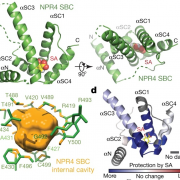
Structural basis of salicylic acid perception by Arabidopsis NPR proteins (Nature) ($)
Salicylic acid (SA) is a critical hormone in plant-pathogen responses. The main receptors of this hormonal signal are a small family of NPR proteins (NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES). Although NPR1 is a positive regulator of defense signaling, NPR3 and NPR4 serve as negative regulators; they…
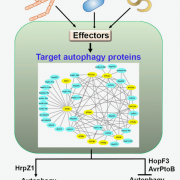
An interactome of plant autophagy proteins and pathogen effectors (Cell Host Microbe) ($)
Autophagy is a regulated process whereby select cytoplasmic components are degraded. It is involved in a variety of biological processes, including defense against pathogens. As such, plant pathogens have evolved mechanisms to target host autophagy machinery to gain virulence. However, we still lack…

Cell-cell adhesion in plant grafting is facilitated by b-1,4-glucanases (Science) ($)
Plant grafting has been used in crop improvement for centuries and more recently to study systemic and long-distance signaling in the plant vascular system. In order to better understand graft compatibility and its mechanism, Notaguchi et al. used Nicotiana to study interfamily graft combinations. Interfamily…
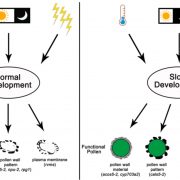
Slow development restores the fertility of photoperiod-sensitive male-sterile plant lines (Plant Physiol.)
There are many well-known advantages to hybrid seeds. However, one obstacle is the tendency of some plants to self-pollinate. The development of genetically male-sterile lines greatly facilitates hybrid seed production, as the maternal male-sterile plant cannot self-fertilize and depends on donor pollen…
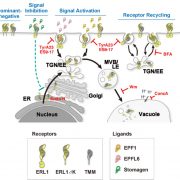
The manifold actions of signaling peptides on subcellular dynamics of a receptor specify stomatal cell fate (eLife)
Stomatal development requires cell-to-cell communication and follows one cell spacing, with a minimum of one cell space between two stomata. Key to this communication are the ERECTA and ERECTA LIKE (ERL) Leucine-Rich Repeat domain-Receptor Like kinases (LRR-RLKs) and their ligands, the EPIDERMAL PATTERNING…

DNA damage triggers reprogramming of differentiated cells into stem cells in Physcomitrella (Nature Plants) ($)
Wounding and other types of cellular damage, such as DNA damage-induced stem cell death, trigger cellular reprogramming to confer stem cell identity to damage-adjacent cells, thus establishing a new stem cell niche capable of repairing the injury. Studies in angiosperm models have identified the phytohormone…
Lipo-chitooligosaccharides as regulatory signals of fungal growth and development (Nature Comms)
During symbiosis, the rhizobia bacteria rely on their lipo-chitooligosachharide signals (LCOs) to associate with plants. This signal is perceived by plant receptor like kinase, LysM-containing receptors which activate the common symbiosis signaling pathway (CSSM). Fungal symbiosis with plants has also…
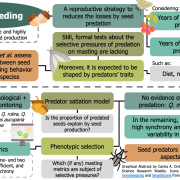
Seed predation selects for reproductive variability and synchrony in perennial plants (New Phytol.) ($)
Instead of regularly flowering and fruiting each year, some long-lived species exhibit annually variable reproduction events. This phenomenon, known as masting, is considered an adaptation to reduce the losses from seed predation: in years of high reproduction, seeds are so abundant that predators become…
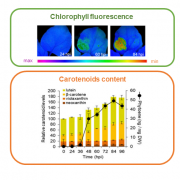
Synthetic conversion of leaf chloroplasts into carotenoid-rich plastids reveals mechanistic basis of natural chromoplast development (PNAS) ($)
Biofortification aims at increasing the content of health-promoting nutrients in edible parts of the plant. As an example, enhancing the production of carotenoids - natural pigments that provide the yellow to red color – in crops could prevent vitamin A deficiency in humans. In nature, carotenoids…

