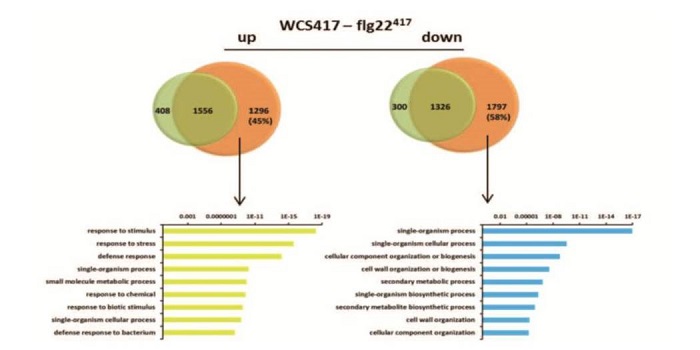
Signatures of adaptation to mutualists revealed by root transcriptional dynamics
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogA plant's rhizosphere consists of a huge array of pathogenic microbes many of which can trigger defense responses, leading to decreased growth. On the other hand, beneficial microbes such as rhizobacteria promote growth and can induce systemic resistance while suppressing local immune responses. A recent…
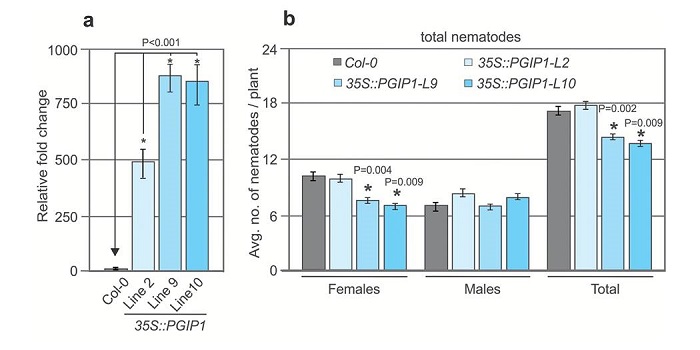
Damage-associated signals differentially impact nematode parasitism
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRoots must protect themselves from a diverse range of microbial and animal pests. To accomplish this, plants have evolved sophisticated signalling machinery to detect the presence of these pests or to quickly react to the damage that they cause. In a recent study, Shah et al. identified host receptor…
To Grow or to Defend: That is the Question for Plant Central Metabolism
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellFusari et al. perform GWAS to explore primary plant metabolism https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00232
By Corina M. Fusari and Rik Kooke
Background: Primary metabolites such as sugars, organic acids, and amino acids are essential chemical compounds that drive plant growth and development by providing…
A Plant Protein That Foils Aphid Feeding
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKloth et al. probe aphid feeding behavior. The Plant Cell 2017 doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00424
By Karen Kloth
Background: Aphids are phloem-feeding insects. They penetrate plants with a piercing-sucking mouth. Once they reach a tube where the plant transports its sugar-rich phloem sap, they can take…

"Blue halo" light scattering enhances signalling to bees
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogVisual and other cues attract pollinators. Bees vision is skewed towards blue colors, but they also visit non-blue flowers. Moyroud et al. looked at how petal surface textures affect bee responses. The authors observed that similar parallel cuticular striations in diverse angiosperm lineages show convergent…
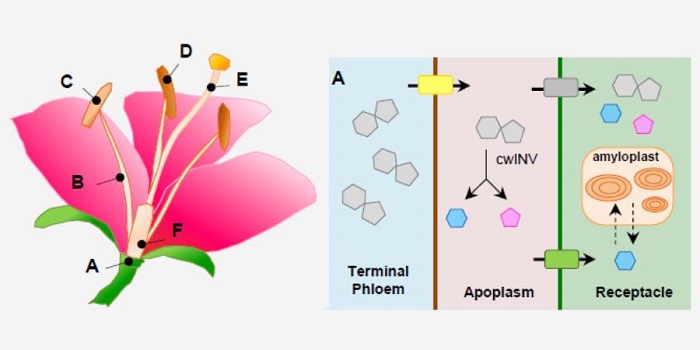
Update: Flower primary metabolism, pollinators’ preferences and seed and fruit set
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogBecause of their important roles in attracting pollinators, the secondary or specialized metabolites of flowers (color, fragrance) get a lot of attention. Borghi and Fernie argue that flower function is equally dependent on primary (central) metabolites, which not only provide the precursors for secondary…
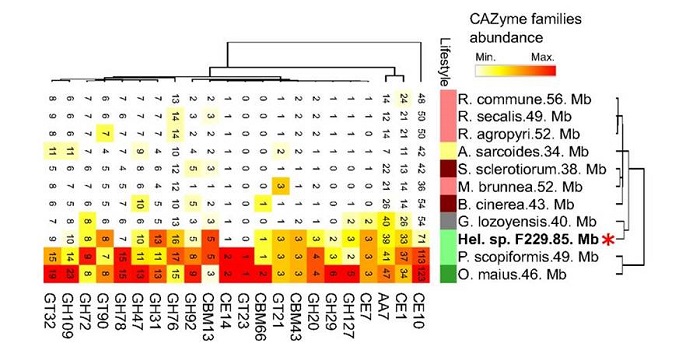
Phosphorus nutrition and root-associated fungal microbiota of nonmycorrhizal Arabis alpina
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogAssociations with mycorrhizal fungi greatly enhance phosphorus (P) uptake for most plants, but the Brassicaceae are nonmycorrhizal due to the loss of essential symbiosis genes. Almario et al. investigated the fungal microbiota of Arabis alpina, a Brassicaceae species that grows in very-low P soils. The…
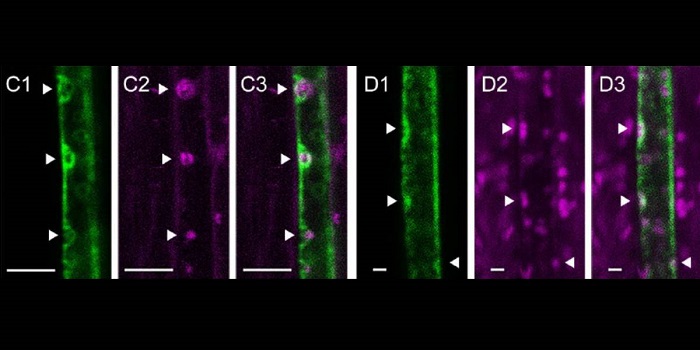
A Phloem Protein Contributes to Aphid Resistance and Heat Stress Tolerance
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAphids are highly destructive insect pests—in addition to robbing plants of sugar-rich phloem sap, they carry viruses that can be deadly to the plant. To reach the phloem sap, aphids must penetrate the plasma membrane of sieve elements. Mature sieve elements, which are virtually empty, translocate…
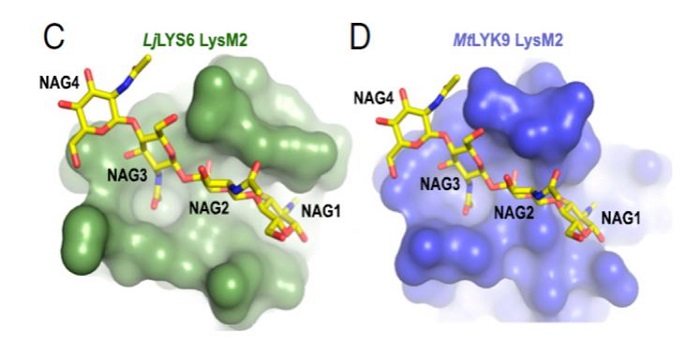
Receptor-mediated chitin perception in legume roots is functionally separable from Nod factor perception ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSmall molecules are crucial for the recognition of friends and foes. For example, Nod factors are N-acetylglucosamine-derived “friend” signals produced by bacterial microsymbionts. Chitin is an N-acetylglucosamine-derived fungal wall polymer that plants perceive as indicating the presence of an enemy. …

