Review: MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plant–environment interactions (Annu Rev Plant Bio) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate the expression of target genes through mRNA cleavage, translational repression and DNA methylation. The last decade has seen an exponential increase in the studies performed to understand the biogenesis of plant miRNAs, their…
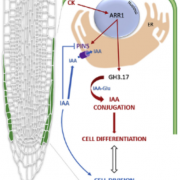
The lateral root cap acts as an auxin sink that controls meristem size (Curr Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring root growth, cellular activities need to be coordinated across tissues. Mambro et al. have identified molecular mechanisms involved in root apical meristem maintenance by auxin homeostasis regulation in lateral root cap (LRC) cells. The cytokinin response regulator ARR1 regulates expression of…
Tandem fluorescent protein timers for non-invasive relative protein lifetime measurement in plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProteins are in a dynamic state of synthesis and degradation and their half-lives can be adjusted under various circumstances. Many rapidly degraded proteins function as regulatory molecules, such as transcription factors. The rapid turnover of these proteins is necessary to allow their levels to change…
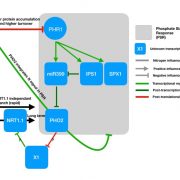
Nitrogen actively controls phosphate starvation response in plants (Plant Cell) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphate and nitrogen are two essential macronutrients for growth of plants. The homeostasis and sensing pathways for these two macronutrients have been investigated extensively, but independently. Recently, -omics approaches have enabled finding interlinks and cross talks between two or more macronutrients.…

A direct connection between PSI & PSII systems in green plants (Plant Cell Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants often optimize their development according to the prevailing environmental conditions, of which light is one of the most important. Arabidopsis uses a PSI-PSII megacomplex as the photosystem reaction center, to transfer the excessive energy from PSII to PSI rapidly. Recently, Yokono et al. proposed…

Review: Brassinosteroid signaling in plant development and adaptation to stress ($) (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this new review, Riverola et al. highlight the significance of the phytohormone brassinosteroid in plant development and responses to stress. The authors discuss BRL1, LRR-RLK receptor mediated signaling mechanism that is crucial for root development and stress response. This signaling mechanism varies…
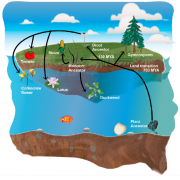
Convergent gene loss in aquatic plants predicts new components of plant immunity and drought response (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants transitioned from water to land around 450 Million years ago. Since their emergence onto land, there have been at least a few reversion events to aquatic environments (e.g., duckweed, humped bladderwort). These big evolutionary events imply adaptation to completely different kinds of biotic and…
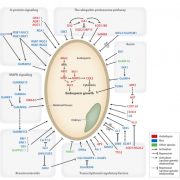
Review: Molecular networks of seed size control in plants ($) (Annu Rev Plant Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrop yield is largely determined by the size of seeds, and studies are being conducted to understand the complex molecular network controlling the seed size. Li et al. review the possible molecular mechanisms and regulatory networks underlying seed size control and growth, including the factors originating…
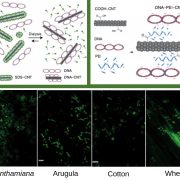
Nanomaterials enable delivery of functional genetic material without DNA integration (Nature Nanotech)
Plant Science Research WeeklyKey to success of crop improvement is the development of easier, faster and safer biomolecules-delivery systems. Here, the main limitation is the cell wall, which compromises the yield of exogenic material transfer to plant cells. In this study, Demirer et al demonstrate the advantages of infiltrated…

