
Smelly plant: What are they feeding you?
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhile flowers are typically associated with pleasant fragrances, every few years a certain part of the rainforests of Sumatra is filled with the pungent odor of rotting flesh. This smell emanates from the inflorescence of the titan arum, or corpse plant, which heats up during flowering in a process known…
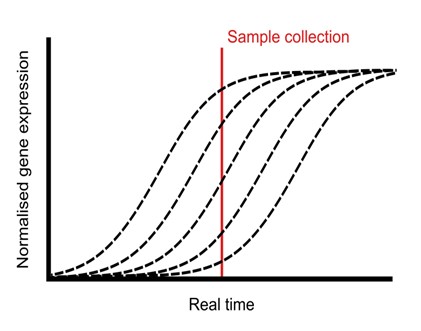
Single-plant omics provides transcriptional insights into the transition from the vegetative to reproductive phases
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants undergo a series of physiological processes when transitioning from the juvenile to the vegetative phase, and then vegetative to the reproductive phase. RNA-Seq offers substantial potential for uncovering the transcriptional landscape underlying these developmental transitions. However, developmental…

Single cell transcriptomics aids gene discovery of complex natural product biosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyFrom an ancient Greek cure-all to a modern treatment for mild depression, Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s wort) is a fascinating weed. Its leaves and flowers produce hyperforin, a metabolite derived from the isoprenoid pathway, which acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Despite partial genome and…

Phylogenomics of rubber trees sheds light on latex production
Plant Science Research WeeklyNatural rubber, primarily derived from Hevea brasiliensis, is an essential global resource, but its production threatened by environmental changes and pest pressures. Fang et al. examined genome assemblies from eight high-quality Hevea accessions comprising different species. The results show unexpected…
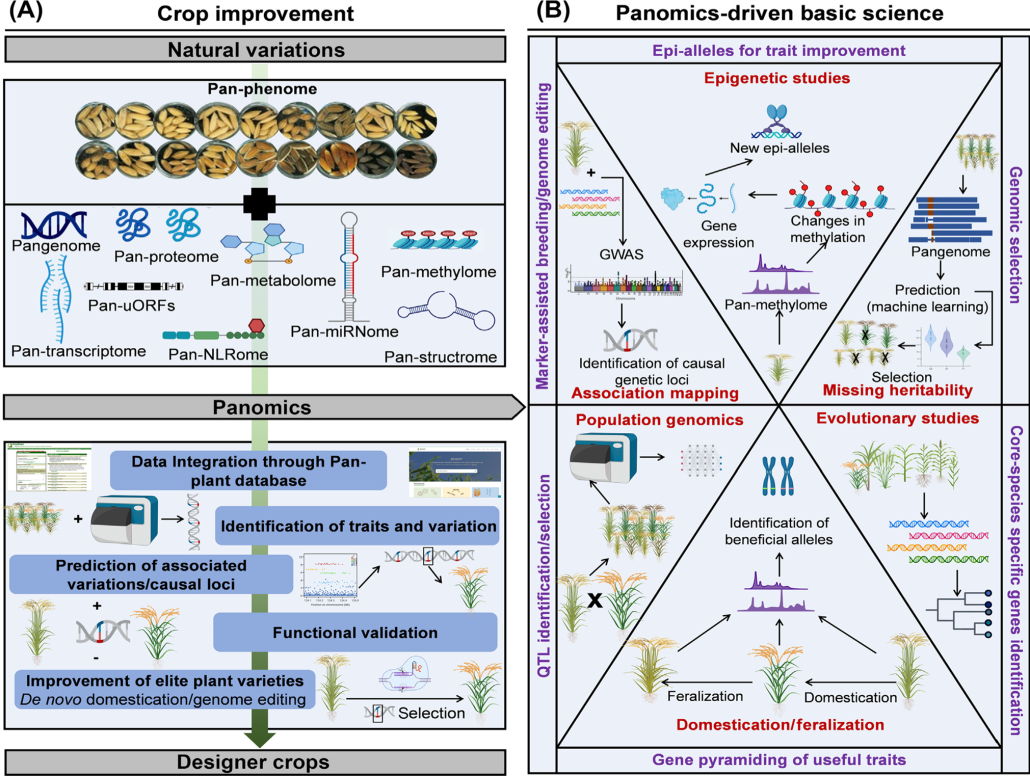
Review: The era of panomics-driven gene discovery in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPanomics, an approach integrating multiple ‘omics’ datasets such as genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, and phenomics, has seen rapid advancement in recent years due to technological improvements, particularly in genomics. This review focuses on the recent developments in panomics-driven gene…
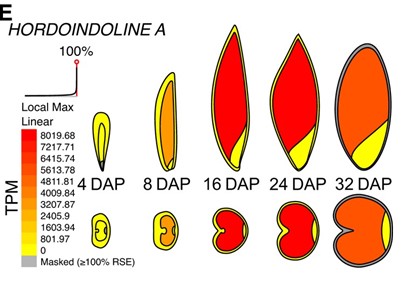
Transcriptional changes during barley grain development
Plant Science Research WeeklyBarley is a globally important cereal crop, so understanding barley grain development is of much interest. Here, Kovacik et al. investigated transcriptional changes in barley grains at five points across development, 4, 8, 16, 24 and 32 days after pollination. For each time point, grains were manually…
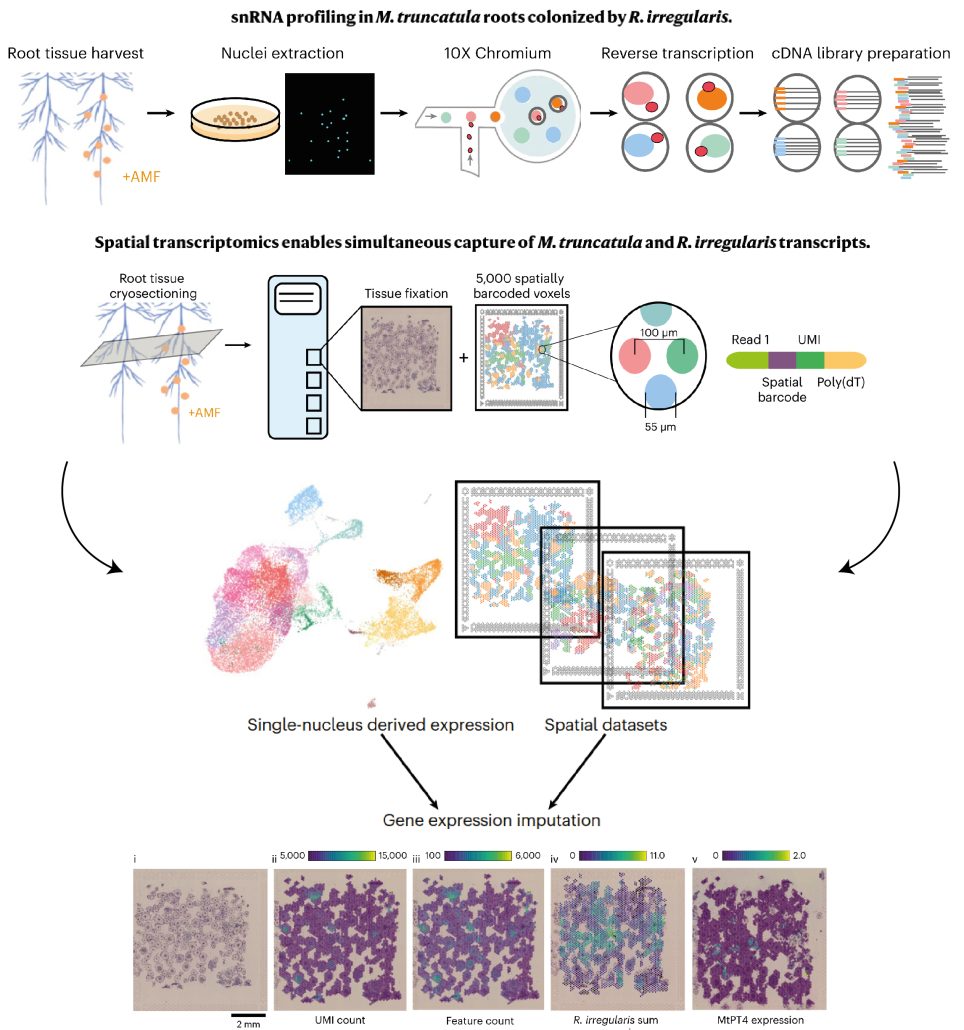
Spatial co-transcriptomics reveals discrete stages of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn recent years, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and single-nuclei RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) techniques have revolutionized plant biology by enabling the identification of novel cell types, modeling developmental trajectories, and analyzing transcriptional activity at the cellular level. However,…
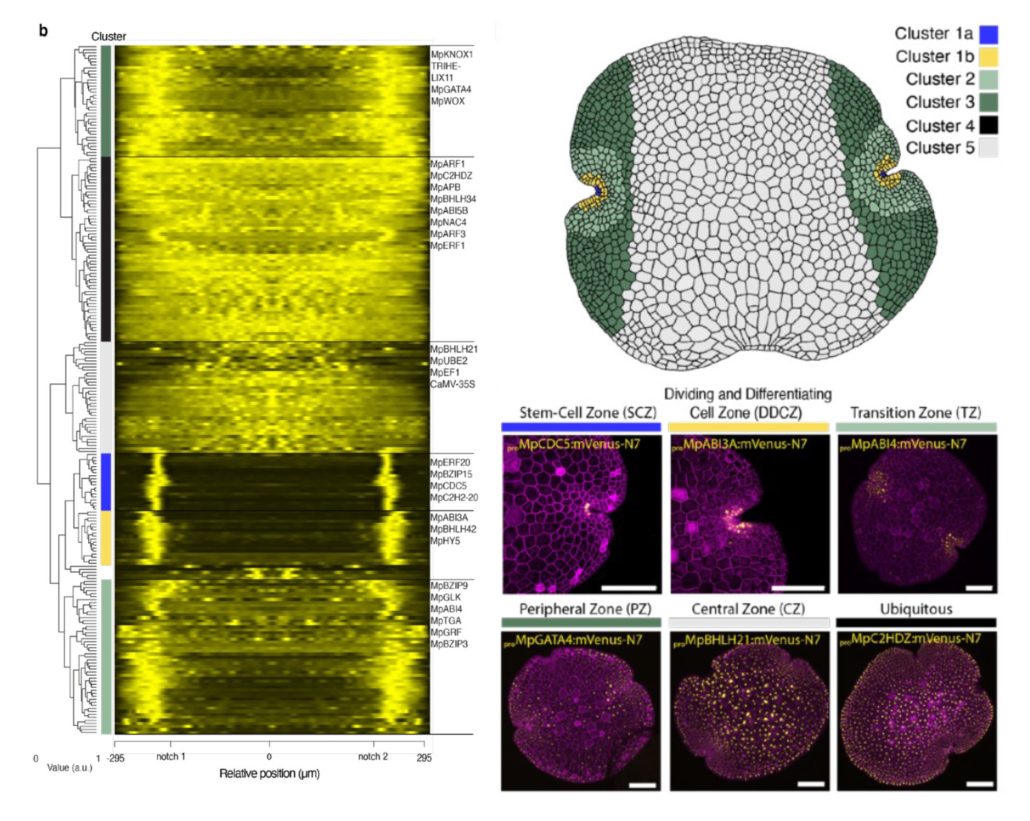
The Marchantia transcription factor atlas
Plant Science Research WeeklyMarchantia’s power as a model organism continues to grow! Here, Ramoni et al. have investigated the expression pattern of the proximal promoters of most of its 450 transcription factor (TF)-encoding genes. The promoter elements were fused to nuclear-localized fluorescent reporters and introduced into…

JGI Plant Gene Atlas: an updateable transcriptome resource to improve functional gene descriptions across the plant kingdom
Plant Science Research WeeklyFunctional genomic studies across plants are incomplete without deciphering the putative gene functions in model as well as non-model plants. With an aim to facilitate gene function identification and cross-species expression analysis, Sreedasyam et al. describe the Joint Genome Institute (JGI) Plant…

