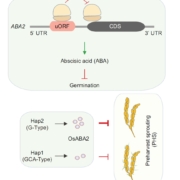
A translational brake on ABA biosynthesis shapes germination timing and sprouting resistance
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed germination is a critical developmental switch that depends not only on stored mRNA but also on the selective translation of these transcripts. In this study, Wang et al. explored how translational control of some genes can fine-tune the timing of germination. Using translation inhibitors and…
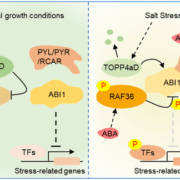
A phosphorylation switch balances growth and stress response in cotton
Plant Science Research WeeklySalt stress can severely affect cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) productivity, especially during early growth. Cao et al. identified a molecular switch in cotton that fine-tunes responses to salt stress and the hormone abscisic acid (ABA), based on the reversible phosphorylation of the ABA signaling phosphatase…
Plant Science Research Weekly: June 27, 2025
WWR Full PostSpecial Science Issue: Plants and Heat
The June 12 issue of Science has a focus on plants and heat that includes several excellent review and research articles. In a very interesting review, Singh Yadav et al. discuss the complex and fascinating question of how plants sense temperature, emphasizing…
Review: Gene discovery, from Arabidopsis to crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis year marks the 25th anniversary of the publication of the first genome sequence of a plant, Arabidopsis thaliana, (see https://doi.org/10.1038/35048692). As this review by Bevan et al. observes, this exciting accomplishment was met with some skepticism by those who felt that it was not likely to…
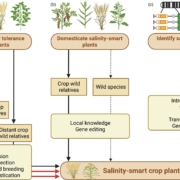
Review: Genomic tools and breeding tools to design salinity-smart food crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost food crops are relatively intolerant to soil salinity, yet globally soils are becoming increasingly salinized. This excellent review by Raza et al. pulls together the myriad approaches that are being used to develop salinity-smart crops. It starts with an overview of how soil salinity affects crops…
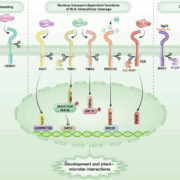
Review. Alternative modes of RLK function: Insights into cleavage-driven plant signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyReceptor-like kinases (RLKs) constitute a large family of membrane-bound proteins in plants. The Arabidopsis genome encodes over 600 RLKs, while the rice genome contains more than 1,000. RLKs are best known for their role in perceiving environmental stimuli and triggering downstream signaling pathways…
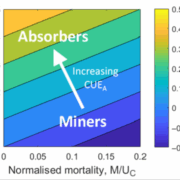
Viewpoint: A new lens on ectomycorrhizal function: exploring the absorber-miner spectrum
Plant Science Research WeeklyMycorrhizal symbiosis is widespread in nature, occurring in approximately 90% of terrestrial plant species, and played a crucial role in enabling plant colonization of land over 450 million years ago. The majority (>80%) of these associations are formed by endomycorrhizae, in which fungi from the…
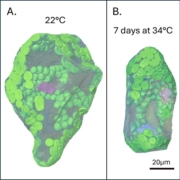
Sweet heat: Organelle-specific carbohydrate metabolism in heat stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant metabolism varies substantially between developmental stages, cell types, and intracellular environments. Similarly, biochemical responses to abiotic stress often deviate between neighboring cell types, but discerning what is changing where becomes more challenging in smaller and more fragile sub-compartments. …
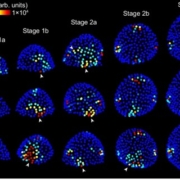
Stochastic gene expression, an ordinary part of multicellular life
Plant Science Research WeeklyStochasticity is an important feature of genes, allowing for variability in their abundance and activity prior to ‘fine-tuning’ at later periods of development. Kong et al. describe this feature in auxin responsive genes, attributing their ‘stochastic’- or inherently random expression – as…

