Brief0 Comments
/
Eukaryotic pathogens are responsible for devastating plant diseases that threaten food supplies globally – think potato blight caused by the oomycete Phytophora infestans, rice blast caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, and wheat stem rust caused by the fungus Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici.…

How Calcium Signals Early Warning
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiu et al. uncover a direct link between calcium signaling and a plant immune receptor http://www.plantcell.org/content/29/4/746.abstract
Plants have evolved a sophisticated system to defend against pathogen attack that involves recognition of an invading pathogen and activation of the immune system.…

Rapid cytosolic calcium elevations in Arabidopsis during aphid feeding
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCalcium signaling is a common plant response to many different stimuli. Vincent et al. used a fluorescent calcium reporter, GCaMP3, to record calcium responses in Arabidopsis to feeding by aphids (specifically, the green peach aphid Myzus persicae). Through analysis of various mutants, key components…
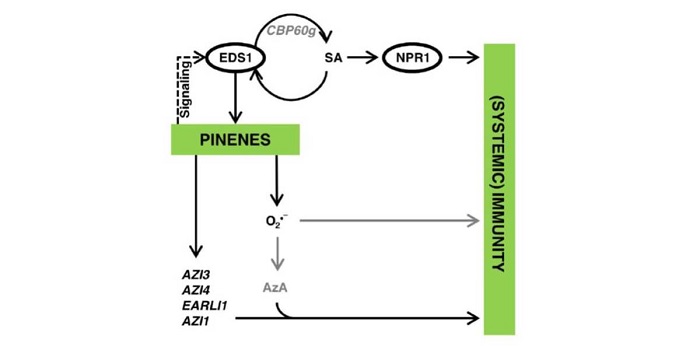
Monoterpenes support systemic acquired resistance within and between plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPathogen perception leads to local and systemic immune responses including systemic acquired resistance (SAR). The nature of the mobile signals and their movements remain uncertain. Riedlmeier et al. demonstrated that certain monoterpenes including α- and β-pinene accumulate in SAR-inducing conditions…
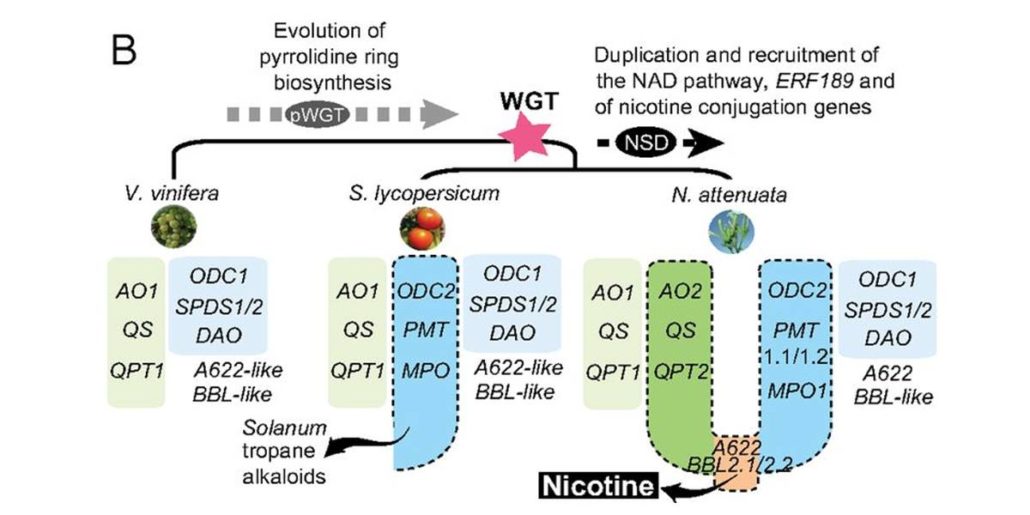
Wild tobacco genomes reveal the evolution of nicotine biosynthesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe genus Nicotiana encompasses several species and hybrids, the most famous being Nicotiana tabacum, cultivated for production of tobacco. Xu et al. sequenced the genome of Nicotiana attenuata and Nicotiana obtusifolia with an interest in identifying the origins of nicotine biosynthesis. Nicotine is…

Review: Ancestral alliances: Plant mutualistic symbioses with fungi and bacteria ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMartin et al. have written a must-read review on the evolution of plant mutualistic symbioses and strategies through which hosts and microbes communicate and coordinate their activities. This review also covers the contributions of hormones in the formation of symbiotic tissues, and how the mutualistic…

Global translational reprogramming of plant immune response, and engineering of disease resistance through regulated translation ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants fight back when pathogens attack, and in the first of a pair of papers Xu et al. have revealed a new insight into this response by demonstrating a significant translational upregulation of many defense-response mRNAs (10.1038/nature22371). Previously, this group showed that the translation of…

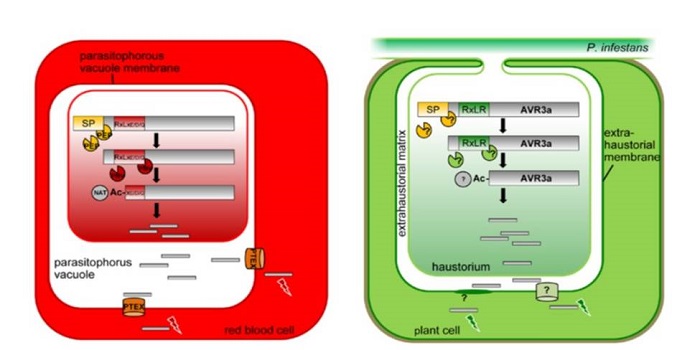
The RxLR motif of the Phytophthora infestans effector AVR3a is cleaved before secretion ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRxLR effectors are proteins secreted from pathogens that enter the cells of the host and support the effectiveness of the pathogen in various ways. Their name refers to the sequence RxLR (Arg-Xxx-Leu-Arg). Previously, this sequence has been thought to be involved the effector’s entry into the host…

Bacterial biosensors for in vivo spatiotemporal mapping of root secretion
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBiosensors are powerful tools that provide readouts for various small molecules so that they can be detected and located. Pini et al. have developed a set of biosensors for expression in bacteria (Rhizobium leguminosarum) that reveal some of the small molecules (including key sugars, polyols, organic…

