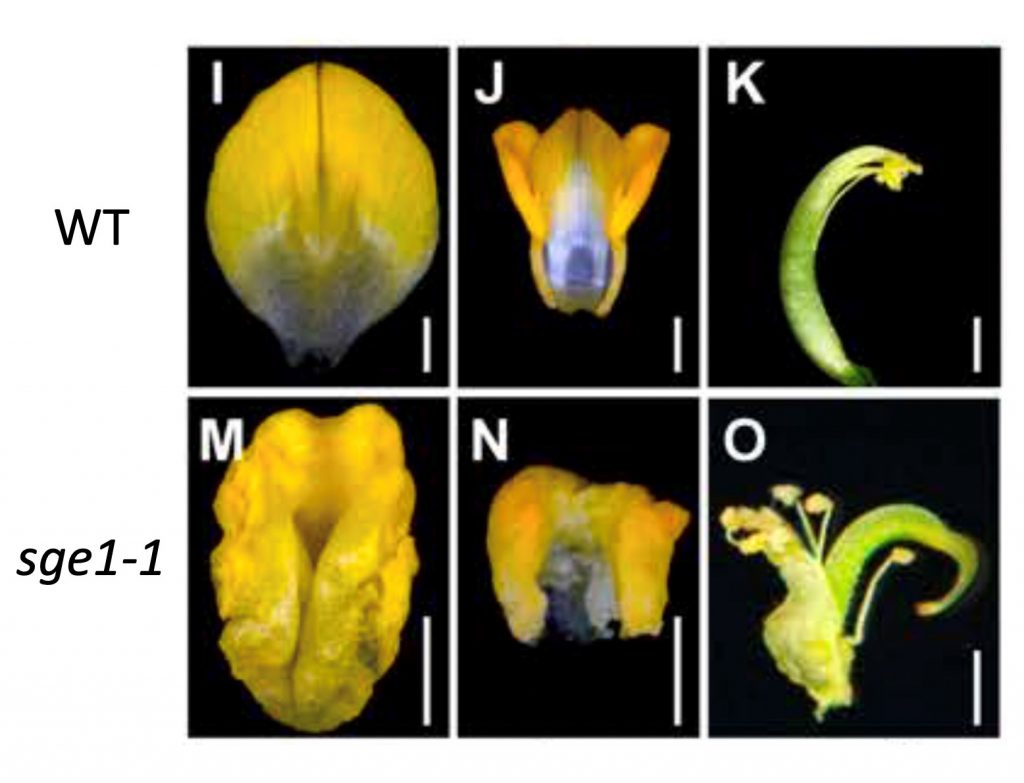
Lipid distribution in cuticles affects flower architecture in Medicago (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFloral architecture influences pollination and reproduction: open flowers facilitate cross-pollination, while closed flowers limit outcross. Some plants of the Leguminosae family (i.e., members of the Papilionoideae subfamily that includes soybean, pea, medicago, lotus) possess a complex architecture,…
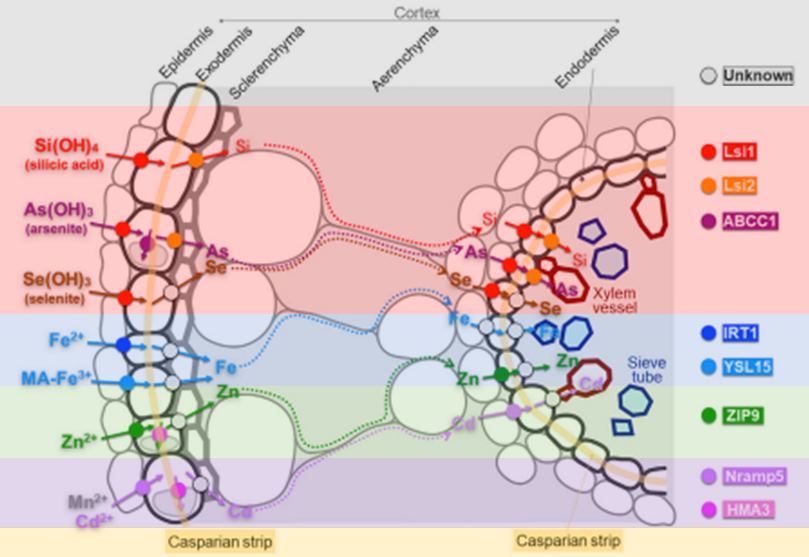
Review. Plant nutrition for human nutrition: Hints from rice research and future perspectives
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmong all the mineral elements transported from the soil to the plant, cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As)- are toxic for all organisms whereas 13 micronutrients, including iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn), are beneficial for both human and plant nutrition. Ideally, food crops should accumulate fewer soil contaminants…
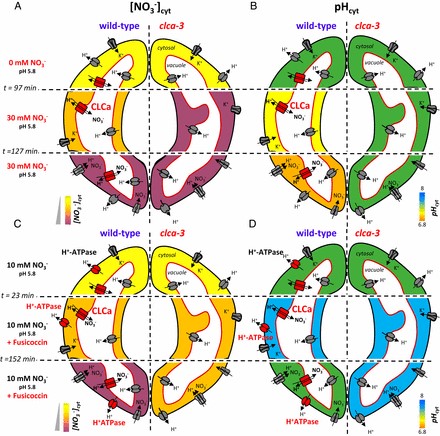
Vacuolar channel CLCa is involved in guard cell pH homeostasis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants, stomata are involved in a host of responses, controlled by ion homeostasis in guard cells. In an attempt to understand the function of a plant chloride channel (CLC), CLCa, which transports chloride (Cl-) and nitrate (NO3-) in guard cells, Demes and colleagues sought to establish a relationship…
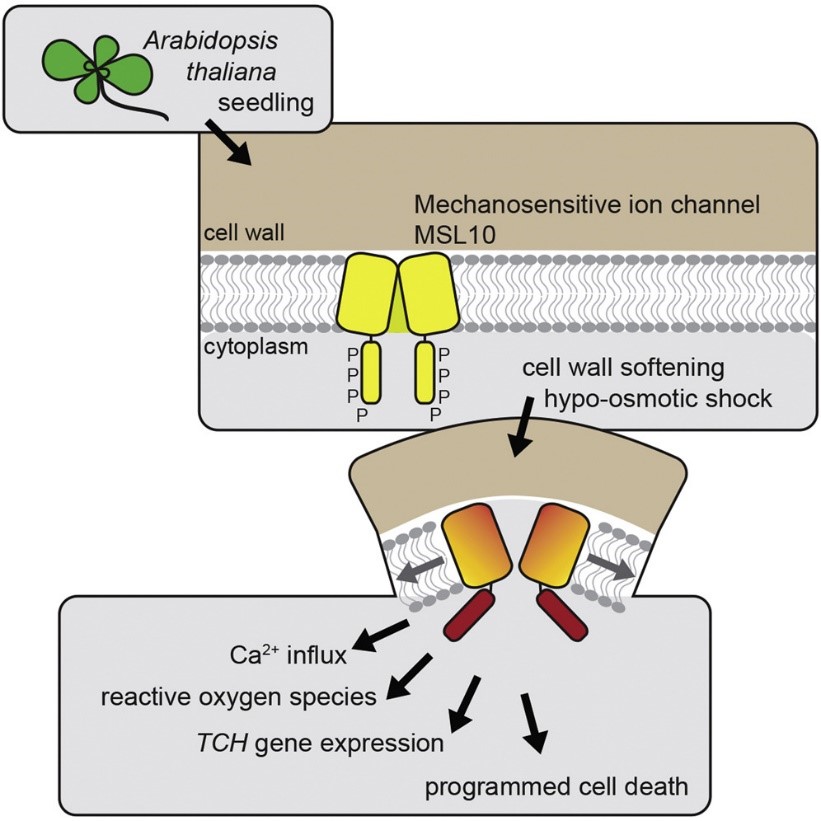
MscS-like 10 as a cell swelling sensor and promotes hypo-osmotic shock responses (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOptimal volume and turgor in the plant cell is important for metabolism, development and growth. Excessive diffusion of water into the cell will cause extreme swelling and a loss of cellular integrity. Members of the plasma membrane MscS-like (MSL) family of mechanosensitive (MS) ion channels play a…
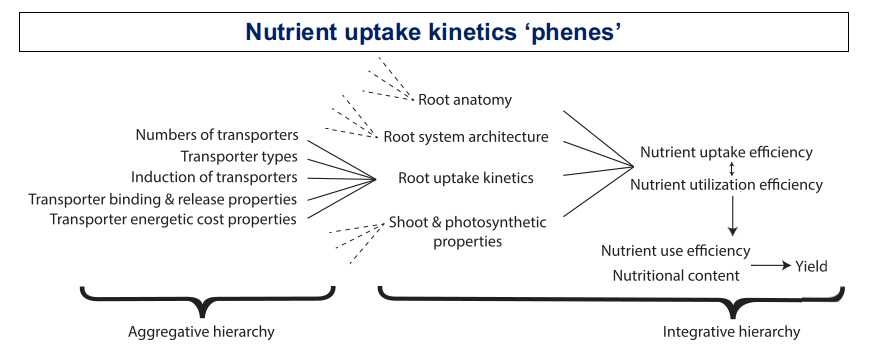
Review: Targeting root ion uptake kinetics to increase plant productivity and nutrient use efficiency (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyContinuous agricultural production is required to feed the growing population, and fertilizers are important factors determining the productivity of today’s high-input agriculture. Fertilizers increase the cost of production, some are produced from finite sources, and some create environmental concern,…
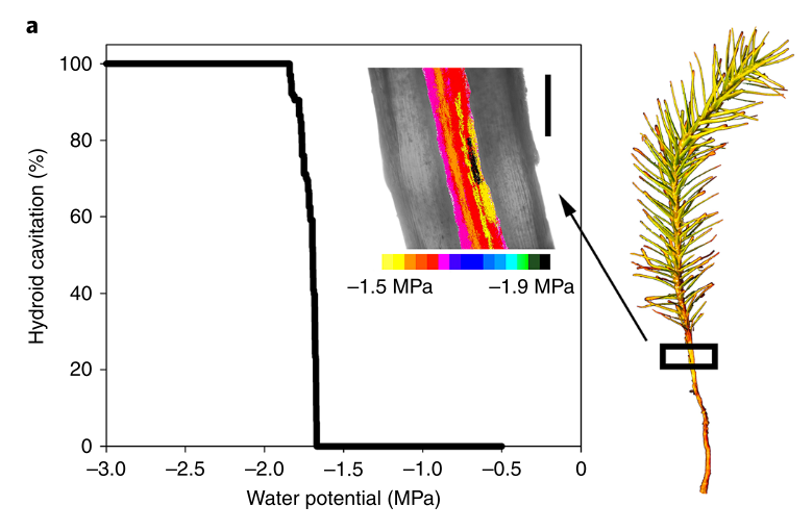
Advanced vascular function discovered in a widespread moss (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn order to grow upwards into the dry atmosphere, plants need to keep their elevated tissues hydrated and functional. In vascular plants this is achieved by a lignified water transport system in conjunction with stomatal regulation of gas exchange and the encasement of photosynthetic tissues in an impermeable…

Symplastic auxin transport: Active, passive or both? (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAdjacent cells in plants are connected by cytoplasmic connections called plasmodesmata (PD) and the movement through PD is called symplastic movement. Studies have shown that auxin transport between cells is protein-dependent, but it is not clear whether it can also move freely in the symplastic pathway.…

Maize aquaporin PIP2;5 alters water relations and plant growth (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAquaporins, also known as water channels, are conserved across all kingdoms. In plants, the plasma membrane intrinsic protein (PIP) subfamily controls membrane water permeability. Maize aquaporin PIP2;5 is highly expressed in roots. By reverse genetic approaches, Ding et al. showed that overexpression…
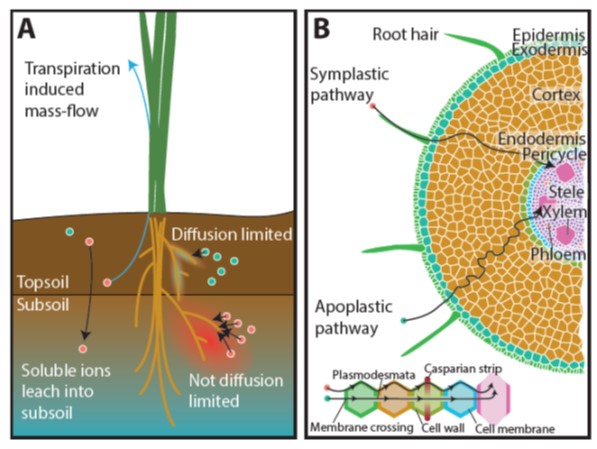
Review: Targeting root ion uptake kinetics to increase plant productivity and nutrient use efficiency (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots anchor plants and take up water, but one of their most important and complex functions is to bring a large number of different essential nutrients into the plant. Root architecture affects and is affected by nutrient uptake, but ultimately uptake is largely controlled by membrane-bound ion transporters.…

