How far does stomatal activator and inhibitor signaling work in the plant epidermis? (bioRxiv)
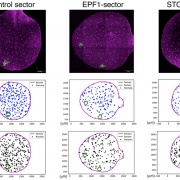
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata are the pores on the plant surface surrounded by a pair of guard cells that control gaseous exchange and water loss. Among the many genes involved in stomatal patterning and development, EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR 1 (EPF1) and STOMAGEN encode signaling peptides and acts as negative (inhibitor)…
Advanced vascular function discovered in a widespread moss (Nature Plants)
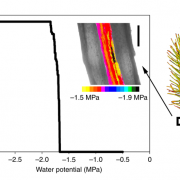
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn order to grow upwards into the dry atmosphere, plants need to keep their elevated tissues hydrated and functional. In vascular plants this is achieved by a lignified water transport system in conjunction with stomatal regulation of gas exchange and the encasement of photosynthetic tissues in an impermeable…
GOLVEN peptide signaling through RGI receptors and MPK6 restricts asymmetric cell division during root initiation (Nature Plants)
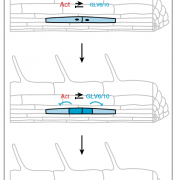
Plant Science Research WeeklyLateral root starts development starts with an asymmetric cell division in the founder cell. In this study, Fernandez et al. explored the role of peptide signaling this process. The authors started with the previous finding that GOLVEN peptides are involved in lateral root initiation, as overexpression…
Melatonin represses oil and anthocyanin accumulation in seeds (Plant Physiol.)
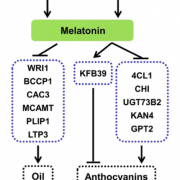
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed oils and anthocyanins play several roles in plant physiology and are promising substances for crop engineering given their benefits for human health. Recent studies proposed that melatonin –a potent antioxidant present in all plant species– regulates the deposition of these metabolites in seeds,…
Accumulation of high value bioproducts in planta can improve the economics of advanced biofuels (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiofuels can be obtained from bioenergy crops such as sorghum, maize and sugarcane. However, the production of bioethanol is still more expensive than that of petroleum. Given the importance of replacing conventional fossil fuels with renewable liquid fuels, the biorefinery system should be improved…
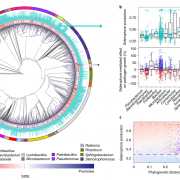
Rhizosphere microbiome protects plants from a pathogen via iron competition (Nature Microbiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIron is an essential element for most living organisms, including plant-associated bacteria. As iron is insoluble in most soils, many soil-borne bacteria scavenge iron using siderophores, a chemically diverse group of secondary metabolites with a high affinity for iron. Siderophores are known to drive…
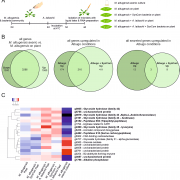
Fungal antagonism of Arabidopsis oomycete infection requires a previously uncharacterized secreted hydrolase (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAntagonist interactions between microbes of the phyllosphere stabilize the microbiome and some “hub” organisms can exert strong effects on community structure. The yeast family Ustilaginales contains several apathogenic species that are microbial antagonists that can inhibit infection from diverse…
Plant Science Research Weekly: May 22nd
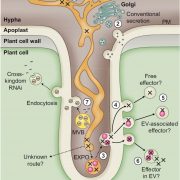
Blog, WWR Full PostReview: Devastating intimacy: the cell biology of plant–Phytophthora interactions
Phytophthora are plant-destroying oomycetes. Within this genus are several infamous disease-causing agents: P. infestans of the potato late-blight fame, P. sojae of soybean root rot, P. ramorum of sudden oak death,…

Silencing Immunity: miR159 Suppresses Pathogen Responses in Tobacco
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMichael J. Skelly
[email protected]
To ensure optimal growth and development, plants must precisely control gene expression networks in a tissue-specific manner. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNA molecules that post-transcriptionally silence genes by binding to complementary…

