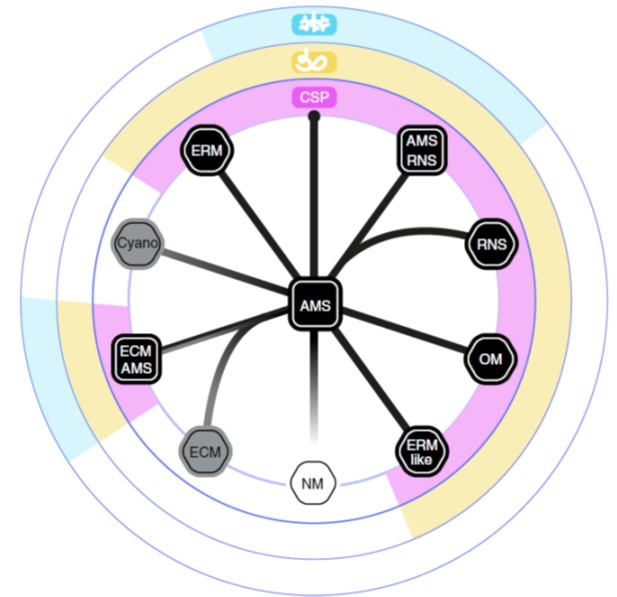
An ancestral signalling pathway is conserved in intracellular symbioses-forming plant lineages ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s widely thought that plants acquired the ability to live on land thanks to a little help from their friends, specifically arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Even now, most land plants form mutually beneficial associations with fungi or bacteria, and these often involve the plant cells acting as hosts…

A CLE–SUNN module regulates strigolactone content and symbiosis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe symbiosis between plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is conditional. Plants that are limited for phosphate release strigolactones into the soil, promoting changes in the fungi that facilitate the symbiosis. Müller et al. found that a Medicago gene encoding a CLE peptide, MtCLE53, is induced…
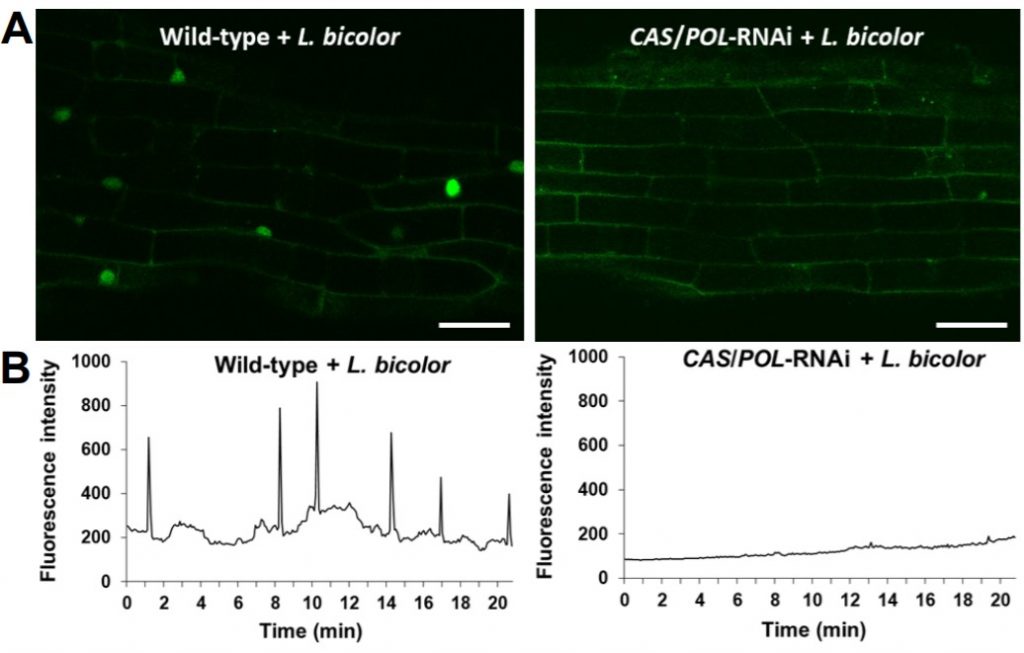
The ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor produces lipochitooligosaccharides and uses the common symbiosis pathway ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNutrient exchange during plant-fungal symbiosis allows assimilation of nutrients necessary for plant growth in a beneficial way. Several plants have evolved to form symbioses with mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia bacteria that allow the plants to efficiently take up nitrogen and phosphorous. In its interactions…
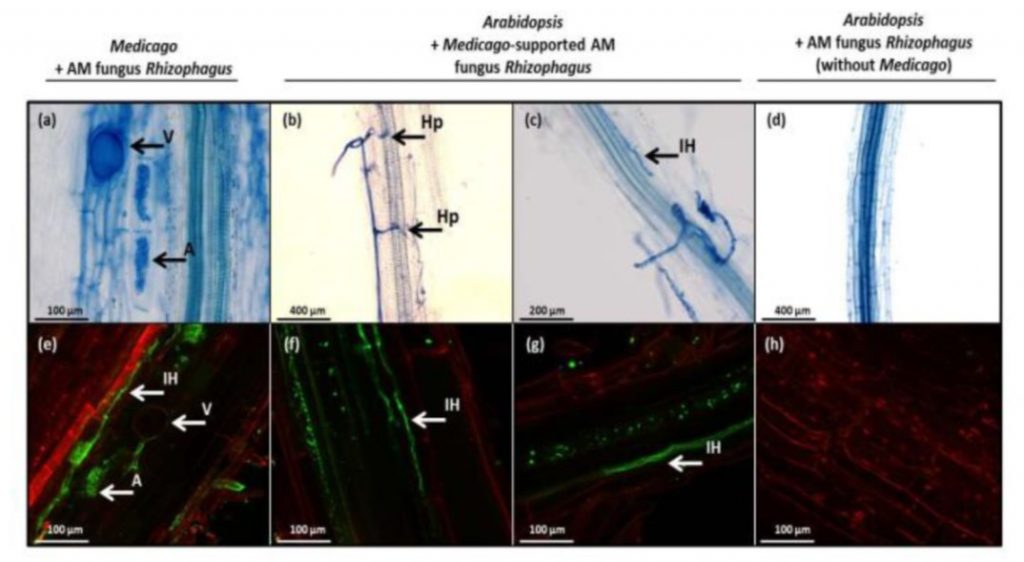
Antagonistic responses to ‘symbiotic’ AM fungi in the non-host Arabidopsis thaliana ($) (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA strikingly vast array of phylogenetically distant plants are able to form intimate interactions with symbiotic arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi for the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients. Several years of intensive research have revealed the complex regulatory networks and genetic ‘toolkits’…

