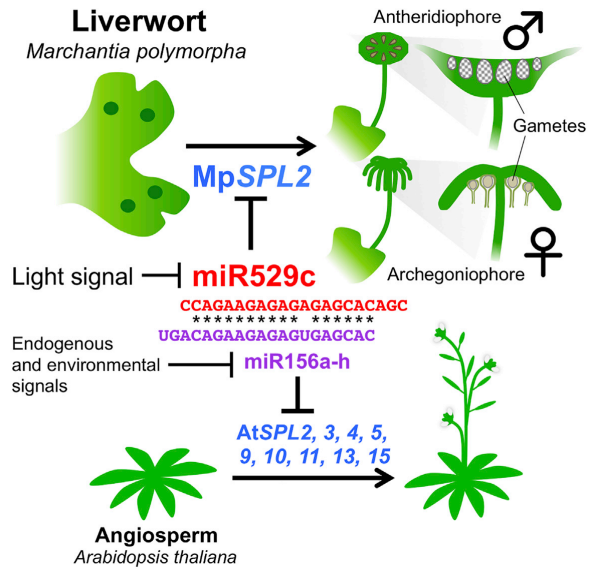
Early origin of miRNA-SPL module in reproductive development revealed by liverwort (Curr. Biol)
In Arabidopsis and other angiosperms, transition to flowering is controlled by a regulatory module that includes transcription factors from the SPL family and a miRNA miR156 targeting them. Marchantia and bryophytes do not make flowers, but there is an equivalent module that includes miR529c and a single…

Update. GMO-free RNAi: exogenous application of RNA molecules in plants (Plant Physiol)
Criticism of transgenic plants and GMOs motivates research into effective GMO-free RNA delivery methods. In this review, Dalakouras et al. discuss different strategies for exogenous application of RNA molecules (dsRNAs, siRNAs) into plants to trigger RNA interference (RNAi) against various targets, such…
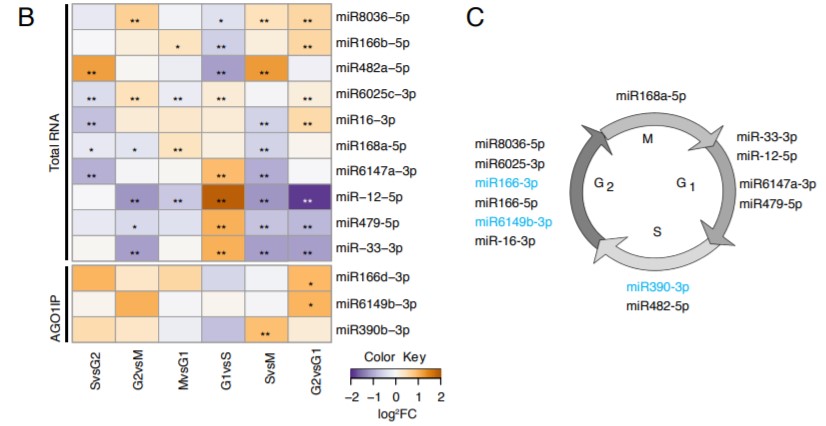
Cell cycle dependent regulation and function of ARGONAUTE1 in plants (Plant Cell) ($)
Regulation of gene expression at transcriptional, translational and post-translation levels is crucial for proper plant growth. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by small RNAs like microRNA (miRNA), siRNA and phasi-RNAs is necessary for meristem maintenance in plants. Unlike in the mammalian system,…
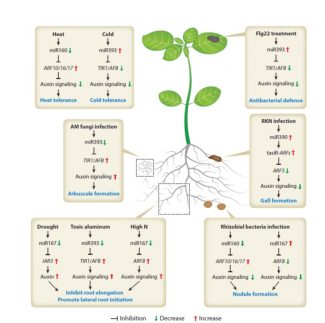
Review: MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plant–environment interactions (Annu Rev Plant Bio) ($)
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate the expression of target genes through mRNA cleavage, translational repression and DNA methylation. The last decade has seen an exponential increase in the studies performed to understand the biogenesis of plant miRNAs, their…
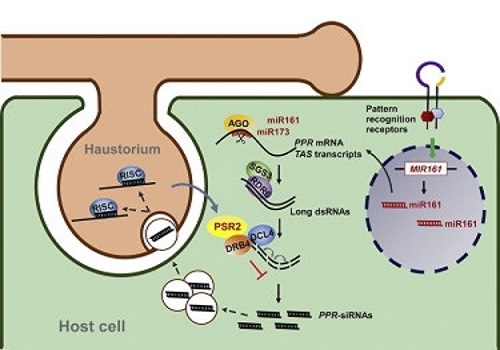
Plant-pathogen arms race: A pathogen effector protein inhibits trans-kingdom RNAi (Cell Host & Microbe)
Phytophthora spp. are highly aggressive fungus-like pathogens that cause various blight and rot diseases in many crops. Upon invasion of host cells, Phytophthora delivers thousands of effector proteins. Some of these effectors suppress the host RNA silencing pathway, which is mediated by a diverse…
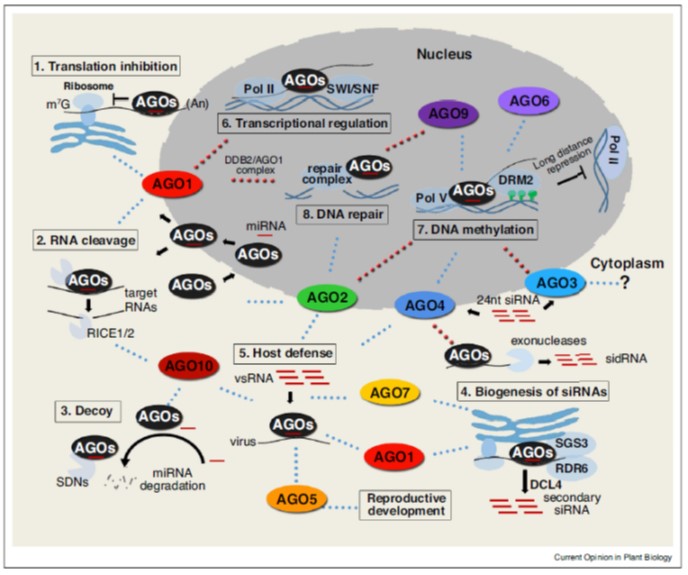
Review. Actions of plant Argonautes: Predictable or unpredictable? (COPB $)
The Arabidopsis genome encodes nine Argonaute proteins and an AGO pseudogene. The nine functional proteins fall into three clades based on sequence. Ma and Zhang update what we know about these proteins. It turns out, the simple assumptions made early on have not entirely been borne out. For example,…
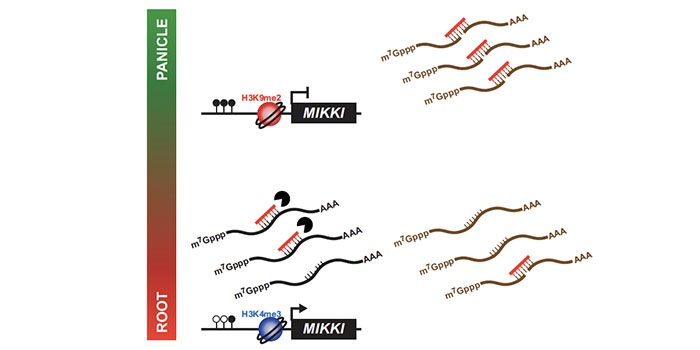
Regulation of rice root development by a retrotransposon acting as a microRNA sponge
Transposable elements are known to affect their neighboring genes, but they were so far unknown to affect the function of distant genes. Cho and Paszkowski observed a high level of transposon transcription expressed in rice. A transposon with root specific expression, MIKKI, was found to contain an imperfect…

