Oxford University Press to publish American Society of Plant Biologists journals
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding the American Society of Plant Biologists’ Partnership with Oxford University Press
The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is delighted to announce that it will partner with Oxford University Press (OUP) to produce and disseminate the ASPB journals…
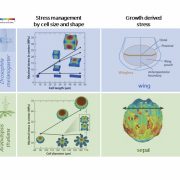
REVIEW: Shared Structural Principles Across Kingdoms ($) (Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol)
Understanding how a single fertilized cell develops into a complex multicellular system has always been a challenging but fascinating topic of developmental biology. In both animal and plant species, it all starts with a simple spherical cell; afterward, two axes of polarity generate flat shapes,…

REVIEW: Multi-parent populations in crops: a toolbox integrating genomics and genetic mapping with breeding (Heredity)
Biparental populations (BPPs) obtained by crossing two diverse inbred lines have long been used for dissecting the complex traits owing to their simplicity, ease of development and high power of detecting QTLs with a few hundred markers genotyped. Nonetheless, poor resolution and low genetic diversity…
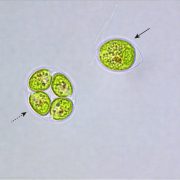
Cold, but not freezing: the ICE-L genome ($) (Current Biology)
When sea water freezes, it forms not a solid mass of ice, but rather a frozen matrix criss-crossed by tiny brine-filled channels. It is within these brine channels in the Antarctic sea ice that the psychrophilic (cold-loving) green alga ICE-L lives. How is it able to thrive in such a seemingly hostile…

Temperature-dependent growth contributes to long-term cold sensing ($) (Nature)
Seasonal changes in ambient temperature greatly influence plant development. While the response to acute heat stress has been widely studied, the regulatory mechanisms that integrate naturally fluctuating temperatures – such as the progression of winter - remain largely unknown. This paper sheds…
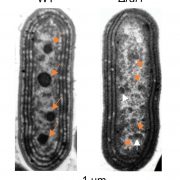
Rubisco accumulation factor 1 and carboxysome biogenesis (PNAS)
Carbon concentration mechanisms (CCMs) refer to a diverse set of strategies by which photosynthetic organisms increase the amount of carbon dioxide available to the carbon-fixing enzyme Rubisco. The cyanobacterial CCM relies on the carboxysome, a membraneless microcompartment with a core of densely…
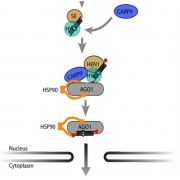
A new miRNA complex assembly partner – Intrinsically disordered but an important scaffold ($) (Plant Physiol)
Gene regulation through microRNAs (miRNA) starts in the nucleus with transcription and processing into mature miRNA duplexes. Loading of miRNA into ARGONAUTE1 (AGO1) and the assembly of the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex was thought to be exclusively a cytoplasmic process, but new research reports…

Epicotyl morphophysiological dormancy and storage behaviour of seeds of Strychnos ($) (Seed Sci. Res.)
Seed dormancy and desiccation tolerance impact on germination timing and soil seed bank formation. Here, Muthuthanthirige et al. conducted a thorough series of experiments and anatomical observations to determine the dormancy class and desiccation tolerance of three Strychnos (Loganiacae) species:…
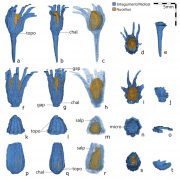
Ancient seeds reconstruction and the evolution of integuments (New Phytologist)
The origin of seeds - the specialized structures that contain and protect the developing embryos- is a key event in plant evolution. Primitive seeds comprise an exposed nucellus surrounded by a lobate integument; in contrast, extant seeds have one or more integuments fully enclosing the nucellus.…

