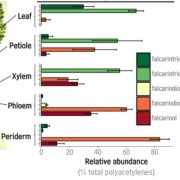
Polyacetylene Biosynthesis in Carrot
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePolyacetylenic lipids accumulate in various Apiaceae species after pathogen attack, suggesting
that they are naturally occurring pesticides and potential targets for crop improvement. These chemicals are also of interest because they exhibit cytotoxic activity against human cancer cell lines and slow tumor…
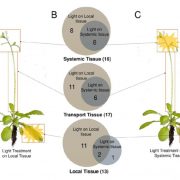
Local and Systemic Metabolic Responses in Response to Light Stress
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideNot every leaf of a plant is subjected to the same light intensity or quality in nature. As a consequence, plants have evolved multiple signaling pathways to transduce light‐related signals between different leaves. These systemic acclimation processes optimize the overall light perception of the…
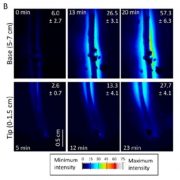
New Advances in the Imaging of Sugars
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe in vivo imaging of sugars is useful for understanding how assimilated carbon, in the form of sugars, moves in plants and how this process is differentially regulated. Voothuluru et al. (10.1104/pp.18.00614) developed a gel-based enzyme-coupled colorimetric and fluorometric assay to image glucose…

Transcription Factors and Apple Drought Tolerance
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideWater deficit is one of the main limiting factors in apple (Malus × domestica) cultivation. Root architecture plays an important role in the drought tolerance of plants. Due to the difficulties associated with the visualization of root systems, however, there is currently a poor understanding of the…
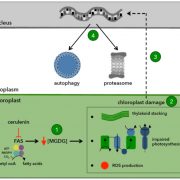
Chloroplast Damage Triggers Autophagy
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideUnder normal growth conditions, there is a constitutive or basal level of autophagy in plant cells that helps to recycle unnecessary cell contents. Autophagy provides essential building blocks (e.g. amino acids and fatty acids) and energy sources that promote cell homeostasis and survival. Autophagy…
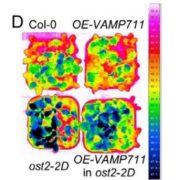
A SNARE Protein that Regulates Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase activity
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays an important role in plant drought responses. Previous studies have indicated that ABA inhibits plasma membrane H+-ATPase (PM H+-ATPase) activity, and the resultant decrease in PM H+-ATPase activity promotes stomatal closure under drought stress, thereby reducing…

Chloroplast Accumulation Enhances Photosynthesis and Biomass Production
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideLight-induced chloroplast movement is one of the most important responses for utilization of photosynthetic light. Chloroplasts move toward weak light-irradiated areas to efficiently absorb light (the accumulation response), whereas they move away from excess light to avoid photodamage (the avoidance…

A Tapetal Boric Acid Channel Involved in Pollen Cell Wall Formation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideBoron (B) is an essential plant micronutrient that plays a major role in cell wall structure and function by providing cross-linking of the rhamnogalacturonan II (RG-II) pectin component of the cell wall. Under normal pH conditions, B is found principally as boric acid. Although boric acid permeates…
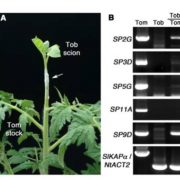
RNA Mobility and the Regulation of Flowering
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn addition to hormones, proteins, and metabolites, many plants use mRNAs as mobile molecules for long-distance communication. It has been demonstrated that many mobile mRNAs are trafficked through phloem, probably by forming an RNA-protein complex to allow the stable translocation of mRNA molecules.…

