
Arabidopsis DEFECTIVE KERNEL1 regulates cell wall composition and axial growth in the inflorescence stem
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants can reach impressive heights, thanks to the mechanical stability provided by the cell walls. The required strength is ensured by coordination of cell wall deposition and cell expansion. Plant-specific calpain (DEK1) regulates axial stem growth, as lines overexpressing the calpain domain develop…
How do trees transport carbohydrates?
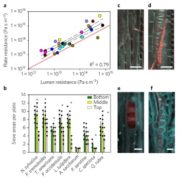
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogAs a tree grows in height, increasing the length of the transport pathway, the hydraulic resistance of the vascular tissues should increase. It is not clear if trees only rely on passive transport mechanisms (no active loading of sugars) to move carbohydrates from shoots to roots. To answer this question,…

Trees are particularly robust to fixed somatic mutations
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants lack a developmentally defined germline and gametes originate only late during plant development. This allows mutations acquired during the vegetative growth (somatic mutations) to be transmitted to the reproductive organs. The accumulation of mutations is relatively low in annual plants such…

Genome-wide identification of Medicago peptides involved in macronutrient responses and nodulation
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants are highly plastic and can modulate their growth and development to better respond to abiotic and biotic surroundings. Among the molecules involved in the adaptation to the environment, a crucial role is played by small secreted peptides (SSPs). In their paper, integrating 144 transcriptomic experiments,…
The Brassicaceae family displays divergent, shoot-skewed NLR resistance gene expression
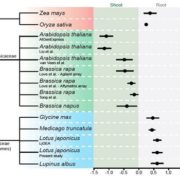
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNLR (Nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat resistance) genes help plants recognize pathogens. Munch et al. looked at expression pattern data of 1,235 NLRs from nine plant species. The distribution of NLR gene expression between shoot and root is relatively constant within a species, and for most…
The rust fungus Melampsora larici-populina expresses distinct sets of secreted protein genes during infection of its two host plants, larch and poplar
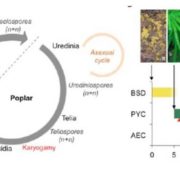
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRust fungi represent an important group of plant pathogens, many of which have heteroecious lifestyles (meaning that they require two alternate hosts). However, the molecular mechanisms used by these pathogens for suppression and colonization of multiple hosts are poorly understood. Lorrain et al.…
Plant extracellular vesicles are incorporated by a fungal pathogen and inhibit its growth ($)
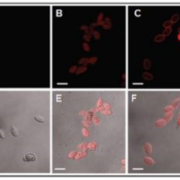
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogExtracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-released structures that play a role in cell-to-cell communication. These vesicles in plants have been poorly studied although they are predicted to have a role in defense upon pathogen infection. Regente et al. have characterized EVs from sunflower by transmission…

What we're Reading: December 15th
Blog, Research, Research Blog, WWR Full PostPoint of View: A transatlantic perspective on 20 emerging issues in biological engineering studies
“Horizon scanning” describes the process of trying to rationally predict the future. Wintle et al. describe the results from a horizon-scanning exercise to identify emerging issues in biological…

Update: Seedling establishment: a dimmer switch-regulated process between dark and light signaling
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Charlotte M.M. Gommers and Elena Monte
Abstract
By being exquisitely sensitive to their light surroundings, plants are able to continuously adjust their growth to optimize fitness. Darkness is an important cue for plants and a time when they actively grow and develop through regulation of the…

