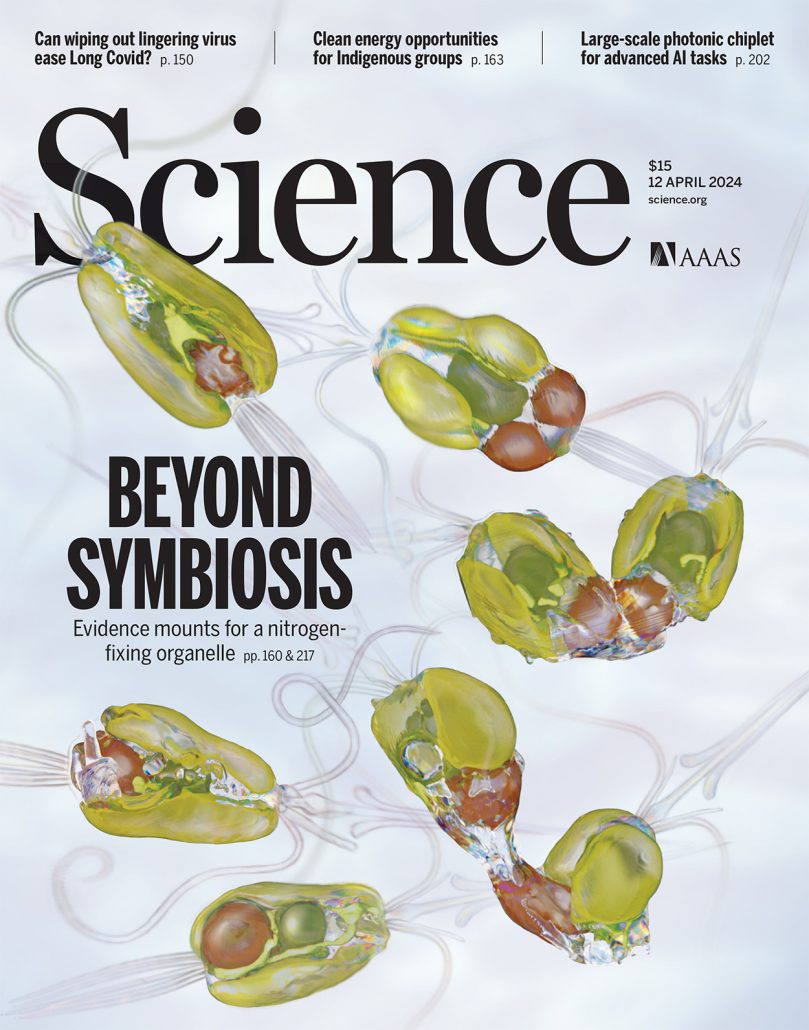

A nitrogen-fixing algal organelle
Plant Science Research Weekly
Coale et al. provide an exciting peek into the evolution of a nitrogen-fixing organelle (called a nitroplast) in their studies of a tiny marine alga, Braarudosphaera bigelowii and its endosymbiont cyanobacterium, Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa (UCYN-A). Plant biologists are familiar with…
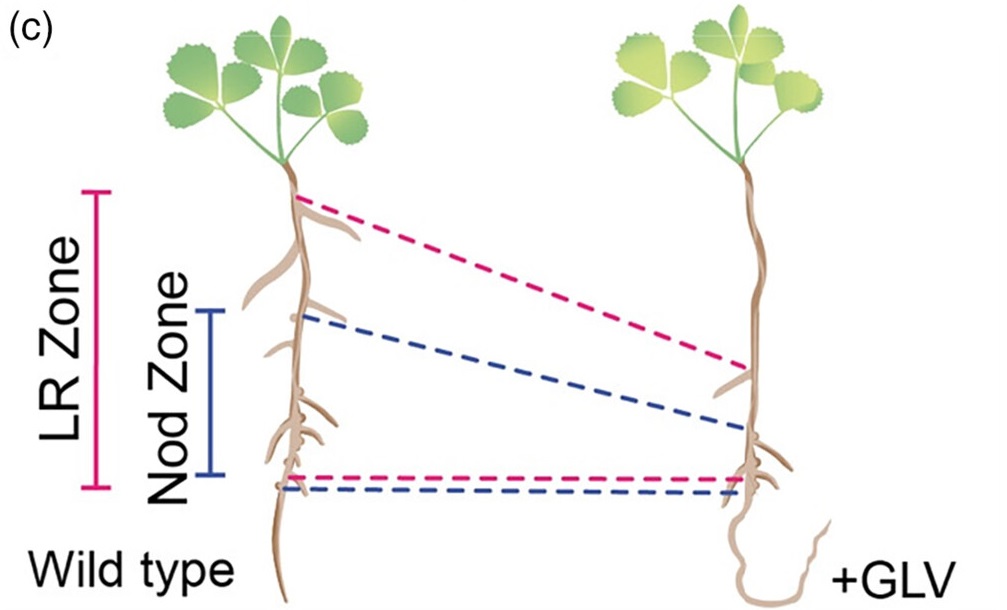
Peptide GOLVEN10 alters root development and noduletaxis
Plant Science Research WeeklyFor many years, biologists argued about whether plants have peptide hormones like animals have, and ever since it was first shown that plant peptides do have hormone-like functions, I’ve said a little cheer as new functions are discovered (Yay plants!). A few years ago, Sonali Roy and colleagues wrote…
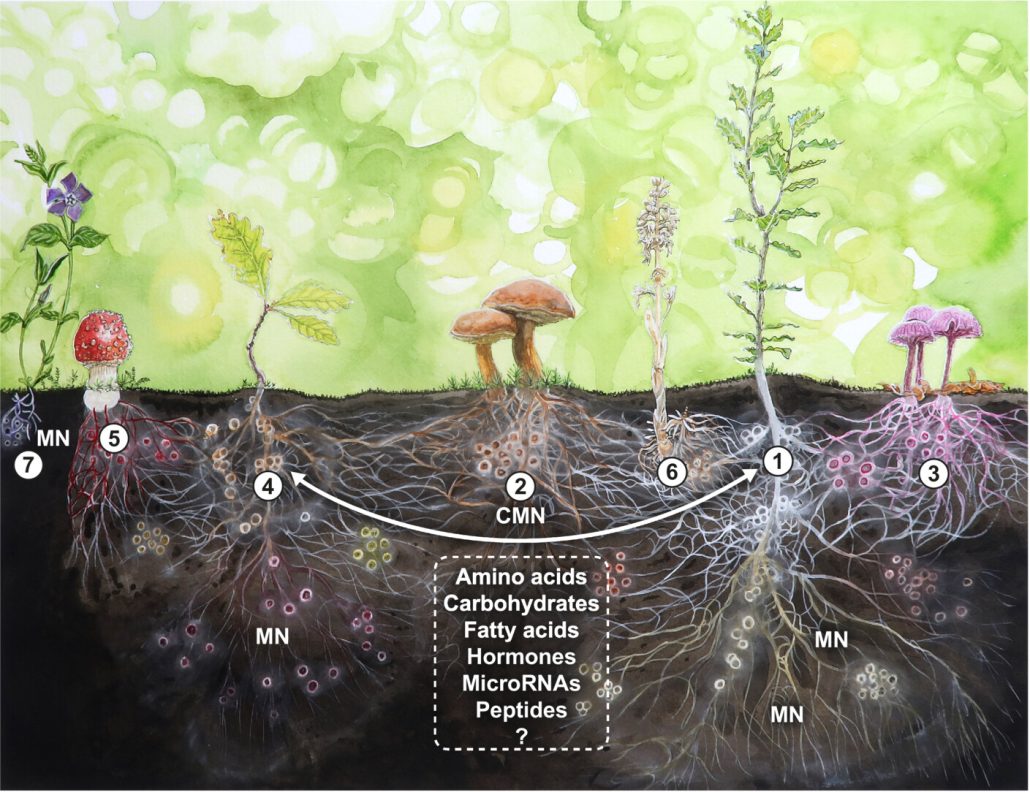
Review. Mycorrhizal symbiosis: Genomics, ecology, and agricultural application
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis outstanding Tansley review by Martin and van der Heijden spans the scale of research on mycorrhizal symbiosis from molecules to ecosystems, and spans time from the earliest encroachment of plants and fungi onto land to the future applications of our understanding. This very comprehensive review…
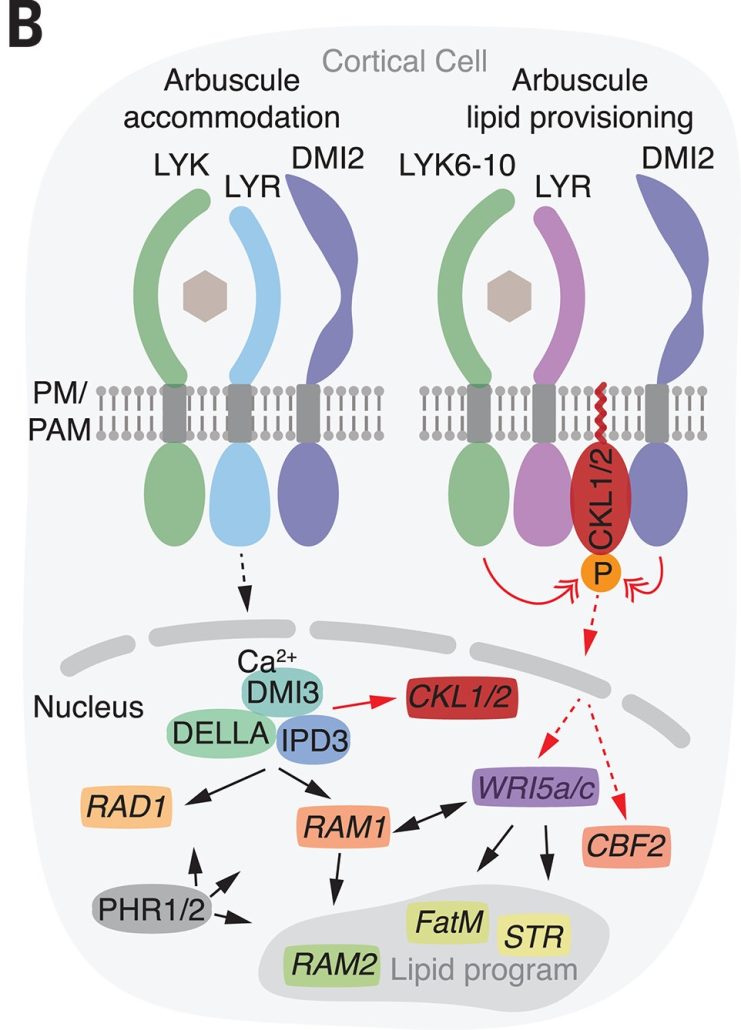
Receptor-associated kinases control lipid provisioning in plant–fungal symbiosis
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost plants benefit from symbiotic associations with fungi, in which the fungi aid in nutrient update particularly of phosphate, and the plant returns the favor by supplying the fungi with lipids. Several but not all of the molecular players required for these important pathways have been identified.…
Review: Scripting a new dialogue between diazotrophs and crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyAll organisms need nitrogen to produce nucleic and amino acids, but nitrogen-limitation is common for many plants. Although nitrogen is very abundant in the atmosphere, most is inaccessible due to the triple bond that renders N2 relatively inert. Tremendous crop yields in recent decades are attributable…

Essay: The coming golden age of lichen biology
Plant Science Research WeeklyLichens are remarkable, complex symbiotic organisms. They have evolved multiple times independently, but all lichen include at least one fungal partner (the mycobiont) which they usually resemble morphologically, and at least one cyanobacterial or algal photosynthetic partner (the photobiont). This partnership…
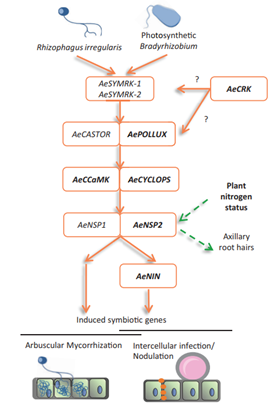
Modus operandi of Nod-independent symbiosis in Aeschynomene evenia (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbioses and nodule organogenesis processes that occur independently of Nod-factors are relatively unexplored. Quilbe et al. investigated the semi-aquatic legume Aeschynomene evenia, which has recently been shown to establish symbioses with Bradyrhizobium sp. that do not produce Nod factors. The authors…
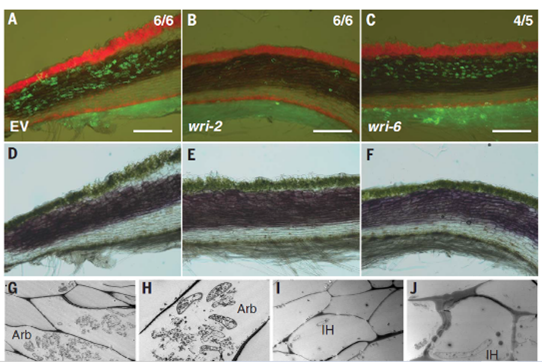
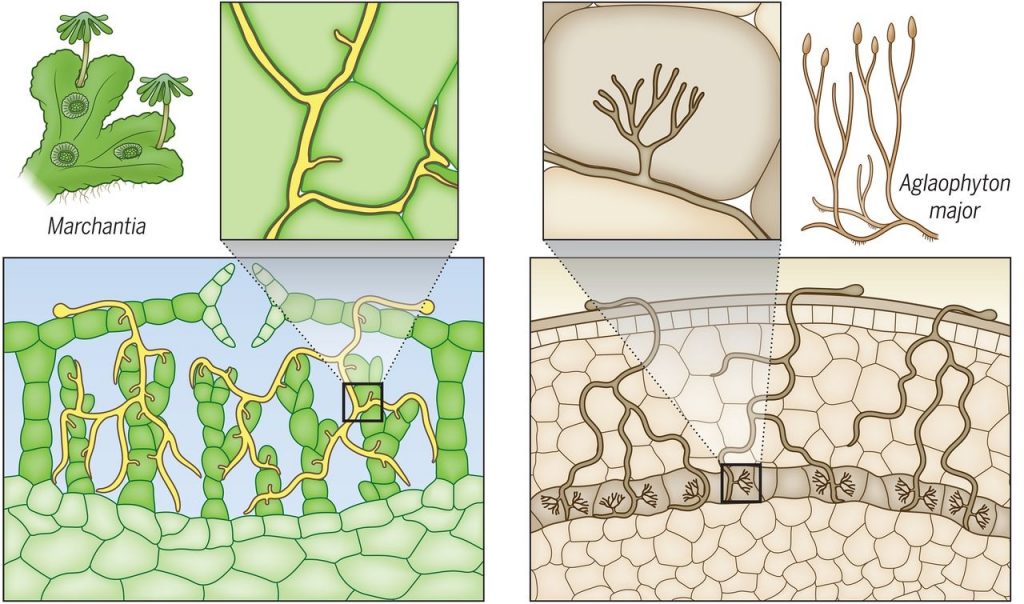
Give and Take: Lipid exchanges drove the evolution of mutualism during plant terrestrialization (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants form symbiotic associations with a variety of microbial partners, among which arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are prominent. AMF are known to enrich plants with a host of vital nutrients including the essential macronutrient phosphorus. While the finer details of plant-AMF association are known…

Review: Plant evolution driven by interactions with symbiotic and pathogenic microbes (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the great questions in plant science has been, “How do plants recognize friend from foe?” Like most great questions, this one benefits from a historical perspective. In their new review, Delaux and Schornack look at plant evolution through the lens of plant interactions with symbiotic and…

