
Rhamnose-containing cell wall polymers suppress helical plant growth independently of microtubule orientation
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
Saffer et al. identified an Arabidpsis mutant with swirled petals and with petal epidermal cells that show a left-handed (but never right-handed) twist. They mapped the mutation to the RHAMNOSE BIOSYNTHESIS1 (RHM1) gene, which is most highly expressed in petal epidermal cells and encodes an enzyme that…

LAZY1 family contributes to gravity signaling within statocytes and branch angle control of roots and shoots
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIt’s easy to demonstrate that plants sense gravity, and we also know that statocytes are involved in the perception of gravity. Statocytes are gravity-sensing cells that contain dense starch-containing amyloplasts that move within the cell in the direction of gravity. Differential growth to accommodate…
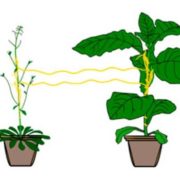
Stem parasitic plant Cuscuta australis (dodder) transfers herbivory-induced signals among plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogParasitic plants such as Cuscuta astralis (dodder) form connections with their host plants through which nutrients and other molecules pass. Using mutant plants and transcriptomic assays, Hettenhausen and Li et al. showed that two or more plants connected by Cuscuta bridges shared information through…
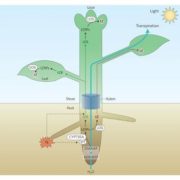
Systemic transport of trans-zeatin and its precursor have differing roles in Arabidopsis sho
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant hormones are made in one tissue and usually transported to act in another. One example of this is the transport of cytokinin. In the root, the precursor trans-zeatin riboside (tZR) is synthesized, then xylem loaded and transported to the shoot. Once at a site of action like the leaf or shoot…
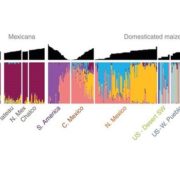
Genomic estimation of complex traits reveals ancient maize adaptation to temperate North America
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMaize (corn), an important staple of the diet in ancient and modern times, was cultivated at higher altitudes in the southwestern United States, around 2,000 years after its introduction to the lowland US regions. In order to better understand how maize later adapted to high altitudes, authors sequenced…
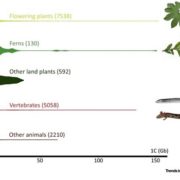
Opinion: Is there an upper limit to genome size? ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThere are only ten organisms known to have genomes larger than 100 Gb in size and six of those are plants. Both Numbers 1 and 2 on the list are plants with genomes that are nearly 50x the size of the human genome (which is 3 Gb), and over 1000x that of Arabidopsis: the 148.8 Gb-genome Paris japonica…

Informational Interviews: What, who, why?
Blog, Careers, Careers - Blog, Finding Your Next Position, General InformationWe all know that your PhD studies and postdoc prepare you for a career in academia. Your advisor, who has been pursuing a career in academia, should be able to advice you on submitting your research to journals, writing grants, and interviewing for other academic jobs, but may not have much to say about…

Taproot Podcast S1E4: Embracing Uncertainty in Science and Science Careers with Siobhan Braybrook
Blog, The Taproot Season 1, The-TaprootIn this episode Ivan and Liz talk with Siobhan Braybrook, Career Development Fellow at The Sainsbury Laboratory, University of Cambridge and soon-to-be Assistant Professor of Molecular, Cell and Developmental Biology at UCLA. Siobhan trained as a plant developmental biologist in Canada and the US before…

Where Will Your Next Job Be? - August 7, 2017
Blog
ASPB and Plantae have already set a tone of collaboration and constant improvement by and for plant scientists. In keeping with our commitment to providing the best recruitment resources for our members, we are excited to announce the launch of our new and expanded online employment resource: the…

