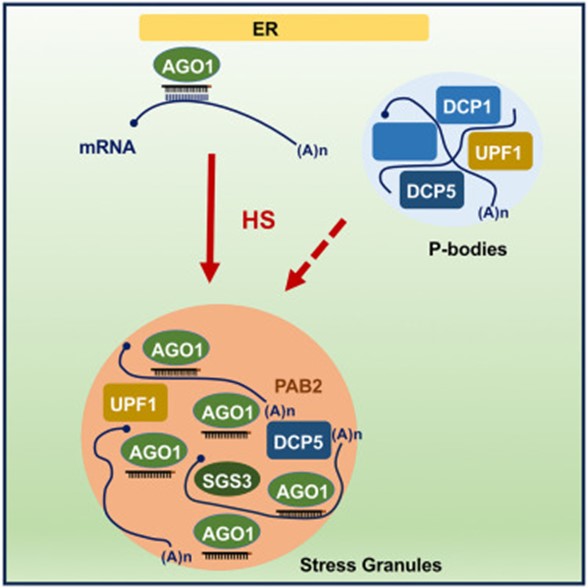
Heat stress promotes Arabidopsis AGO1 phase separation and association with stress granule components
A new article by Blagojevic, Baldrich, and Schiaffini et al. reveals that Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1 (AGO1) protein, a pivotal agent in miRNA and siRNA-mediated gene silencing associated with the rough endoplasmic reticulum, dynamically localizes within stress granule components during heat stress (HS).…
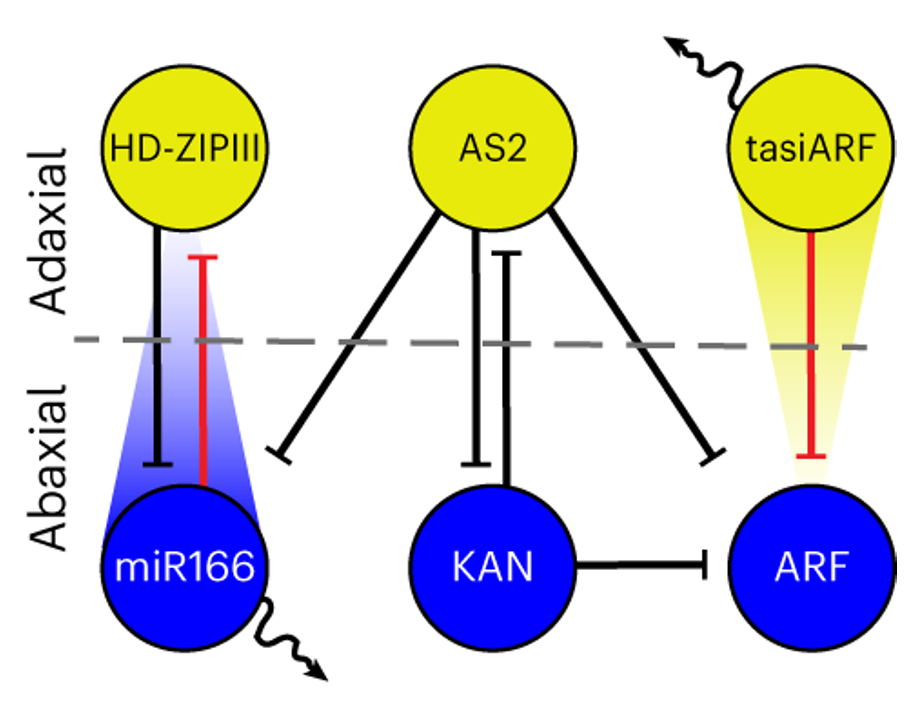
A diffusible small-RNA-based Turing system dynamically coordinates organ polarity
The establishment of adaxial-abaxial polarity during the growth of the leaf primordium is a prerequisite for the formation of the flat, thin leaves observed in most (but not all) plants. The micro-RNAs tasiARF and miR165/6, which form concentration gradients within leaf primordia, are major contributors…
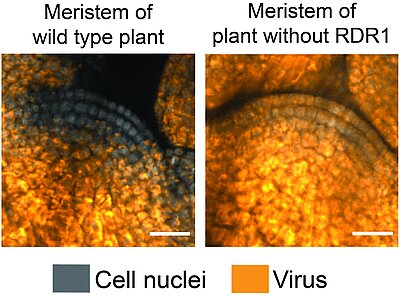
Mechanism by which viruses are excluded from plant stem cells
Horticulturalists have long used the technique of meristem culture to propagate plants, as meristems are generally considered to be free of viruses. However, the mechanism by which the stem cells in meristems exclude viruses has been unclear. Here, Incarbone and Bradamante et al. identified roles for…

Review: Improving RNA-based crop protection through nanotechnology and insights from cross-kingdom RNA trafficking
The German physician Paul Ehrlich (not to be confused with the American scientist of the same name) coined the term “magic bullet” (zauberkugel) to describe something that is perfectly and accurately effective. As much as we dream of magic bullets, they are rarely found, but the idea of using spray-on…

Small RNAs and nutrient deprivation in Chlamydomonas
Li et al. find a class of small RNAs that might affect algal tolerance to nutritional stress.
Yingshan Li and Heriberto Cerutti - School of Biological Sciences and Center for Plant Science Innovation, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, NE 68588-0666, USA
Background: Noncoding RNAs are not translated…
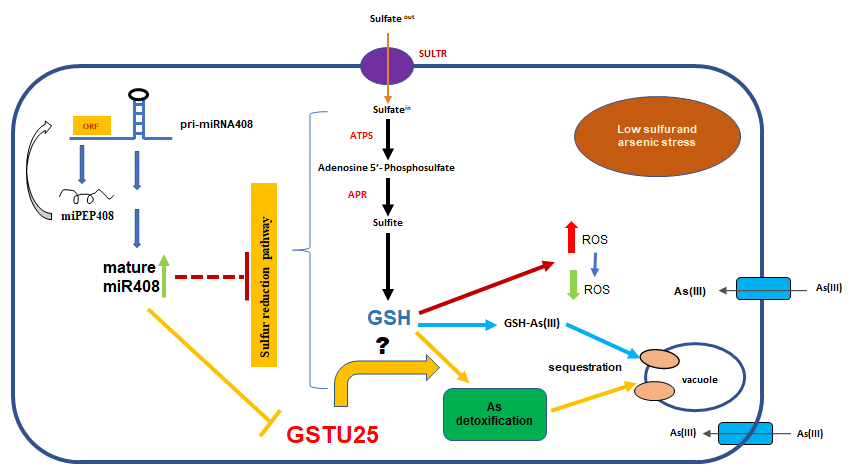
MicroRNA encoded peptide affects arsenic sensitivity
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that down-regulate their targets through translational repression or mRNA cleavage. Some pri-miRNAs encode small regulatory peptides (miPEP) which regulate plant growth and development by modulating subsequent miRNA expression. How different biotic or abiotic…
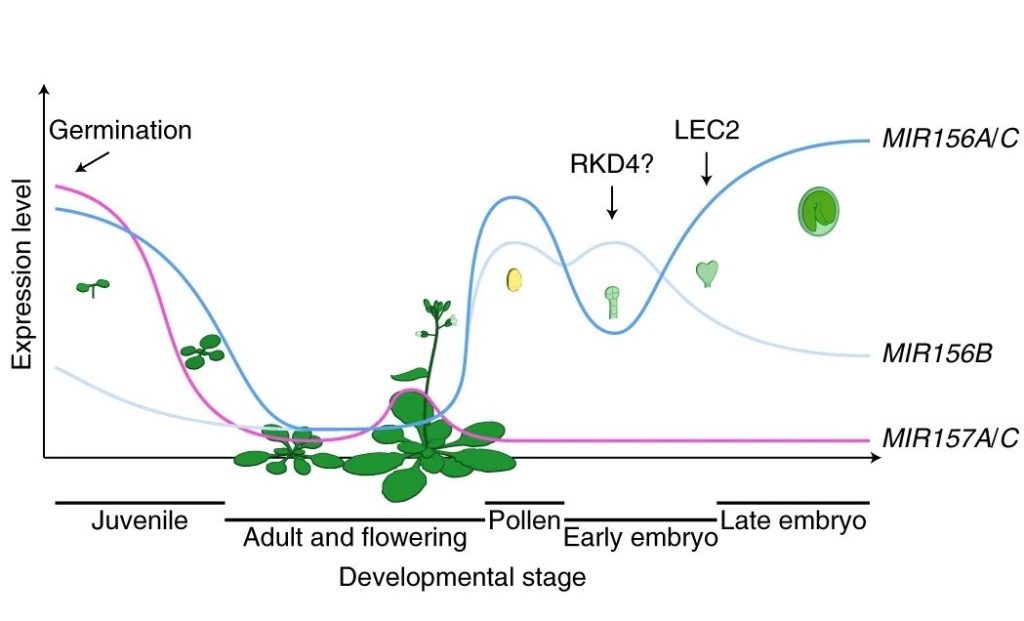
A robust mechanism for resetting juvenility during each generation in Arabidopsis (Nature Plants)
Proper development requires an aging program that is regulated throughout the entire lifespan of an organism as well as across generations. In plants, reproductive cells are derived from differentiated cells, and thus the aging program encoded in these reproductive cells must be rejuvenated per generation.…
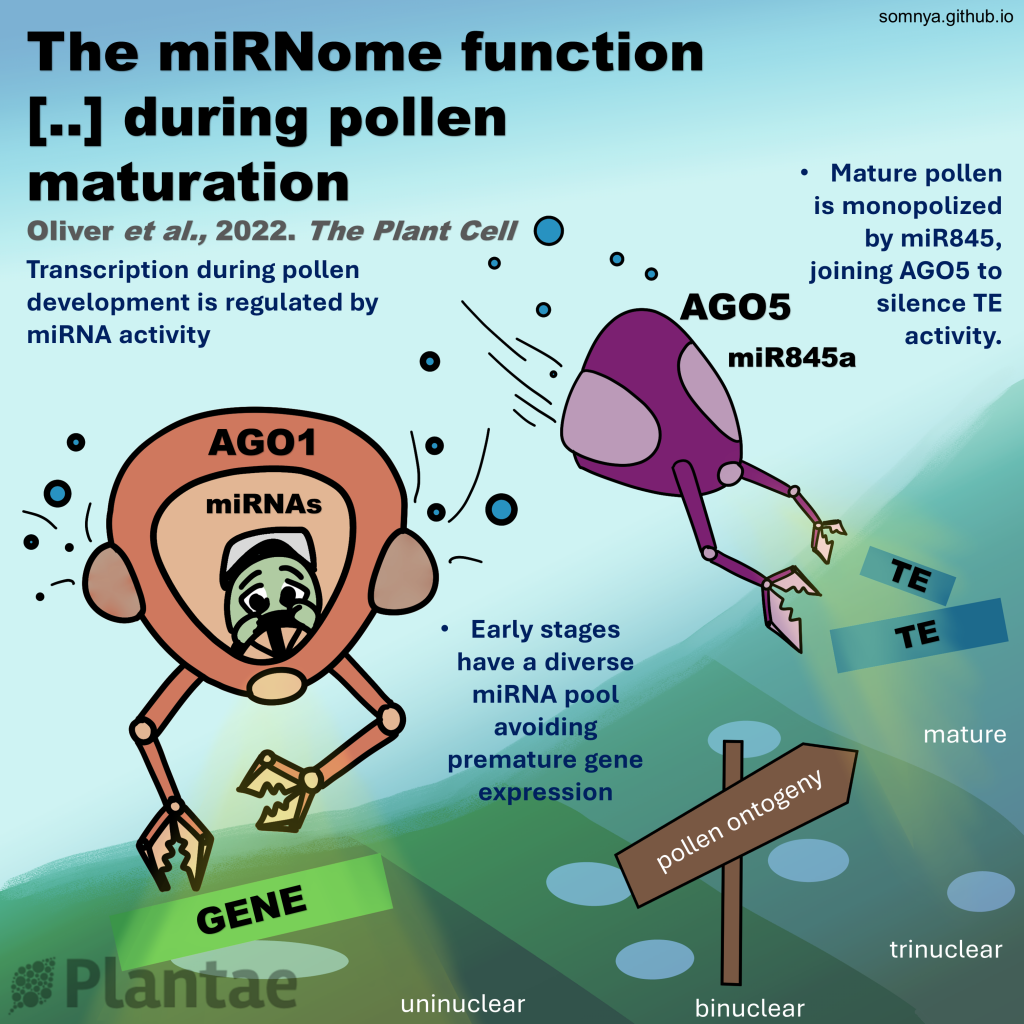
The miRNome function transitions from regulating developmental genes to transposable elements during pollen maturation (Plant Cell)
Genes (protein-coding or noncoding) and transposable elements (TEs) are the main characters in the genomic landscape, but there are few reported systems where we have seen all acting together to produce a phenotype. Oliver and collaborators analyzed miRNA populations during pollen maturation in an outstanding…
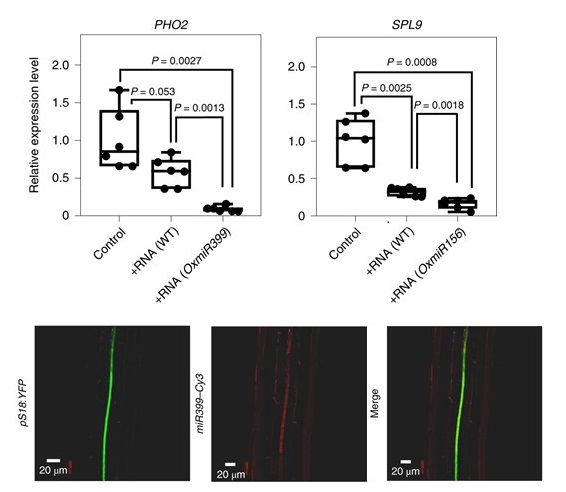
Exogenous miRNAs induce post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants (Nature Plants)
Small RNAs (sRNAs) are 21- to 24-nucleotide non-coding RNAs that induce gene silencing by targeting specific mRNAs for degradation. They regulate a plethora of developmental and physiological processes. Based on their biogenesis they are classified into two groups: micro-RNAs (miRNAs) and siRNAs. Within…

