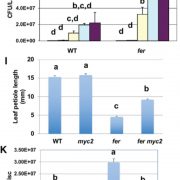
FERONIA receptor kinase contributes to plant immunity by suppressing jasmonic acid signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana (Curr. Biol. - $)
Receptor-like kinase FERONIA plays important role in the regulation of plant growth as well as interactions with the environment. In order to understand how FER affects plant growth Guo et al. examined global transcriptome changes in fer mutant. The authors observed that genes up-regulated by stress…
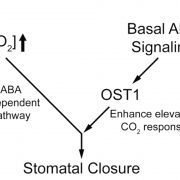
Abscisic acid-independent stomatal CO2 signal transduction pathway and convergence of CO2 and ABA signaling downstream of OST1 kinase (PNAS - $)
The global increase in CO2 concentrations results in the reduced opening of the stomata. Although reduction in the stomatal opening in response to drought relies on abscisic acid (ABA), less is known about the mechanism controlling stomatal aperture in response to elevated CO2. Hsu et al. examined stomatal…
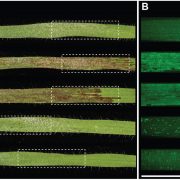
The genetic architecture of colonization resistance in Brachypodium distachyon to non-adapted stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis) isolates (PLOS Gen.)
The host range of a pathogen depends on its ability to overcome various plant defense barriers and successfully complete its life cycle. Although host “jumps” are considered rare, the pathogens are able to infect plants other than their usual host with varying degree of success. Yellow stripe rust…

The number of meiotic double-strand breaks influences crossover distribution in Arabidopsis (The Plant Cell)
The new genetic variation is generated by recombination of the chromosome during meiotic cell divisions. The programmed double-strand breaks are initiated by DNA Topoisomerase VI-a Subunit (SPO11). As the repair of the double-strand breaks is tightly controlled, the number of breaks usually exceeds the…

Modularity of genes involved in local adaptation to climate despite physical linkage (Genome Biol.)
Studying local adaptation is a tricky as the environmental parameters that we measure might affect the organism’s fitness. When local adaptation is driven by complex and non-covarying stresses, it is predicted that loci with similar pleiotropic effect are favored. Lotterhos et al. developed a framework…
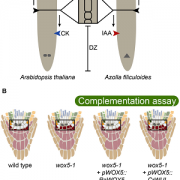
Review - Getting to the Roots: A Developmental Genetic View of Root Anatomy and Function From Arabidopsis to Lycophytes (Frontiers in Plant Sci)
Plant roots are essential organs for water and nutrient uptake, and aboveground biomass support. While these organs are important for many plant functions, the evolutionary history of the root is still unclear. The fossil record suggests that roots evolved in both the lycophyte (clubmosses and their…

The Arabidopsis negative regulator of root hydraulics XND1 is involved in abiotic and biotic stress responses (Nature Comm.)
Proper uptake and management of water is essential for plant growth and adaptation to stress. However, there are gaps in the understanding of the genetics of root hydraulics, including the regulatory components. Tang et al. used a genome-wide associate analysis approach to identify XYLEM NAC DOMAIN 1 (XND1),…

ABA-mediated regulation of stomatal density is OST1-independent (Plant Direct)
Stomata are not only important for CO2 uptake, but are also important in limiting water loss when the water availability is running low. Stress hormone ABA activates protein kinase OPEN STOMATA 1 (OST1) leading to opening of ion channels, water efflux and stomatal closure. Increased levels of ABA decrease…

Insights into the evolution of multicellularity from the sea lettuce genome (Current Biol. - $)
The transition from unicellular to multicellular life forms occurred across multiple kingdoms, and in plants is correlated with the expansion of gene families involved in extracellular matrix formation and cell cycle regulation. Green seaweeds acquired their plant-like body independently of other lineages…

