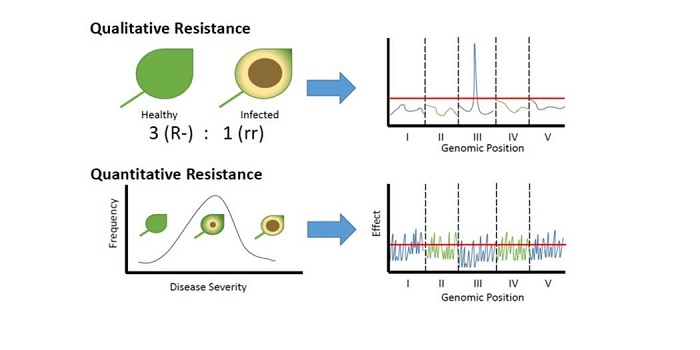
Review: Quantitative resistance: More than just perception of a pathogen
0 Comments
/
Some forms of pathogen resistance function like an on/off switch: if a plant has an appropriate receptor it recognizes a pathogen and shows resistance. Corwin and Kliebenstein review the other kind of resistance, quantitative resistance, in which many genes make small contributions to the plant’s resistance.…
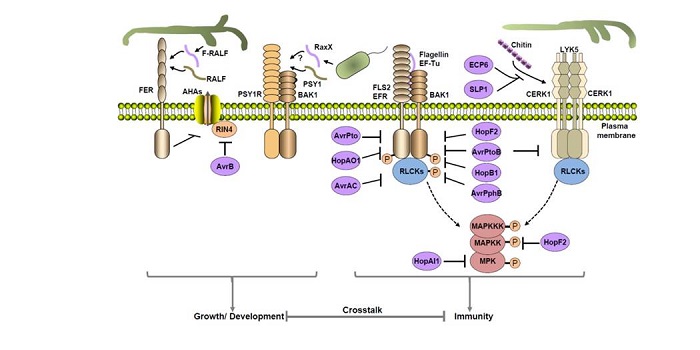
Review: Receptor kinases in plant pathogen interactions: More than pattern recognition
Zhou et al. review the contributions of Receptor-Like Kinases (RLKs) and Receptor-Like Proteins (RLPs) as Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) that contribute to the recognition of pathogens, as well as the contributions of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs). The authors summarize recent studies…
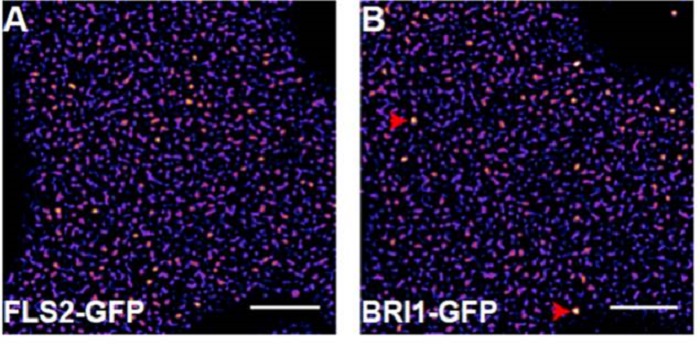
Plant immune and growth receptors share common signaling components but localize to distinct plasma membrane nanodomains
Signal transduction in plant and animal cells is often initiated at the plasma membrane (PM) and involves common signaling components, raising the question of how receptor complexes elicit distinct signaling outputs. To address this question, Bücherl et al. investigated physical characteristics of the…
A Salivary Effector Aids in Brown Planthopper Feeding on Rice Plants
Herbivory-induced plant cell wall modifications play an important role in deterring herbivory. Modified cell walls not only act as physical defenses against herbivores by enhancing the mechanical hardness of plant tissues but also reduce the digestibility of food for herbivores, thereby functioning as…
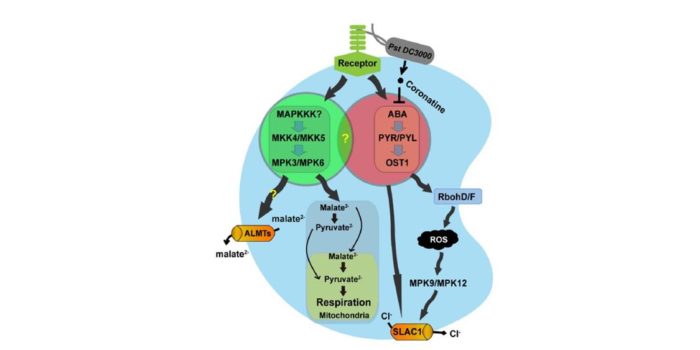
Stomatal immunity: Roles of MAP kinases and cytokinin
When a pathogen is perceived, plants have the ability to induce stomatal closure to prohibit the pathogens from passing into the inner tissues; this response is known as stomatal immunity. Two new papers in The Plant Cell investigate mechanisms by which pathogen perception is transduced into stomatal…
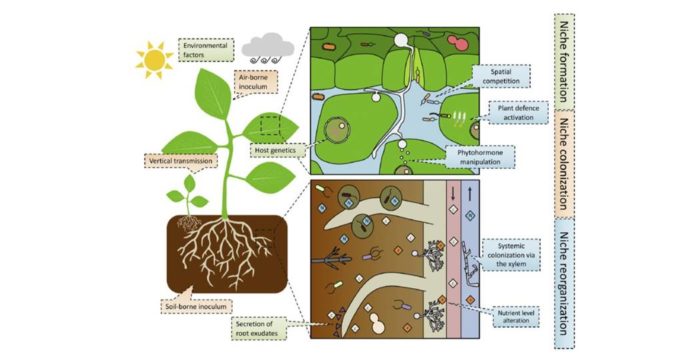
Review: Host-microbe and microbe-microbe interactions for plant breeding ($)
The idea that the microbes on and within an organism (the microbiota) influence an organism in positive, neutral and negative ways has been a hot topic in popular science, especially the role of the gut microbiota in human health and nutrition. Plants are similarly influenced by their microbiota, as…

The importance of pollen chemistry in evolutionary host shifts of bees
Some bees are generalist pollinators that gather pollen from a wide range of species, whereas others are specialists that visit only one or a few species. Vanderplanck et al. examined floral traits of the host plants of two different groups of generalist bees. There was no significant correlation between…
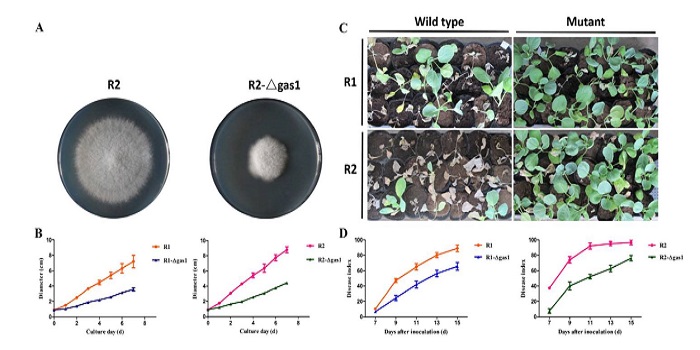
Proteomics of two differently pathogenic races of Fusarium oxysporum
Fusarium oxysporum is a fungal pathogen of plants. F. oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans (Foc) causes fungal wilt in cabbage. Two races have been identified, with Race 2 being much more pathogenic than Race 1. Li et al. used a proteomic approach to investigate the origin of Race 2’s enhanced pathogenicity.…
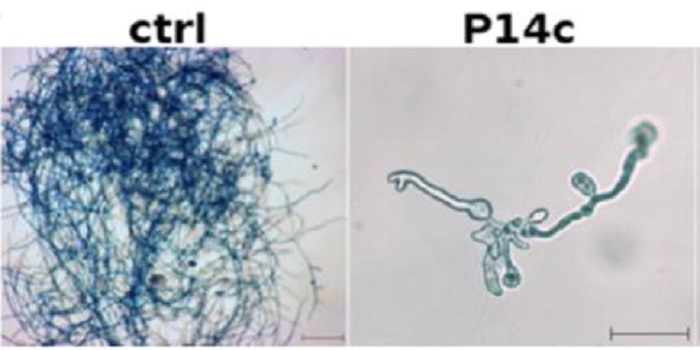
Sterol-binding activity of PR-1 contributes to its antimicrobial activity ($)
PATHOGENESIS-RELATED 1 (PR-1) protein was identified 50 years ago as a small protein induced in response to pathogens, but its mode of action has remained obscure. PR-1 is a member of the CAP family (cysteine-rich secretory protein, antigen 5, and pathogenesis-related 1). These proteins share a 150…

