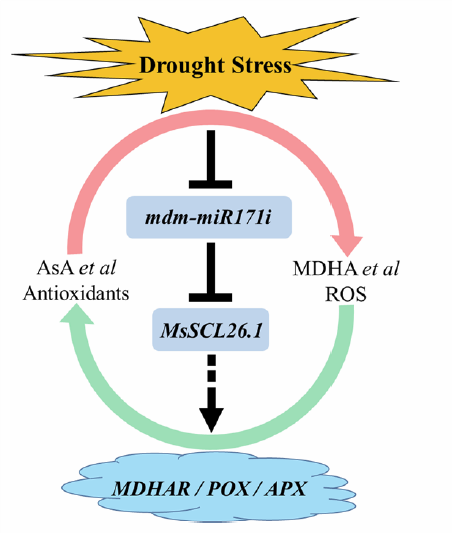
The Apple miR171i and its target SCL26.1 enhance drought tolerance (Plant Physiol.)
Drought is one of the most important abiotic factors affecting plant growth and development. MicroRNAs are a class of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) consisting of 21-24 nucleotides, that play critical roles in many biological processes by regulating target gene expression. Apple is one of the most economically…

Plant 22-nt siRNAs mediate translational repression and stress adaptation (Nature)
Among the myriad small interfering RNAs, 21- and 24-nucleotides siRNAs control plant development and immunity through mRNA cleavage and RNA-directed DNA methylation, respectively. Still, the regulation and biological function of 22-nt siRNAs remain unresolved. In this report, Wu and coworkers investigated…
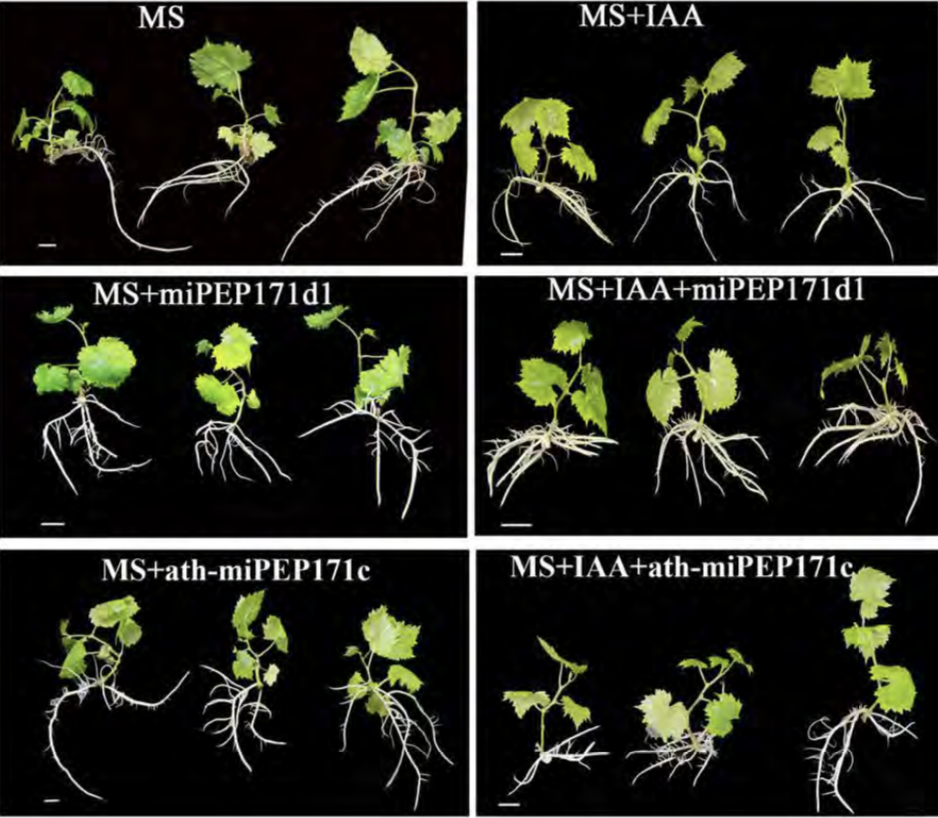
Mystery of adventitious root formation in grapevine (Plant Physiol)
Grapevines (Vitis vinifera L.) are clonally propagated by stem cuttings, which depends on the formation of adventitious (stem-borne) roots. In this paper Chen at al., showed the function of microRNA encoded peptides (miPEPs) in adventitious root formation of cultured grape plantlets. MicroRNA biogenesis…
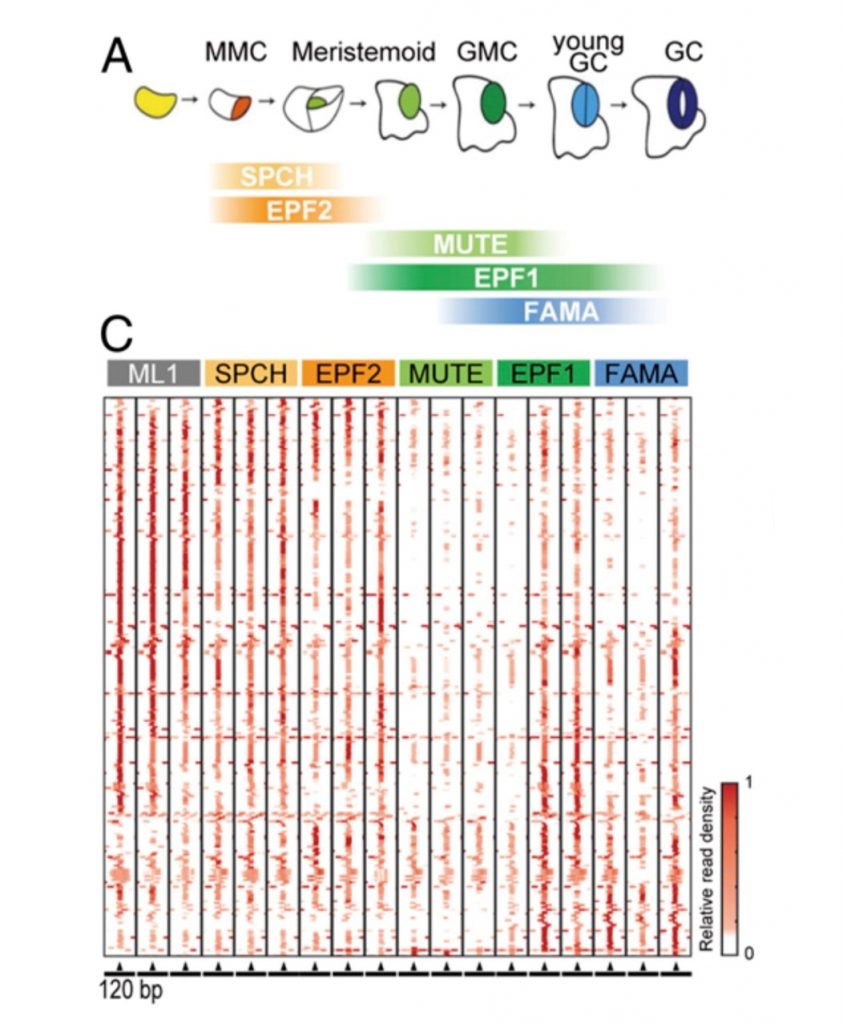
MicroRNAs and the control of stomatal development (PNAS)
Stomata mediate critical functions in plant life: gas exchange, water loss, and some environmental responses. At the molecular level, some bHLH transcription factors and a MAP-kinase pathway control a series of asymmetric and symmetric cell divisions of stomatal stem cells to form a guard cell. In…

Silencing Transposons is Important for Pollen Development in Capsella
Wang et al. reveal that viable pollen formation in Capsella requires the function of a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00938
Background: Transposons, or “jumping genes”, are kept silent by a plant-specific pathway that starts with DNA-dependent RNA…
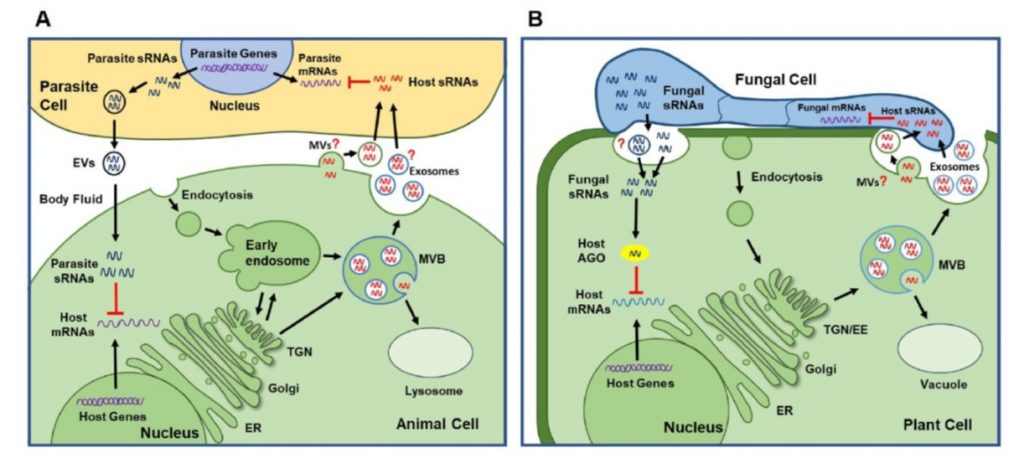
Review. Small RNAs and extracellular vesicles: New mechanisms of cross-species communication and innovative tools for disease control (PLOS Pathogens)
We have only recently begun to appreciate the phenomenon of cross-species or cross-kingdom small RNA transfer, and its applications. Using examples from plants and animals, Cai et al. summarize how some pathogens have evolved the capacity to introduce small RNAs into their host to suppress host defense…
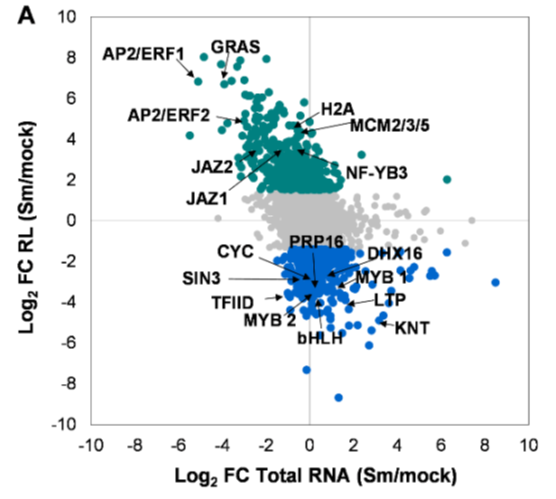
Reprogramming of root cells during nitrogen-fixing symbiosis involves dynamic polysome association of coding and non-coding RNAs (Plant Cell)
Knowing RNA abundance is nice, but in most cases protein abundance is more biologically interesting. Traubenik et al. used TRAP (Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification) to examine efficiency of translation and contributions of non-coding and alternatively spliced RNAs during the establishment…
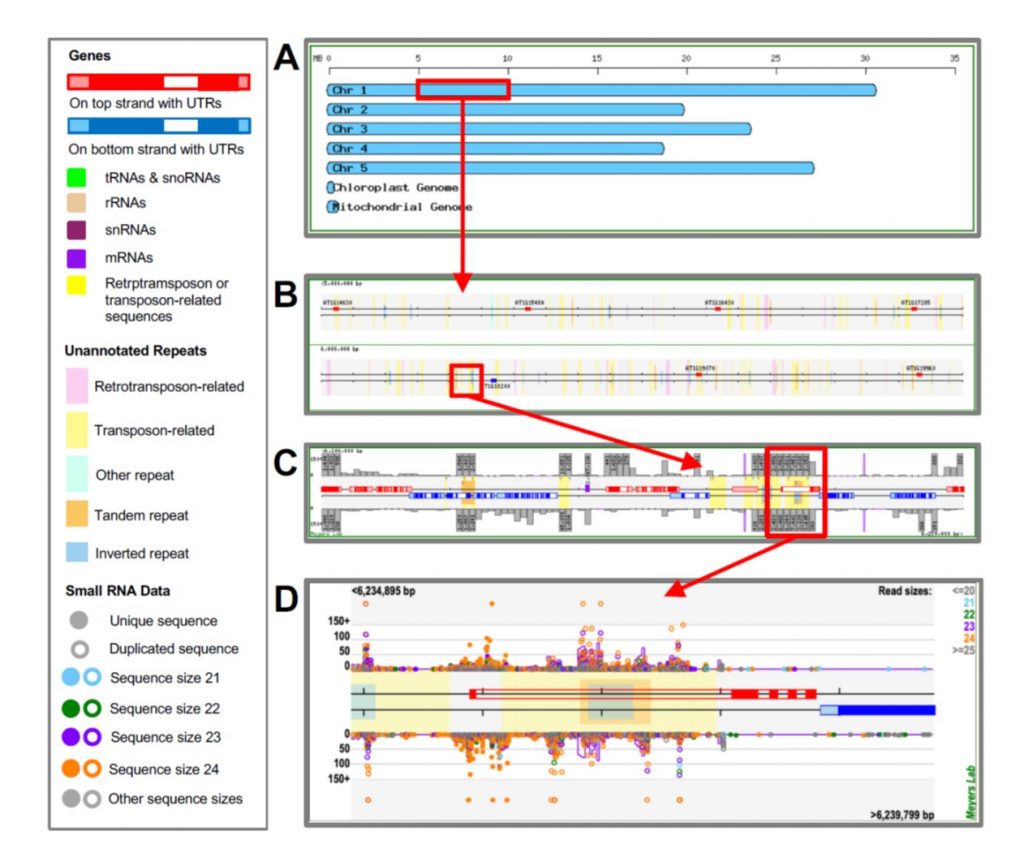
Next-Gen sequence databases: RNA and genomic informatics resources for plants (Plant Physiol)
Drawing on more than 15 years of improvements, Nakano et al. have released public websites and resources for data access, display, and analysis of plant small RNAs, from Arabidopsis to wheat and with many crops and model species represented. The tools can analyze, integrate and display the abundance…
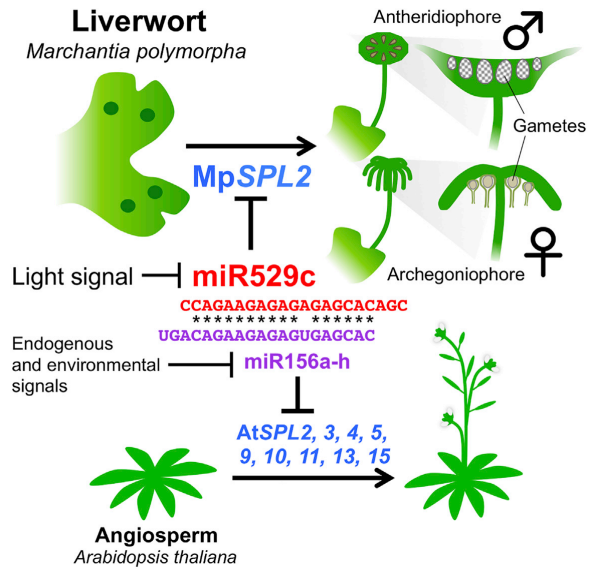
Early origin of miRNA-SPL module in reproductive development revealed by liverwort (Curr. Biol)
In Arabidopsis and other angiosperms, transition to flowering is controlled by a regulatory module that includes transcription factors from the SPL family and a miRNA miR156 targeting them. Marchantia and bryophytes do not make flowers, but there is an equivalent module that includes miR529c and a single…

