Light Triggers the Search for Light
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchPlants rely on light for photosynthesis. As a consequence, plant growth is strongly shaped by light availability, to optimize photon absorbance in the green tissues. Seedlings that germinated underground grow quickly to escape from the darkness, while plants that are threatened to be overgrown by neighbors…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Charlotte Volpe
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesCharlotte Volpe, co-first author of Loss of ALBINO3b insertase results in a truncated light-harvesting antenna in diatoms
Current Position: PhD candidate at the Department of Biotechnology and Food Science - Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) – Trondheim, Norway
Education: PhD…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Marianne Nymark
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesMarianne Nymark, co-first author of Loss of ALBINO3b insertase results in a truncated light-harvesting antenna in diatoms
Current Position: Research scientist at the Cell, Molecular Biology and Genomics group at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU)
Education: PhD in Biology from…
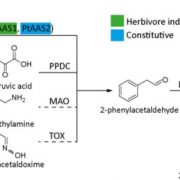
Do all roads lead to 2-phenylethanol in Populus?
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchPlants emit scented volatile compounds to attract pollinators, or alternatively, as direct or indirect plant defense mechanisms. Direct defense involves compounds that are toxic, whereas an indirect defense uses volatiles to attract parasitoids of insect herbivores (Unsicker et al., 2009; Maag et al.,…

Turnip Mosaic Virus is Released into Extracellular Space
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideTurnip Mosaic Virus (TuMV) is a +RNA virus that belongs to the order Picornavirales. +RNA viruses reorganize the endomembrane system to generate quasi-organelle structures called “viral factories”. In the case of TuMV, these factories are motile vesicles of ~100 nm in diameter that contain the TuMV…

Regulation of Imprinting in Arabidopsis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe seeds of flowering plants consist of three genetically distinct components: the diploid embryo with one genome copy from each of the parents, the triploid endosperm with two maternal copies and one paternal copy, and the seed coat having the same genotype as the diploid mother plant. Balanced parental…

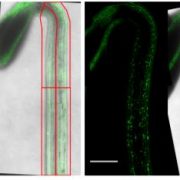
Salicylic Acid Influences Root Meristem Patterning at Low Concentrations
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideHigh exogenous concentrations (>50 µM) of salicylic acid (SA) stimulate systemic acquired resistance (SAR), a vitally important adaptive immunity response that protects against a broad spectrum of pathogens. The transcription of PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENE 1 (PR1) is rapidly induced in leaves upon…

The Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll in Leaves
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe biochemistry of photosynthesis and biophysical processes that constrain it are intrinsically linked within the landscape of the inner leaf. Because leaf tissue is heterogeneous in structure as well as photosynthetic capacity, it follows that chlorophyll may also be spatially heterogeneous. Yet, while…

Domestication Affected Root System Architecture in Common Bean
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideComparative analyses of wild and domesticated accessions have previously identified several aboveground domestication-related traits in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Genetic analyses of these traits suggested the presence of several major quantitative trait loci (QTLs) with large effects. However,…

