
Recognizing featured Plant Cell first authors, February 2017
The Plant Cell: Author Profiles0 Comments
/
Masanori Izumi, featured first author of Entire Photodamaged Chloroplasts Are Transported to the Central Vacuole by Autophagy
Current Position: Assistant Professor, Frontier Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences, Tohoku University.
Education: Ph.D. (2012), Graduate School of Agricultural…
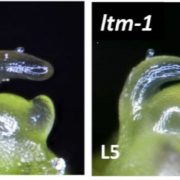
Meristem Doming and the Transition to Reproductive Development in Tomato
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefDuring vegetative growth, the shoot apical meristem (SAM) produces lateral organ primordia but remains roughly the same size, as WUSCHEL–CLAVATA signaling modulates the balance between cell division and differentiation. During the transition to reproductive growth in many species, the SAM expands in…
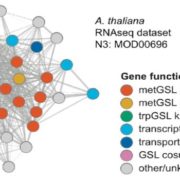
Chasing Scattered Genes: Identifying Specialized Metabolite Pathway Genes through Global Co-expression Analysis
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants produce scores of specialized metabolites (SMs) to attract or repel the organisms around them and to cope with life in a variable environment. For thousands of years, we have been exploiting these compounds to feed, heal, and adorn us. Many more SMs remain to be discovered: the chemical constituents…
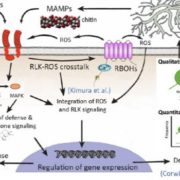
The Plant Cell Reviews Plant Immunity: Receptor-Like Kinases, ROS-RLK Crosstalk, Quantitative Resistance, and the Growth/Defense Tradeoff
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefTender green leaves and tasty tubers, roots, and stems are vulnerable to a wide range of pathogens, pests, and herbivores. Perhaps it should not be surprising that they have evolved an equally wide range of defense mechanisms. This issue of The Plant Cell includes reviews of just a few of the many facets…
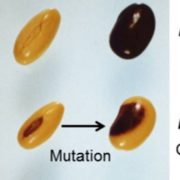
Saddle Up, Soybean Seed Pigments: Argonaute5 in Spatially Regulated Silencing of Chalcone Synthase Genes
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefMost soybean seeds you see, whether in bins at the store, or in train cars as a commodity crop, have a yellow seed coat that may have only a tiny fleck of dark pigment at the hilum, where the seed attaches to the pod. The predominant yellow color results from silencing of chalcone synthase (CHS) genes…
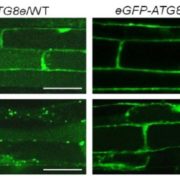
Family Chores: TRAF-Family Proteins Help Recycle Cellular Rubbish by Regulating Autophagy Dynamics
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Jennifer Lockhart [email protected]
Plant cell components that are no longer needed are degraded in the vacuole, but they don’t get there by magic. Sack-like double-membrane structures called autophagosomes engulf this cellular rubbish and neatly transport it to the vacuole for degradation.…
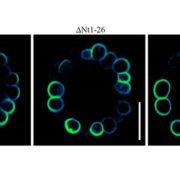
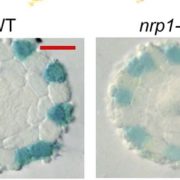
Threonine Phosphorylation Regulates Polar Localization of the Boric Acid Transporter NIP5;1 in Root Cells
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Gregory Bertoni [email protected]
Proper localization of proteins in the plasma membrane is critical for proper functioning of plant cells, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood (Łangowski et al, 2016). This is especially true for transporter proteins that move necessary…

A Kinase- and Proteasome-Mediated Link Between Lipid Biosynthesis and Energy Homeostasis
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Nancy R. Hofmann [email protected]
The economy of living cells includes energy production, energy utilization, and energy storage. Thus, a plant’s energy budget must connect the decision to produce lipids (for energy storage) with its overall energy status. Energy sensor kinases, such…
A Histone Chaperone and a Specific Transcription Factor Modulate GLABRA2 Expression in Root Hair Development
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF by Jennifer Mach [email protected]
To navigate its essential function of producing mRNAs, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) must navigate the thread of DNA, which winds around thousands of nucleosomes. If you’ve ever tried to use a sewing machine but got your bobbin thread tangled, then the task faced…

