
Special issue: Parasitic plants
Plant Science Research Weekly
Special issue: Parasitic plants
Runo, Wicke, and Thorogood have edited a special issue of Plants, People, Planet on the topic of parasitic plants. (Note - the Special Issue will be launched on February 19, but the articles are already online in Early View). It’s nice to see a collection…

BOOSTER: Unlocking photosynthetic efficiency for enhanced plant productivity
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is a fundamental biological process for carbon fixation and capturing light energy to drive plant growth. However, excessive sunlight can cause photodamage, which is detrimental to plant health. To protect the photosynthetic machinery from over-excitation and subsequent damage, plant cells…
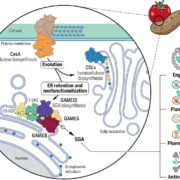
A “GAME” changer in plant secondary metabolism
Plant Science Research WeeklyCholesterol, an essential structural component of membranes and a precursor for steroid hormones, serves as a key metabolite at the interface of primary and secondary metabolism. However, the mechanisms regulating the balance between its diverse downstream metabolic pathways remain poorly understood.…
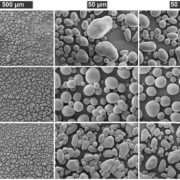
A fresh starch: Creating new starch granule morphologies in potato tuber
Plant Science Research WeeklyStarch is the major storage carbohydrate in plants and is organised into semicrystalline granules. The size, shape, and composition of these granules greatly affects how they are digested, and which industrial applications they are suitable for. Therefore, the enzymes controlling starch synthesis are…
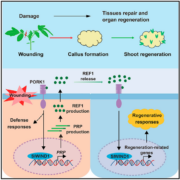
Unveiling REF1: A key regulator of plant regeneration
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants frequently encounter damage during growth and development, necessitating remarkable regenerative abilities to repair damaged tissues. Plants can regenerate organs or even entire plants from callus or a single cell, a capacity underpinning asexual reproduction and various biotechnological applications.…
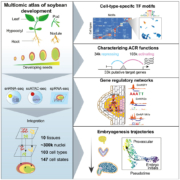
Spatially resolved, single-cell multi-omics atlas of soybean development
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this exciting paper, Zhang, Luo, Marand et al. combined several powerful techniques to investigate the program underlying soybean seed development. They used RNA sequencing to profile gene expression from single nuclei (snRNA-seq). They also carried out single-cell sequencing of assays for transposase-accessible…
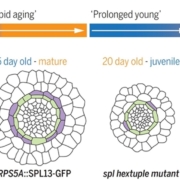
Key regulators of juvenile-to-adult phase change
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe precise control of cell division orientation drives plant 3D structure formation, enabling radial and longitudinal growth. The SPL pathway is closely linked to age-related processes in the shoot, driving the vegetative transition from juvenile to adult phases by regulating specific morphological…
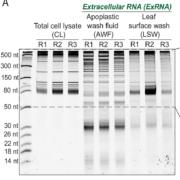
Abundant, unusual RNAs on the leaf surface
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt seems that there is no end to the surprises that RNA provides. To the old-school trio of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, the past 20 years have added miRNA, siRNA, tasiRNA and others, all with unique and specific roles in regulating gene activity. More recently, evidence has been accumulating that demonstrates…

Plant Science Research Weekly: January 10, 2025
WWR Full PostFocus Issue: Hypoxia and Plants
The January 2025 issue of Plant Physiology has a focus on “Hypoxia and Plants”. This field has made a lot of progress recently in understanding plant responses to low oxygen, from the molecular to physiological and developmental levels. The focus issue includes…

