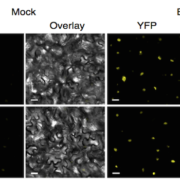
Dual impact of elevated temperature on plant defense and bacterial virulence in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHuot et al. describe how elevated temperature (30 °C) enhances Arabidopsis thaliana disease susceptibility to the bacteria Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000): this includes an increase of bacterial type III secretion suggesting that increased Pst DC3000 virulence at 30°C is linked…

Different gene expression patterns in Arabidopsis grown under different densities
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWhen grown at high density (HD), plants compete for nutrients, water and light. Guo and collaborators characterized Arabidopsis gene expression under two different growth densities: seeds sown at low density (LD), 10 cm apart and high density (HD), 2 cm apart. RNA sequencing analysis showed that only…

VERNALIZATION1 modulates root system architecture in wheat and barley
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog
Root angle determines the rooting depth and was recently associated with the VERNALIZATION1 locus. Using hexaploid wheat, Voss-Fels et al. mapped the root angle to the locus encoding the MADS-box transcription factor, which was previously associated with flowering time. The group found that the lines…
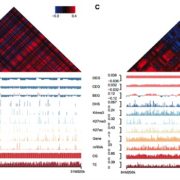
Arabidopsis and crop plants differ in their 3D genome architecture ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThree-dimensional organization of the genome is critical for proper gene expression. Comparison of the extremely compact genome of Arabidopsis with mammalian genomes revealed reduced local intra-chromosomal contacts (also know as Topologically Associated Domains, TADs) and fewer chromatin loops in the…
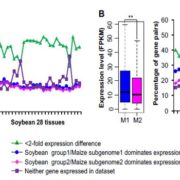
Patterns and consequences of subgenome differentiation provide insights into the nature of paleopolyploidy in plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMany plants are polyploid, meaning that instead of the normal, diploid “2n” complement of chromosomes (one from each parent), they have more than 2n. Following whole-genome duplication, redundancy can allow the duplicated regions to diverge or become silenced. In some cases, silencing occurs preferentially…

Increasing leaf vein density in rice results in an enhanced rate of photosynthesis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIncreased leaf vein density is considered to be a key early step in the evolution of C4 photosynthesis. Feldman et al. analyzed five mutants with high vein densities in the C3 crop rice to determine if photosynthetic assimilation was improved. The mutants all had higher photosynthetic rates under…

Intracellular distribution of manganese by NRAMP2 critical for photosynthesis and redox homeostasis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogManganese is a micronutrient essential for the function of several proteins including manganese superoxide dismutase (localized in the peroxisome and mitochondria) and the photosystem II reaction center (localized in the chloroplast). Mn is transported via NRAMP (Natural Resistance-Associated Macrophage…
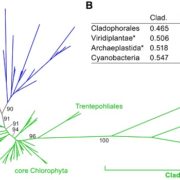
The plastid genome in Cladophorales green algae is encoded by hairpin chromosomes ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlastids, the cellular sites for light reaction of photosynthesis, have a reduced genome which is circular and double stranded, ranging in the size from about 100 to 200 Kb. Some exceptions to this circular nature of plastid genomes are found in some groups of phytoplanktons, namely dinoflagellates,…
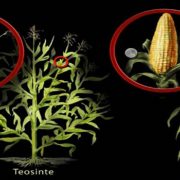
Review. Artificial evolution: Creating genetic diversity in the lab ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHumans have been domesticating plants for 10,000 years, having an impact on the gene pools of multiple species chiefly through selective breeding approaches. Although plant domestication ensured food availability to early civilizations, plants were, and still are, mainly selected based on their morphology…

