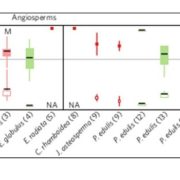
A multi-species synthesis of physiological mechanisms in drought-induced tree mortality
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogGlobal change forecasts include projections of severe droughts that could affect many forested biomes, largely influencing future energy and element fluxes. There are two physiological mechanisms associated with tree mortality in response to drought: hydraulic failure (inhibition of water transport)…

Phototropin perceives temperature based on the lifetime of its photoactivated state
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogFujii et al. studied the role that blue-light perceiving phototropins play in sensing temperature. They studied the temperature response in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, which has only one phototropin. At 5°C, blue-light perception by phototropins induces a cold-avoidance response in which chloroplasts…

4D root gene expression
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIt becomes more and more clear that regulation of complex traits and processes, such as root growth and lateral root growth, involves not only gene expression quality (which genes are expressed), quantity (how much transcript is present) and space (in which cell-type transcripts are accumulating) but…
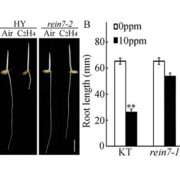
OsEIL1 affects auxin biosynthesis in ethylene-inhibited rice root elongation
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe role of crosstalk between auxin and ethylene in primary root development has been studied in the dicot model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, but is less well understood in monocots. Through a genetic screen for roots that elongate in the presence of ethylene , Qin, Zhang et al. identified a mutant rice…
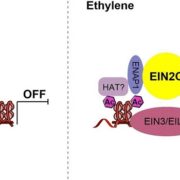
EIN2 mediates direct regulation of histone acetylation in the ethylene response
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPerception of the phytohormone ethylene results in the cleavage of EIN2 and translocation to the nucleus of its C-terminal end, EIN2-C. Zhang et al. showed that EIN2-C is essential for chromatin modification that allows EIN3, the main ethylene signaling transcription factor, to transcriptionally regulate…
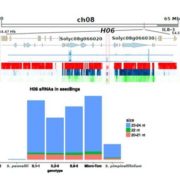
Frequent paramutation-like features of natural epialleles in tomato
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogParamutation is a natural epigenetic process that occurs in plants and animals that is associated with methylation-mediated gene silencing. The curious thing about a paramutated allele is than it can transfer its silenced state to its homologous and active allele. This freshly paramutated allele then…
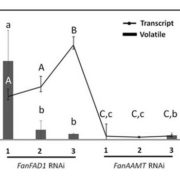
Identification of a methyltransferase catalyzing the final step of methyl anthranilate synthesis in cultivated strawberry
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMethyl anthranilate (MA) is a volatile chemical that contributes to the aroma of strawberry (Fragaria spp.), but several modern varieties do not produce this chemical. Pillet et al. tried to identify the biosynthetic pathway of MA. They compared transcriptomes between MA-producing and non-producing varieties…
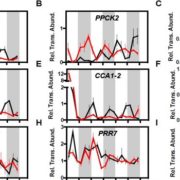
Silencing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase phosphorylation in a CAM plant
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMany plants living in arid environments conserve water by taking up CO2 at night through the action of the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC); this process, which is widespread in the Crassulaceae family, is known as Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM). The nocturnal activity of PPC is regulated…
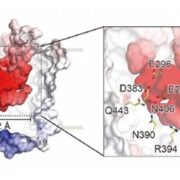
A plant protein structure from the MATE family, an important family of transporters ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe MATE (multidrug and toxic compound extrusion) family is found in all three domains of life. Proteins in this family are secondary transporters, functioning as sodium or proton/organic cation antiporters. This family has diverse functions in plants, including vacuolar sequestration of alkaloids,…

