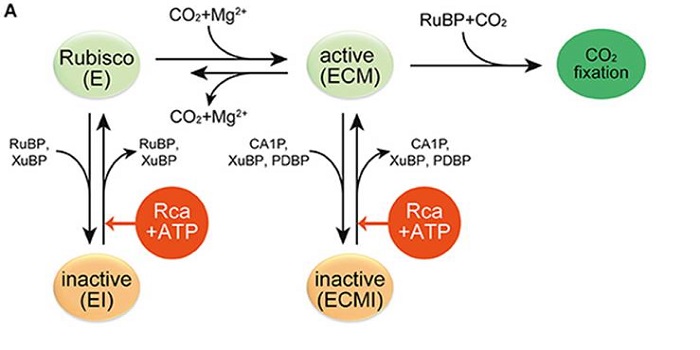
Review: Rubisco activases: AAA+ chaperones adapted to enzyme repair
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Rubisco, the fundamental enzyme required for photosynthetic carbon fixation, is susceptible to inactivation by the inhibitory binding of various metabolites. Rubisco activases (Rca’s) are enzymes that remodel Rubisco and facilitate the elimination of the inhibitor. All photosynthetic organisms have…
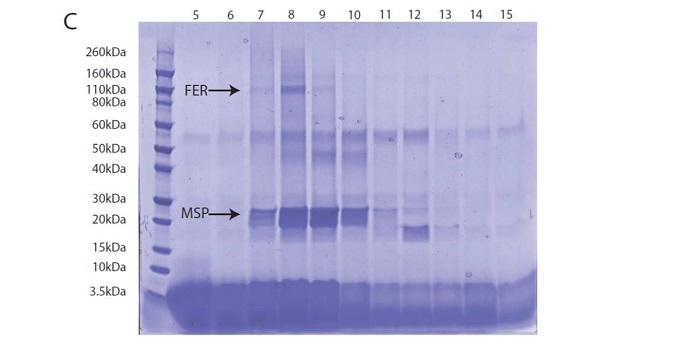
Cell-free membrane protein expression system enables functional characterization of receptor-like protein kinase FERONIA ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMembrane proteins are some of the most interesting cellular proteins, serving as sensors and transducers of diverse signals, yet they also are the most challenging to investigate because they require lipid interactions for proper structure and function. Recently, cell-free expression systems for membrane…

Special issue: Flowering of jasmonate research
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchJasmonates are a family of compounds including jasmonic acid and its derivatives that regulate many plant processes from germination to defense. The Journal of Experimental Botany has a special issue on jasmonate research, which commemorates the advances in this field in the ten years since the JAZ proteins…
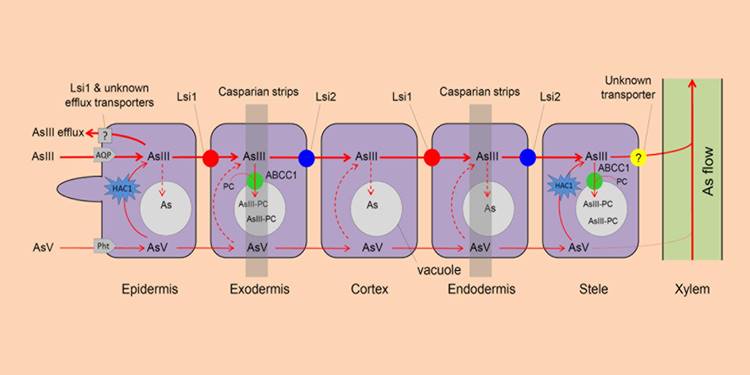
Review: Arsenic transport in rice and biological solutions to reduce risk
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRice is a staple food for half of the world’s population, but it accumulates the toxic metalloid arsenic (As), which is present in soils and in plants in two forms, arsenate (AsV) and arsenite (AsIII). Chen et al. review the genetics and biochemistry of As uptake and sequestration into the rice grain,…
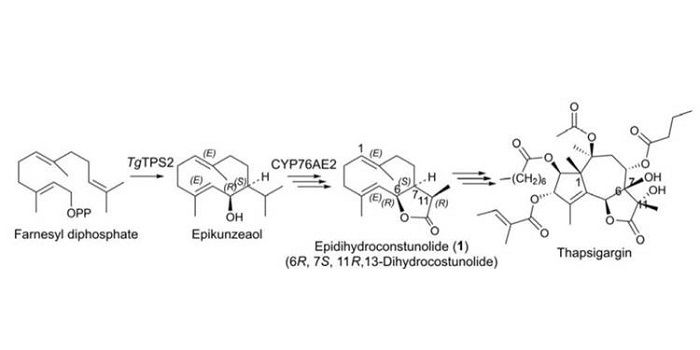
Thapisgargin Formation in Thapsia
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchThe Mediterranean plant Thapsia garganica (Apiaceae), also known as deadly carrot, produces the highly toxic compound thapsigargin. This compound is a potent inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase calcium pump in mammals and is of industrial importance as the active moiety of…
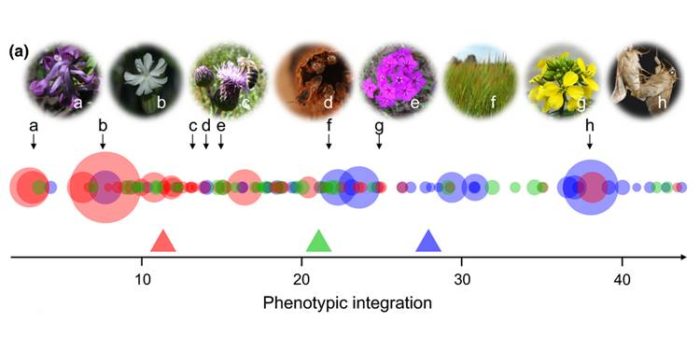
Covariation and phenotypic integration in chemical communication displays ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHumans aren’t very sophisticated at reading chemical communication cues. Towards deciphering the information content of complex chemical mixtures produced by plants and animals, Junker et al. ask to what extent chemical communication displays (CCDs) are replicated between samples and individuals. The…
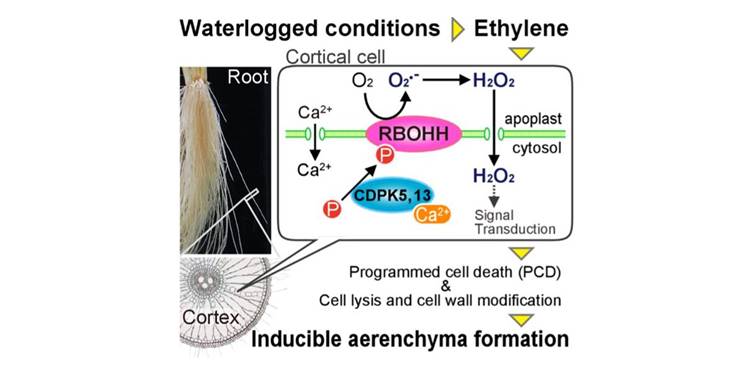
Better understanding how plant roots breathe under water ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWaterlogging, a process by which water saturates soil, results in oxygen-deficient soil conditions and can result in massive crop loss. In order for plants to survive in waterlogged soil, shoots transport oxygen to roots through lysigenous aerenchyma, a specialized tissue type formed by ethylene-induced…
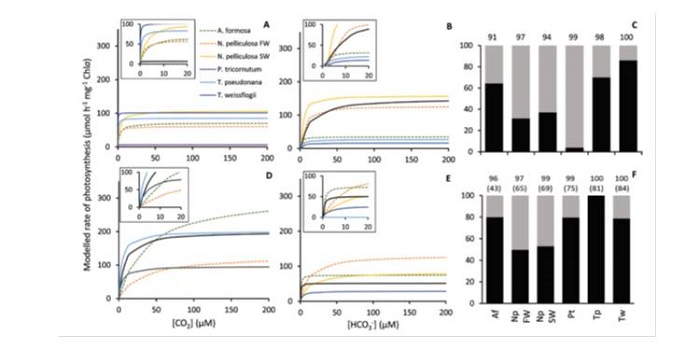
Diversity of CO2 concentrating mechanisms and responses to CO2 concentration in marine and freshwater diatoms ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe CO2-fixing enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) works most efficiently at high concentrations of CO2. Many organisms have evolved CO2-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs), such as the PEP-carboxylation that occurs upstream of Rubisco in C4 plants. Diatoms and other eukaryotic algae use a…
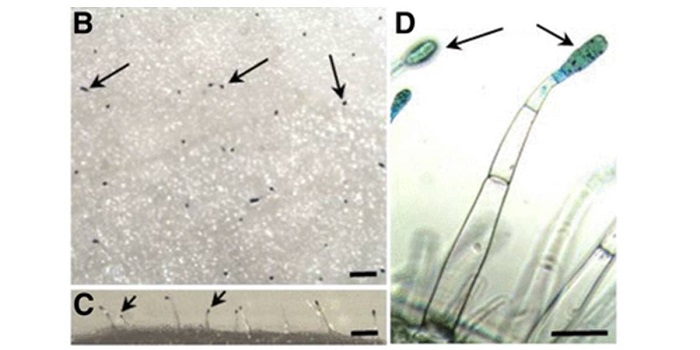
Unusual Rubisco Subunit Found in Trichomes
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchRubisco is responsible for CO2 fixation during photosynthesis. This enzyme is assembled from eight large subunits (RbcL), encoded by a single chloroplast gene, and eight small subunits (RbcS), encoded by a nuclear gene family. Although Rubisco’s catalytic reaction is mostly controlled by the large…

