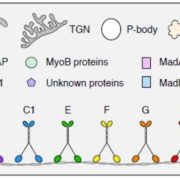
Update on Myosin Motors: Molecular Mechanisms and Physiological Functions
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research Blog By Jennifer M Ryan and Andreas Nebenfuehr
The cytoskeleton is the main organizing principle that defines not only the distribution of cellular components within cells but also the overall shape and growth pattern of cells and entire multicellular organisms. This function is particularly evident in…
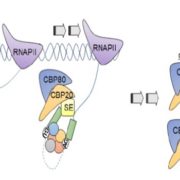
Update: Nuclear Cap-Binding Complex in Abiotic Stress Responses
Blog, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Agata Daszkowska-Golec
The nuclear cap-binding 16 complex (nCBC) in higher eukaryotes specifically binds to the monomethylated (7-methylguanosine (m717 GpppN)) cap structure at the 5¢ end of freshly transcribed mRNA. In addition to protecting mRNAs from degradation by exonucleases, the nCBC functions…
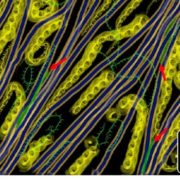
Update: Diffuse growth of plant cell walls
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Daniel J. Cosgrove
Introduction
The primary wall of a growing cell is a versatile, subtle and dynamic structure, with unique properties and functions in the life of the plant (Burton et al., 2010). When a cell grows, its wall stretches irreversibly as the cell enlarges in volume. Cells can start…
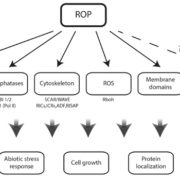
Update: ROP GTPases structure-function and signaling pathways
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Gil Feiguelman, Ying Fu, and Shaul Yalovsky
Introduction
Rho of Plants (ROP) proteins also known as RACs are the plant specific subfamily of Rho small GTP binding proteins, referred to here as small G proteins (Zheng and Yang, 2000; Brembu et al., 2006; Elias and Klimes, 2012). Like other members…
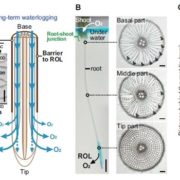
Update: Root plasticity and internal aeration
Blog, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Takaki Yamauchi, Timothy D Colmer, Ole Pedersen, Mikio Nakazono
Introduction
Root acquisition of water and nutrients is essential for plant growth and crop productivity (Lynch, 2015). An improved understanding of root system development and functioning, to identify root traits contributing to…
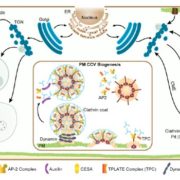
Update. Inroads into Internalization: Five Years of Endocytic Exploration
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Gregory D. Reynolds, Chao Wang, Jianwei Pan, Sebastian Bednarek
Introduction
The plasma membrane (PM) serves as the interface between the cell and its environment. Accordingly, cells have the capacity to modulate their complement of PM-associated receptors, transporters, channels, lipids, and…
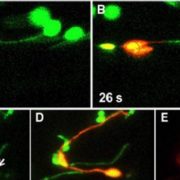
Update. Stromules: Probing formation and function
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Maureen R Hanson, Kevin M Hines
ABSTRACT
Stromules are narrow tubular structures, comprised of stroma surrounded by the envelope membrane, which emanate from all types of plastids found in vascular plants. The mechanism for formation of stromules is not understood, but investigating how they arise…

Update: Signal dynamics and interactions during flooding stress
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Rashmi Sasidharan, Sjon Hartman, Zeguang Liu, Shanice Martopawiro, Nikita Sajeev, Hans van Veen, Elaine Yeung, Laurentius A.C.J. Voesenek
Abstract
Flooding is detrimental for nearly all higher plants including crops. The compound stress elicited by slow gas exchange and low light levels under…
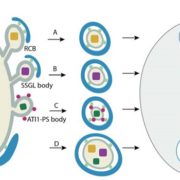
Update on autophagy: Dynamics of autophagosome formation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Junmarie Soto-Burgos, Xiao-Hong Zhuang, Liwen Jiang, and Diane C. Bassham
Autophagy, literally defined as “self-eating”, functions as a degradation process by recycling cytoplasmic contents under stress conditions or during development. Upon activation of autophagy, a membrane structure known…

