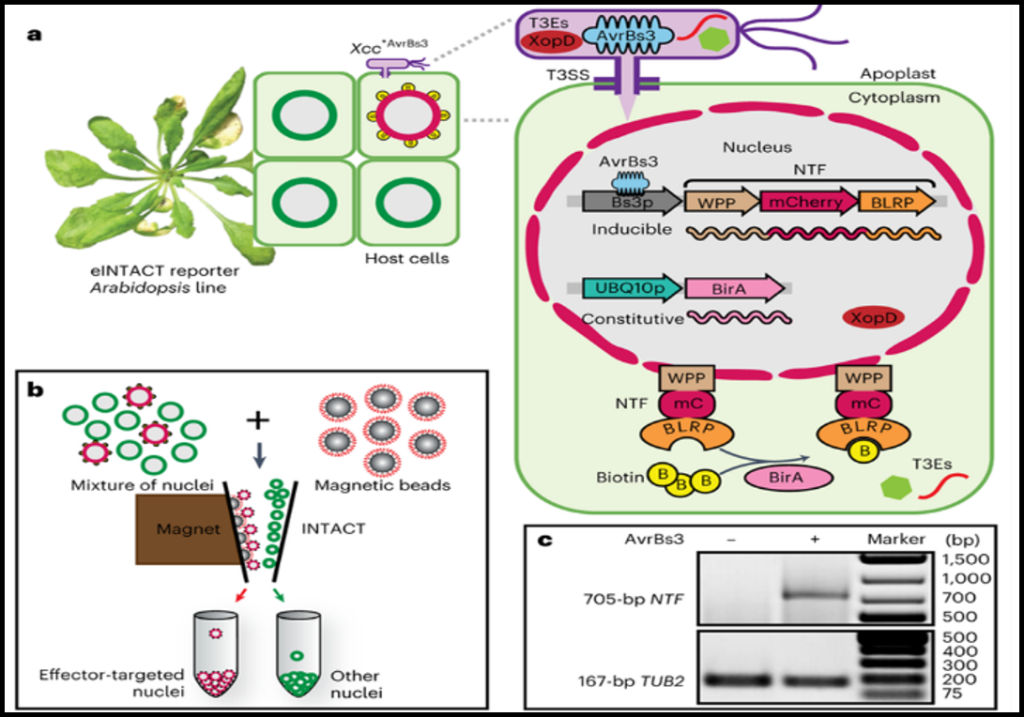
eINTACT – An effective system for isolating effector-recipient cells in plant tissues
Plant Science Research WeeklyBacteria can cause plant diseases by secreting small molecules called effectors. Studies of these effectors on host plants mostly have not accounted for the cellular complexity of plant tissues. The difficulty of detecting and isolating effector-recipient cells means that scientists mostly use bulk-infected…
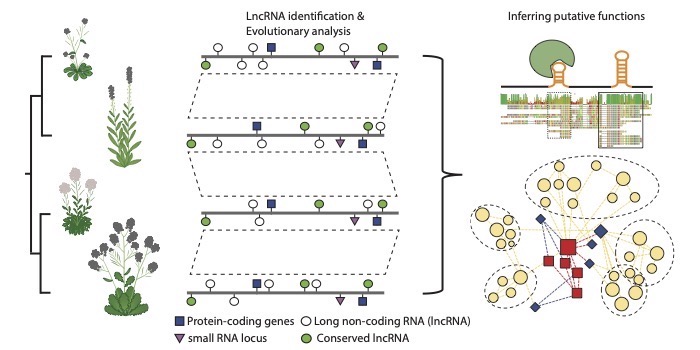
Identifying thousands of RNA genes in Brassicaceae
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellPalos et al. identify thousands of new long intergenic noncoding RNAs using public data.
By Kyle Palos and Andrew Nelson
Background: All plants have thousands of genes in their genomes that contribute to plant form and function. While the functional “end-state” of many of these genes are…

Update: Toward a data infrastructure for the Plant Cell Atlas (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to analyze the information contained within a single cell, for example through single-cell RNA sequening (scRNA-seq) presents exciting possibilities to biologists. Building on this and similar technologies, the Plant Cell Atlas (PCA) (www.plantcellatlas.org/) has the goal of creating an information…

Single seeds exhibit transcriptional heterogeneity during secondary dormancy induction (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySecondary dormancy (SD) of seeds is a natural strategy that allows survival of the plant in environments with unfavourable climatic conditions. However, in Arabidopsis, a variance of dormancy depth in between identical seeds can be explained by population-based threshold models. This single-seed variability…
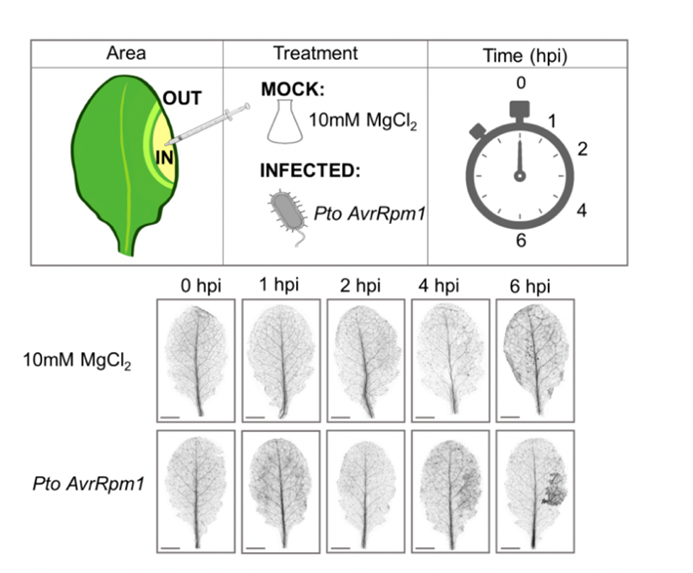
Robust transcriptional indicators of immune cell death revealed by spatio-temporal transcriptome analyses (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany plants trigger a form of cell death, known as the hypersensitive response (HR), immediately upon pathogen recognition. To minimize damage to the plant, this cell death must be highly localized to the site of attack, while more distal cells survive and activate other immune responses. However, the…
ATTED-II v11: A plant gene coexpression database using a sample balancing technique by subagging of principal components (Plant Cell Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenes are generally expressed in concert with one another with data often represented by gene co-expression networks. Gene co-expression data may be useful in identifying genes with unknown functions and are generally utilized in exploring molecular processes occurring during normal development as well…
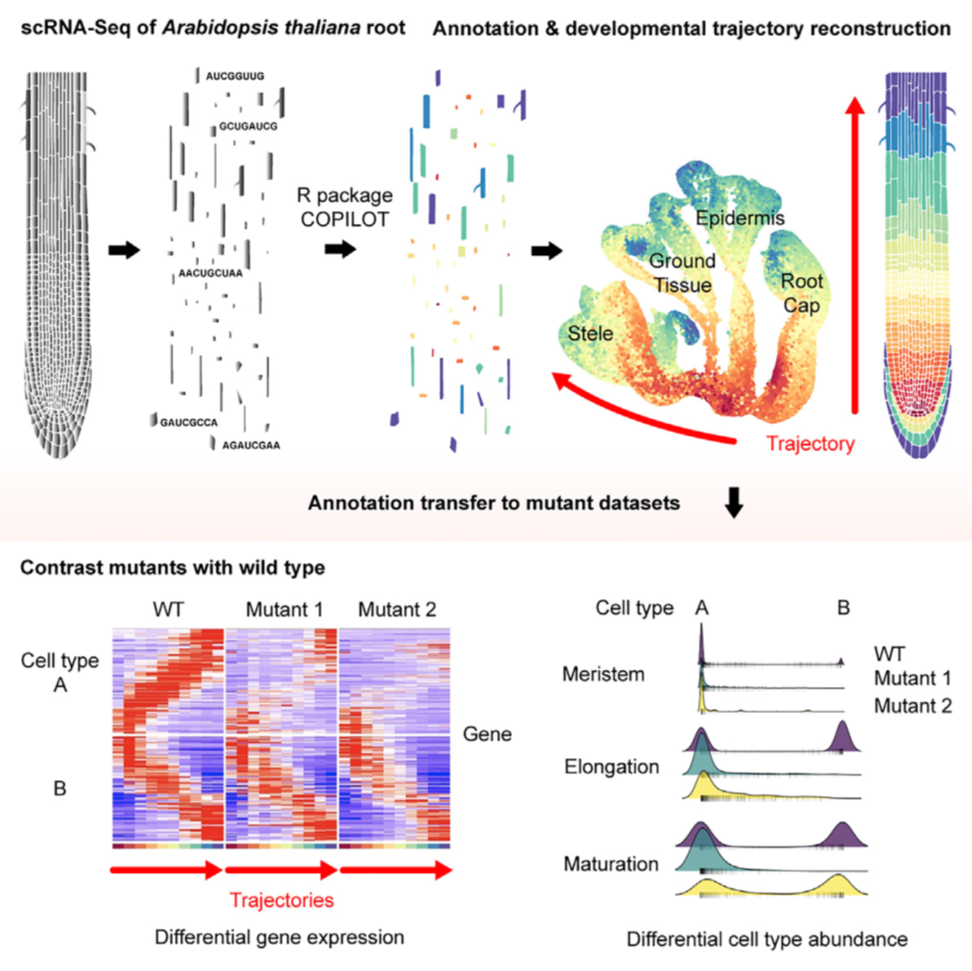
A single-cell Arabidopsis root atlas reveals developmental trajectories in WT and cell identity mutants (Dev. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklySingle-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a powerful tool to identify rare and novel cell types, characterize multiple cell types, and more accurately understand their functions across their life cycles. The Arabidopsis root is a perfect system in which to investigate cellular differentiation due to…
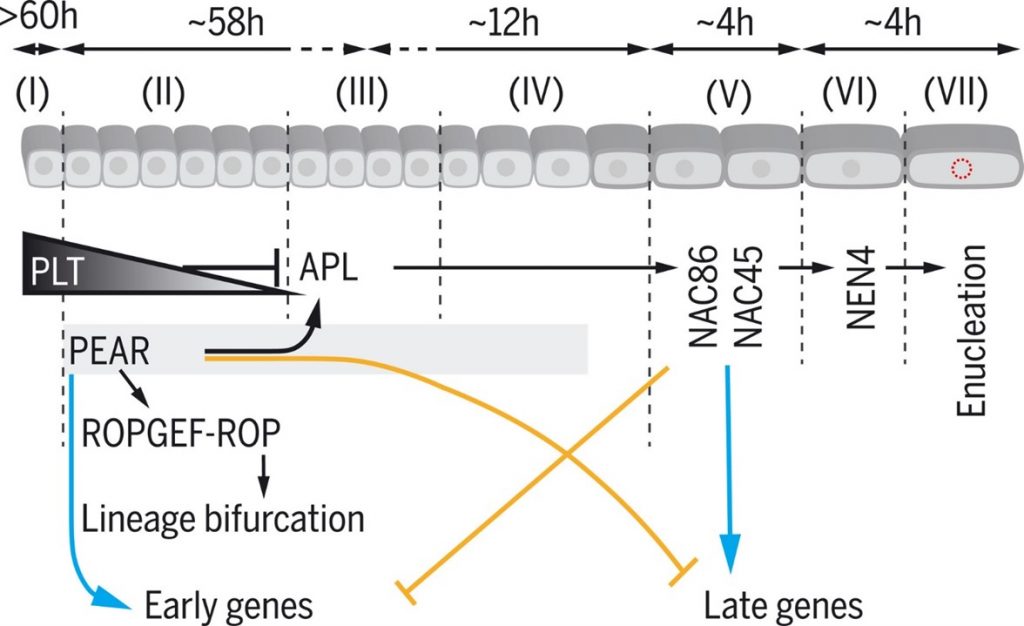
Cell-by-cell dissection of phloem development links a maturation gradient to cell specialization (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this seminal paper, Roszak et al. present a deeper understanding of the development of the protophloem cell lineage. The differentiation process from the phloem stem cell to the enucleated cell state spans approximately 19 cells. Using live imaging, FACS sorting and single-cell RNA sequencing, the…
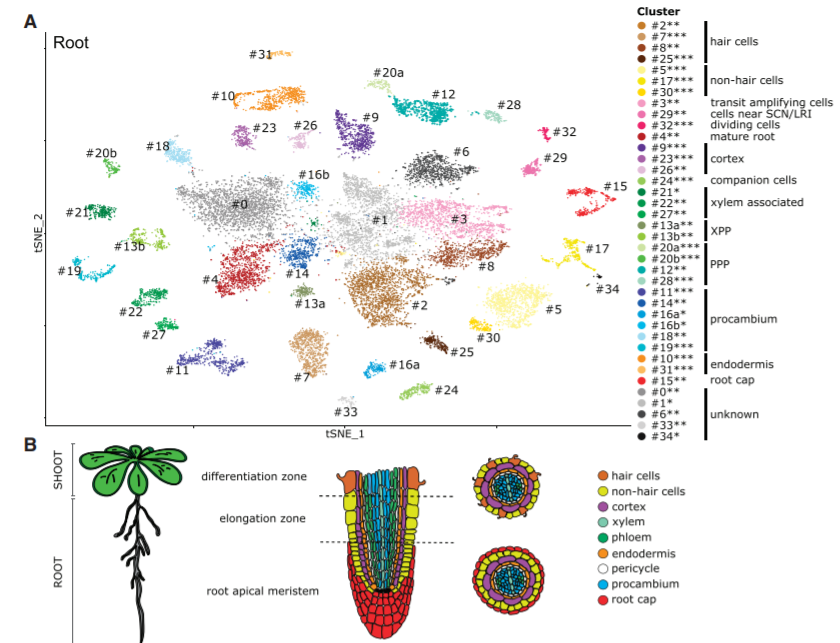
Shoot and root single cell sequencing reveals tissue- and daytime-specific transcriptome profiles (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany biological processes are controlled by the circadian clock in plants, yet studies often don't report sampling timepoints, leaving much to be discovered about the plant circadian rhythm. Apelt et al. have utilised single cell RNA sequencing to examine almost 70,000 Arabidopsis cells from above and…

