
Persulfidation-controlled guard cell ABA signaling
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellShen et al. explore the role of H2S signaling and the reversible modification persulfidation in guard cell signaling. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00826
Yanjie Xie; Laboratory Center of Life Sciences, College of Life Sciences, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095, PR China.
Background:…
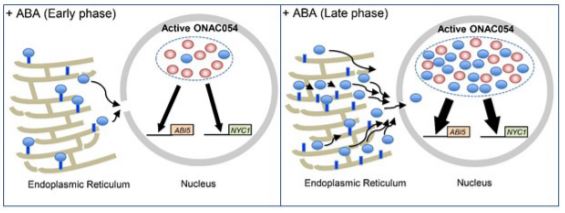
Make, Modify, Move: Multilayered Regulation of ONAC054 During ABA-Induced Leaf Senescence
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In Brief‘Senescence’ originates from the Latin word senescere, to grow old. However, the process of leaf senescence is not simply the passive death of the leaf but instead represents an active and highly regulated process of nutrient remobilization from older leaves into developing parts of the plant to…

Rapid changes: ABA-independent SnRK2s target mRNA decay
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMagda Julkowska
[email protected]
In response to stress, secondary messengers and rapid and reversible protein phosphorylation contribute to signaling cascades that generate unique signatures indicating stress type and severity. Activation of stress-induced signaling cascades…
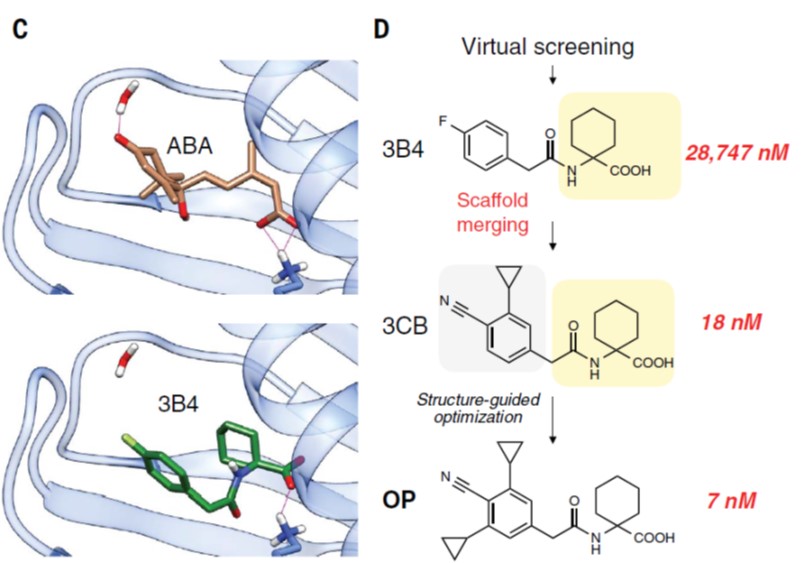
Dynamic control of plant water use using designed ABA receptor agonists (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyABA is synthesized in response to water stress and promotes stomatal closure, thus decreasing transpiration. Crop yields can be increased by controlling transpiration early in the growing season, ensuring that soil water resources persist through the seed-set period. Building upon earlier studies, Vaidya,…
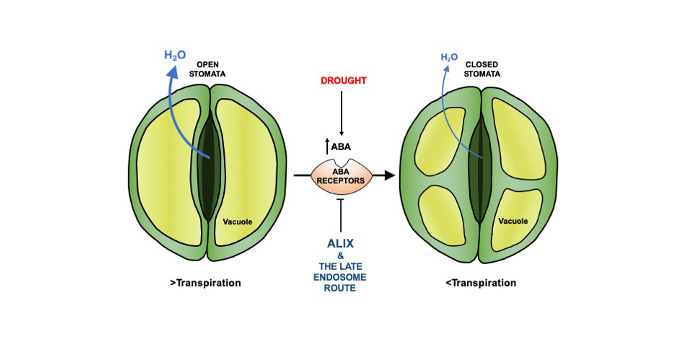
ALIX helps to open the pore
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellGarcía-León et al. reveal a function for a trafficking protein in stomatal aperture regulation.
Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00399
By Marta García-León and Vicente Rubio
Centro Nacional de Biotecnología (CNB-CSIC) Darwin, 3. 28049 Madrid, Spain
Background: Plants protect…
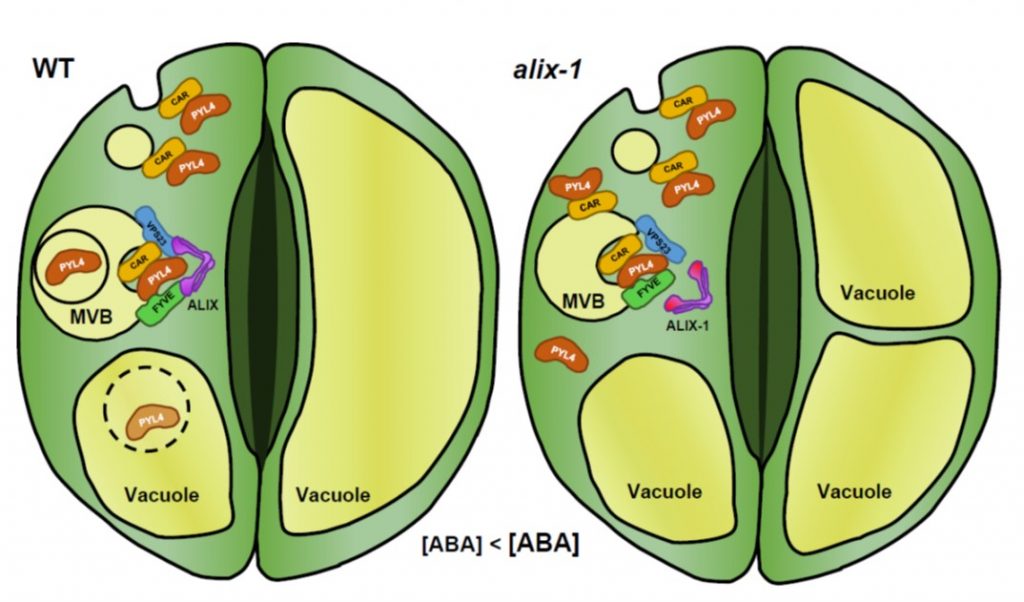
ABA receptor abundance, thus ABA sensitivity, is regulated by ALIX ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo balance water loss and CO2 assimilation, stomatal aperture is tightly controlled in accordance with environmental changes, mediated by ABA signaling. Here, García-León et al. found that ABA sensitivity and stomatal aperture are regulated by the trafficking and vacuolar degradation of ABA receptors…
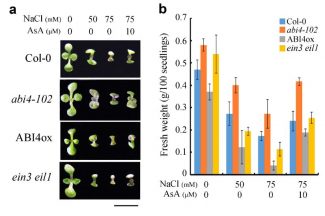
Ethylene and ABA Regulate Ascorbic Acid and Reactive Oxygen Species
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe phytohormones ethylene and abscisic acid (ABA) often interact in controlling plant growth and development processes as well as plant responses to stress. The detailed mechanisms underlying the interaction of these two phytohormones, which may act synergistically or antagonistically with each other,…
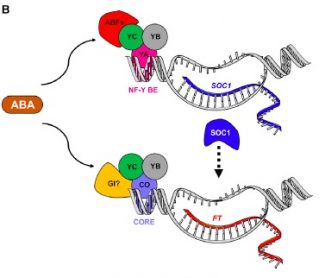
ABA mediated drought-accelerated flowering ($) (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the most plastic developmental process in plants is the timing of flower initiation. Plants select favourable conditions to achieve reproductive success. Light and temperature are continuously monitored through molecular mechanisms that are still poorly understood. Drought escape (DE) is an adaptive…
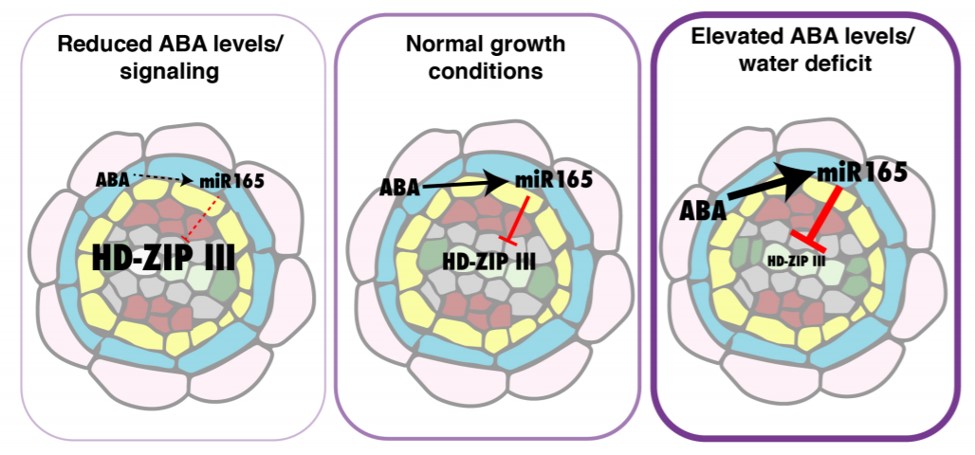
Root xylem formation and vascular acclimation to water deficit involves endodermal ABA signaling via miR166 ($) (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbiotic stress influences plant development, with the phytohormone ABA playing an important role. Ramachandran et al. have demonstrated ABA mediated activation of microRNA 166, which regulates expression levels of the HD-ZIP III transcriptional factor family. Exogenously supplied ABA alters xylem patterning…

