
Bolun Meng: Plant Physiology First Author
Plant Physiology: Author Profiles
Bolun Meng, co-first author of “An SNW/SKI-INTERACTING PROTEIN influences endoreduplication and cell growth in Arabidopsis”
Current Position: PhD Student, Henan University.
Education: Bachelor, Henan University of Technology; Master, South China Normal University
Non-scientific interests:…

Christian Silva: Plant Physiology First Author
Plant Physiology: Author Profiles
Christian Silva, first author of "Botrytis cinerea infection accelerates ripening and cell wall disassembly to promote disease in tomato fruit"
Current Position:
Financial Advisor at Wells Fargo Advisors
Education:
Ph.D. in Plant Biology, University of California, Davis, 2021; B.S. in…
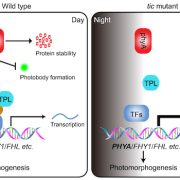
Tick tock: TIME FOR COFFEE regulates far-red light inhibited hypocotyl growth
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. explore how the circadian clock regulates phytochrome A abundance and activity to mediate far-red light inhibited hypocotyl growth.
Background: To enhance plant adaptability to natural conditions, the circadian clock is synchronized and entrained by light via photoreceptors. Intriguingly,…
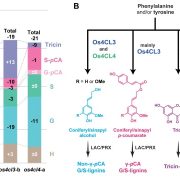
Genome-edited rice deficient in two 4CL genes display diverse lignin alterations (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLignin is one of the most important end-products of the cinnamate/monolignol pathway and it is abundant in the secondary cell wall of vascular plants. In grasses, lignins are derived from monolignols, p-hydroxycinnamates, and a flavonoid tricin. In the proposed cinnamate/monolignol pathway, 4-COUMARATE:COENZYME…
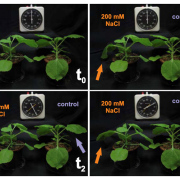
Tobacco leaf tissue rapidly detoxifies direct salt loads without activation of calcium and SOS signaling (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySalinity stress is one of the primary abiotic causes of crop loss worldwide. In roots, the early response to high salt levels is coordinated largely via the well characterized salt-overly sensitive (SOS) pathway, which is dependent on Ca2+ signaling. However, how plants cope with elevated salt levels…

Plant immunity is wired differently in different plants (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants, microbial invasion is sensed by membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors. Our knowledge on the immune signaling that follows microbial recognition is mostly derived from studies on Arabidopsis thaliana. In this plant, receptor activation triggers immune responses that are distinct for each…

Arabidopsis latent virus 1, a comovirus widely spread in Arabidopsis thaliana collections (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArabidopsis thaliana has been established as a versatile and important model plant species, with abundant genetic and genomic resources. Through RNA sequencing, Verhoeven et al. identified an unexpected and previously unnoticed latent comovirus (the name “como” derives from cowpea mosaic virus) lurking…
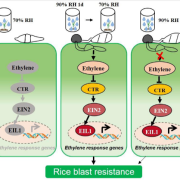
High humidity compromises plant immunity while promoting pathogen growth (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHumidity is considered a key component for the growth of fungal plant pathogens. For many infection assays we either maintain plants in high humidity, or wrap the infected area and keep spraying it with water. This is generally performed to facilitate fungal growth and the assumption that this may not…

Plant Science Research Weekly: October 7th, 2022
WWR Full PostGenome-edited rice deficient in two 4-COUMARATE:COENZYME A LIGASE genes displays diverse lignin alterations
Lignin is one of the most important end-products of the cinnamate/monolignol pathway and it is abundant in the secondary cell wall of vascular plants. In grasses, lignins are derived from monolignols,…

