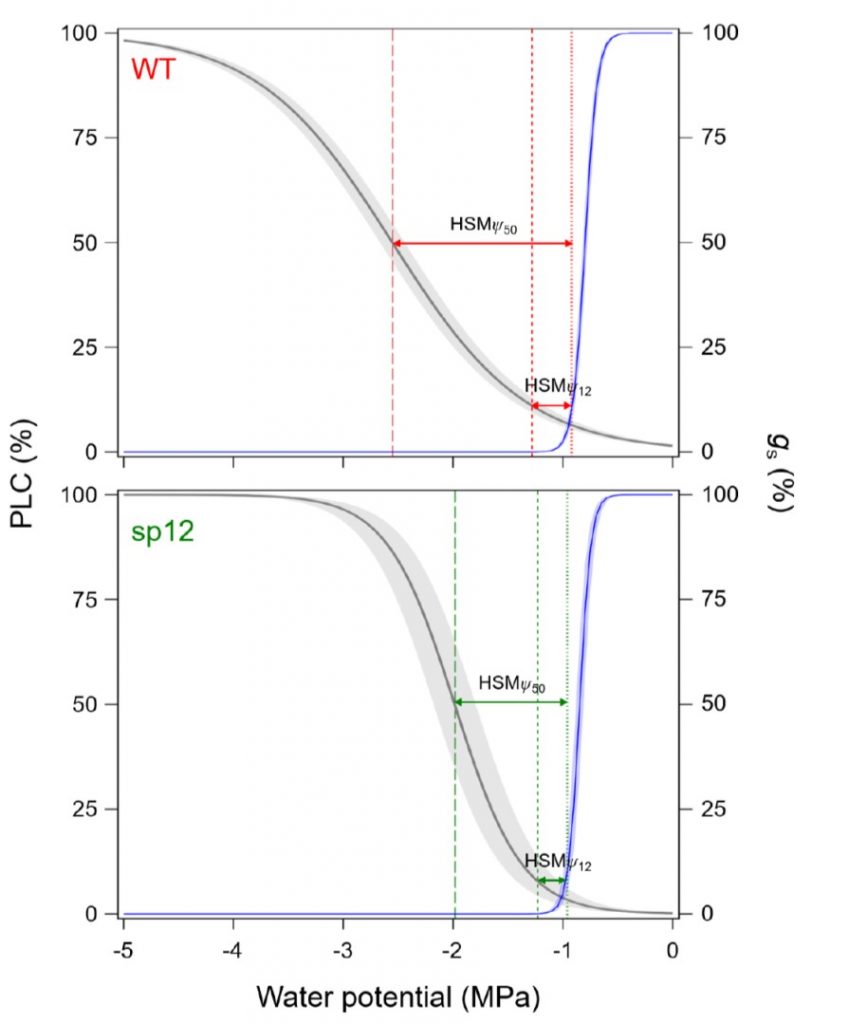
Over‐accumulation of abscisic acid in transgenic tomato plants increases the risk of hydraulic failure (Plant Cell Environ.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyABA enhances stomatal closure and so decreases transpiration. Several studies have shown that increasing ABA levels can increase water-use efficiency, so this strategy has been investigated with the goal of obtaining “more crop per drop”. Lamarque et al. investigated physiological and hydraulic effects…
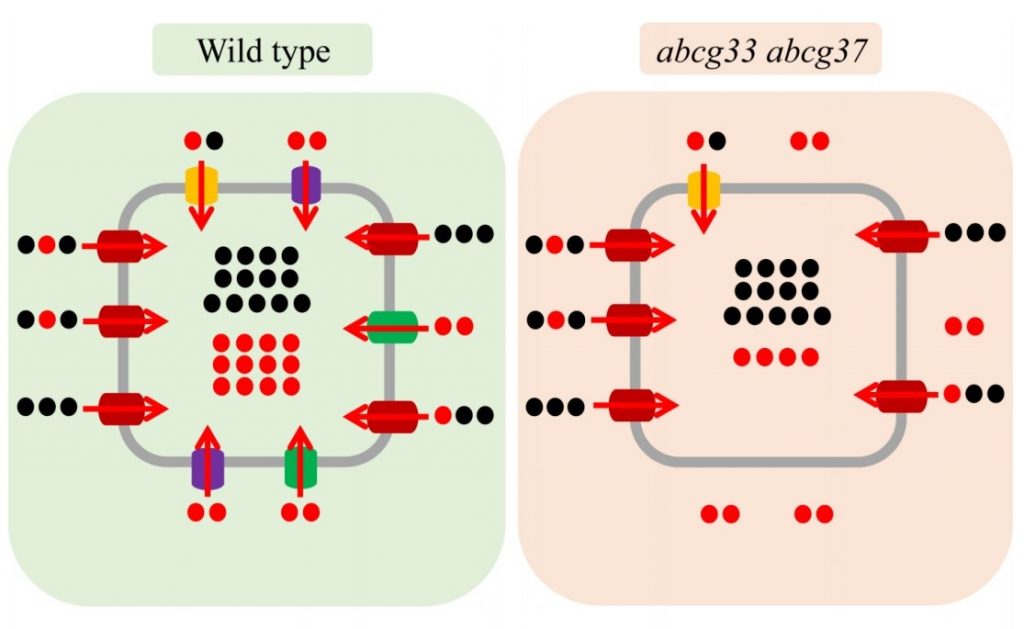
ATP binding cassette proteins ABCG37 and ABCG33 are required for potassium-independent cesium uptake in Arabidopsis roots (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPotassium is one of the major nutrients for plant growth and development. Plants have a well-studied potassium uptake system mediated by transporters and ion channels. Unfortunately, due to the chemical similarity of potassium and cesium, which is toxic for plant growth, cesium is able to to get into…
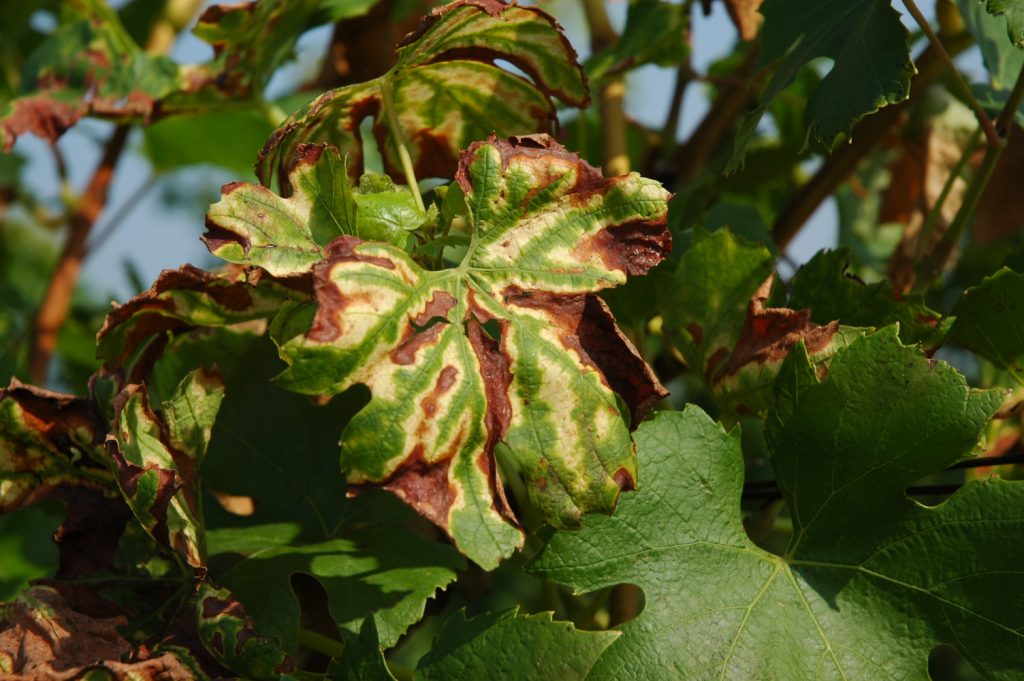

Exploring the hydraulic failure hypothesis of esca leaf symptom formation (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEsca is a leaf scorch (necrosis) disease of grapevine that causes tremendous yield losses. Bortolami et al. have investigated the etiology of this condition, which is known to be a consequence of fungal pathogen infection. But how exactly does the fungal infection contribute to the observed symptoms?…
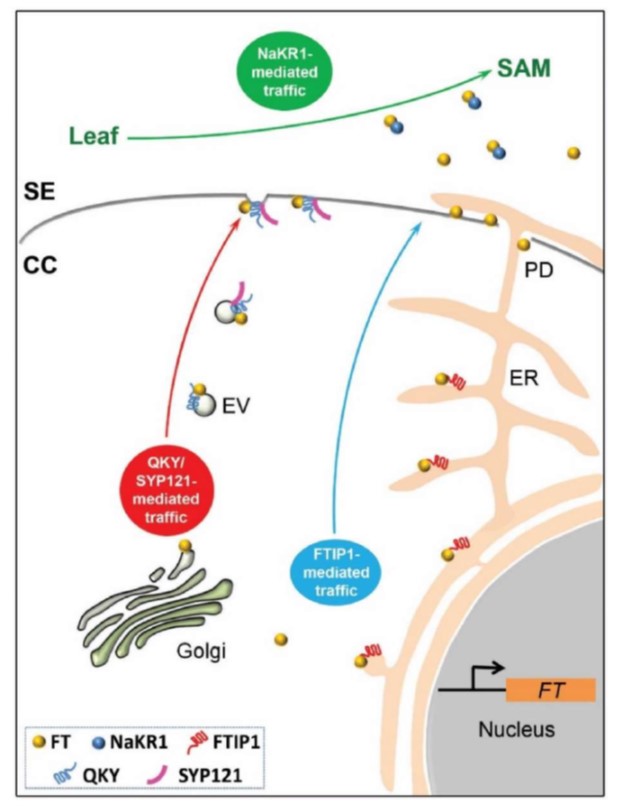
The QKY-SYP121 complex controls long-distance florigen movement ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Arabidopsis thaliana, changes in day-length (photoperiod) activate the expression and transport of phloem-mobile florigen (FT, FLOWERING LOCUS T) to the shoot apical meristem to trigger the transition to flowering. While the role of FT as a long-distance signal is well-established, the underlying…
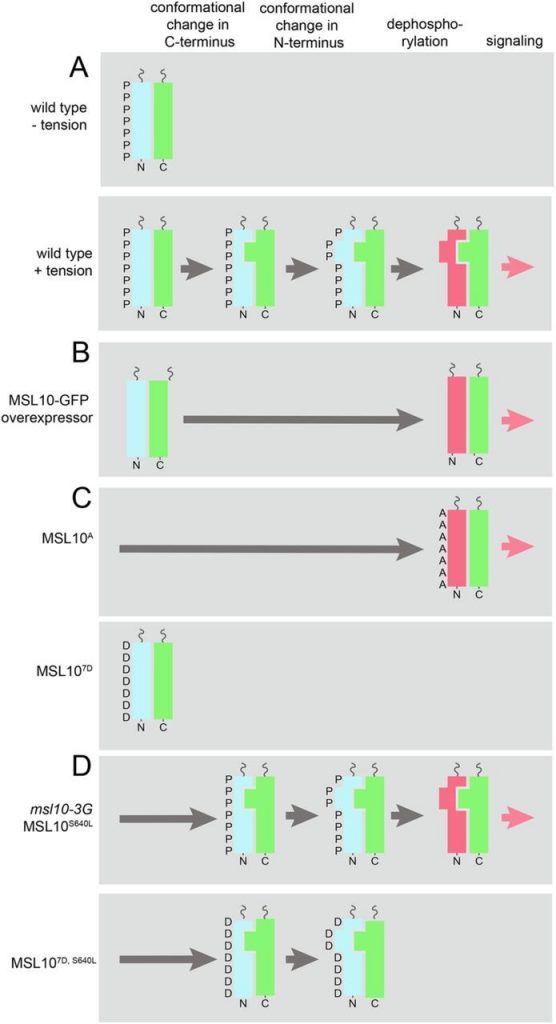
The N-terminus of AtMSL10 interacts with its own C- terminus (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are equipped with multiple mechanosensitive (MS) ion channels that respond to external and internal mechanical perturbations. When one of these, AtMSL10, is overexpressed it leads to a cell death phenotype, although there is no discernible phenotype associated with its loss of function. Recently…
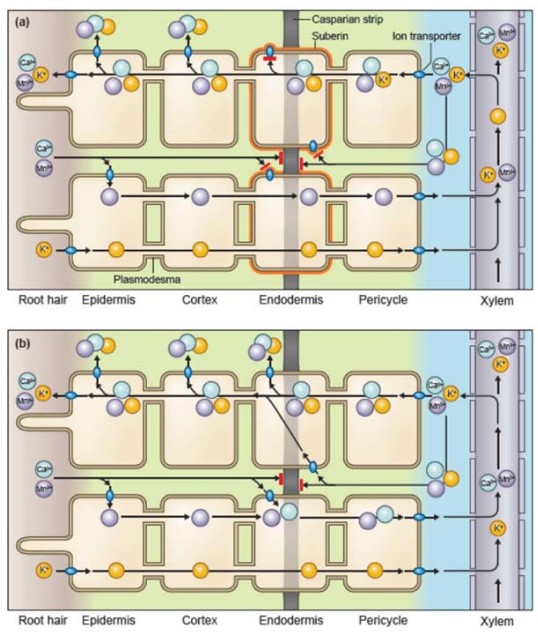
Manganese deficiency affects root endodermal suberization and ion homeostasis (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyManganese (Mn) is an essential plant nutrient necessary for multiple plant process such as photosynthesis. Mn deficiency has a significant impact on crop production particularly in cereals including barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Chen et al. identified how Mn deficiency alters suberin deposition in the …
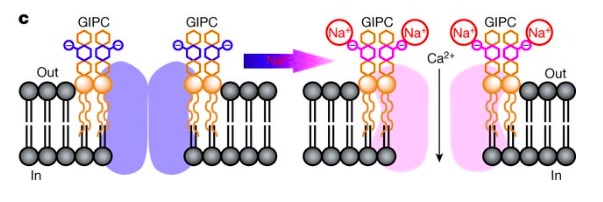
Plant cell-surface GIPC sphingolipids sense salt to trigger Ca2+ influx (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklySoil salinity is one of the most important global problems that negatively affect crop productivity. Jiang et al designed a forward genetic screen in A. thaliana to identify the specific ionic response triggered by salt stress. They mutagenized plants expressing the genetically encoded Ca2+ sensor aequorin,…
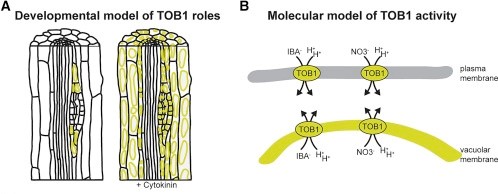
TRANSPORTER OF IBA1 links auxin and cytokinin to influence root architecture ($) (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIndole-3-butyric acid (IBA) is the precursor of the hormone auxin and it controls the formation of lateral roots. Evidence suggests that IBA is converted to IAA, endogenous active auxin. The major study material to distinguish between IBA and IAA was highlighted by the IBA-specific efflux carrier ABCG36/PDR8/PEN3,…
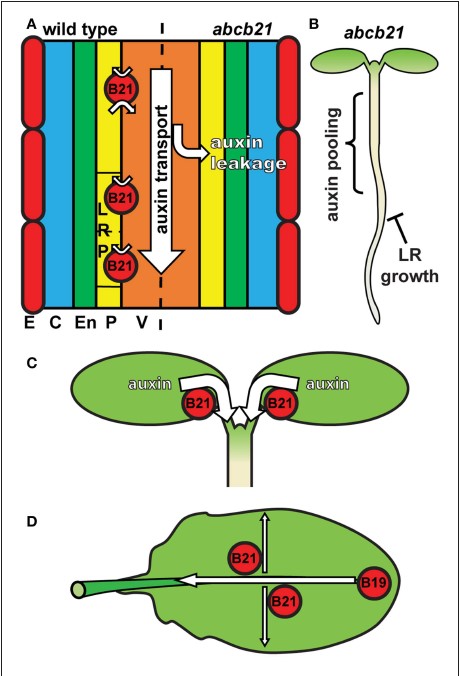
ABCB21 regulates auxin levels in cotyledons, pericycle and leaves (Frontiers Plant Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin activity is maintained through regulated biosynthesis, metabolism and transport. In this paper Jenness et al. characterized the physiological significance of a known IAA transporter, ABCB21 (ATP BINDING CASSETTE TRANSPORTER subfamily B member 21) in Arabidopsis. ABCB21 transports shoot derived…

