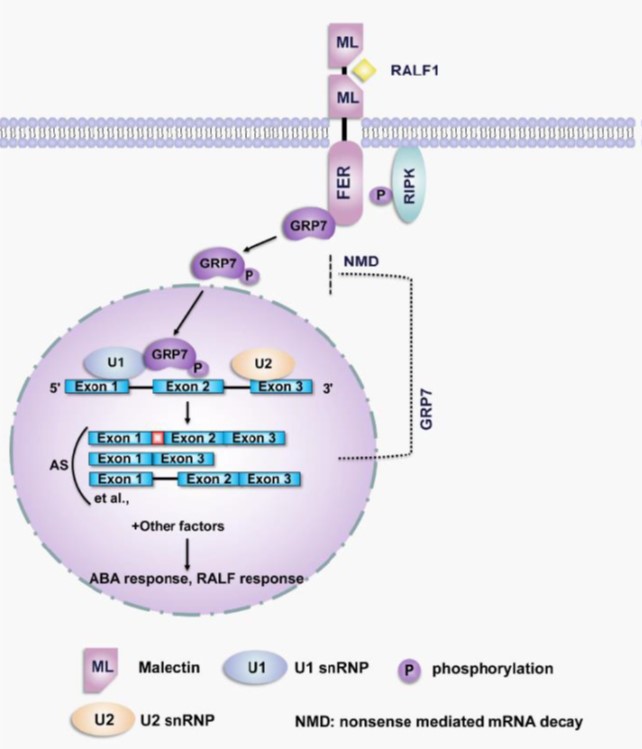
RALF1-FERONIA complex affects splicing dynamics to modulate stress responses and growth in plants (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlternative splicing is a process that can produce two or more transcript isoforms from a single gene and can increase protein diversity. FERONIA (FER) is a receptor-like kinase that serves as a receptor for the rapid alkalinization factor (RALF) peptides that regulate multiple cellular activities in…
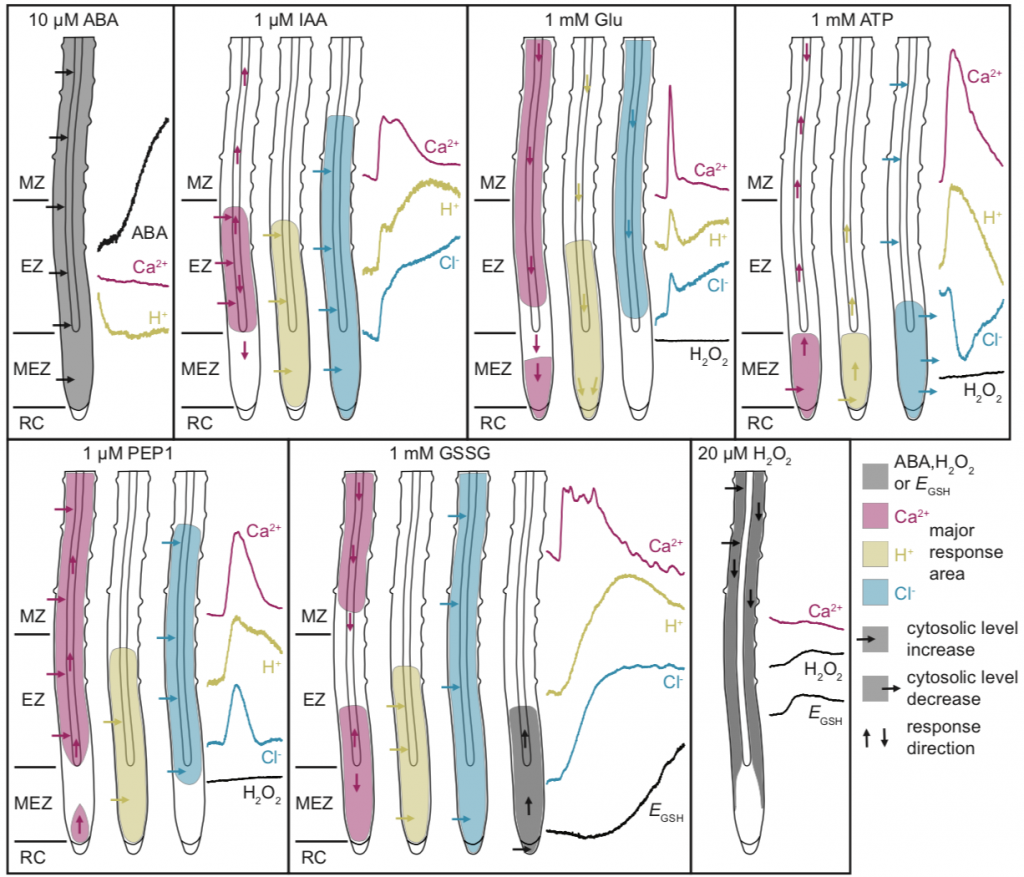
Dual-sensing genetically encoded fluorescent indicators, ABA and second messenger dynamics (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponses to a changing environment require an interplay between primary and secondary messengers. Hormones like abscisic acid (ABA), auxin etc. act as a primary messengers, whereas molecules like Ca2+, reactive oxygen species (ROS), other cations and anions act as a secondary messenger. In this paper,…

The biogenesis of CLEL peptides involves several processing events in consecutive compartments of the secretory pathway (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklySmall signaling peptides are cleaved from precursor proteins by the action of proteases and are also subject to other post-translational modifications. Subtilases (SBT) are mostly extracellular proteases, but SBT6.1 is membrane-localized at the Golgi and plasma membranes. Furthermore, it has been shown…
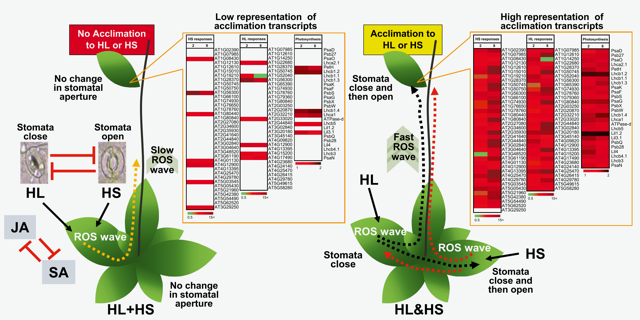
Systemic signaling during abiotic stress combination in plants (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn nature, plants face multiple environmental stresses simultaneously. Plant responses to combined stresses are often not merely the sum of responses to individual stresses; in the tissue that initially perceive stresses (local tissue), plants can integrate different stress signals to elicit unique responses.…
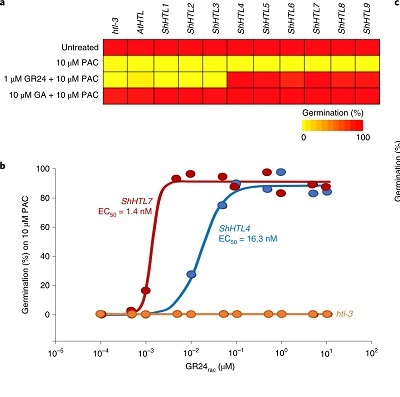
SMAX1-dependent seed germination bypasses GA signalling in Arabidopsis and Striga (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStrigolactones (SL) are germination cues for parasitic plants, as their seeds will not germinate until they perceive SL exuded from the host plant. In contrast, gibberellins (GA) are the dominant germination hormone in non-parasitic plants; GA-mediated degradation of DELLA repressors permits germination.…

STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2 regulates arabidopsis stomatal immunity through phosphorylation of the anion channel SLAC1 ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants detect microbes by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that sense common conserved structures called microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and trigger the innate immunity responses. Chan et al. identified a new player in the Arabidopsis immune response known as STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2…
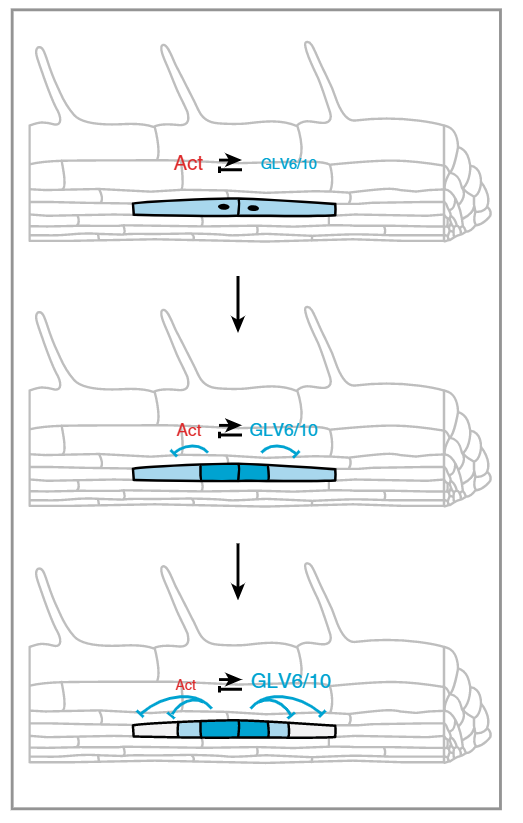
GOLVEN peptide signaling through RGI receptors and MPK6 restricts asymmetric cell division during root initiation (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLateral root starts development starts with an asymmetric cell division in the founder cell. In this study, Fernandez et al. explored the role of peptide signaling this process. The authors started with the previous finding that GOLVEN peptides are involved in lateral root initiation, as overexpression…
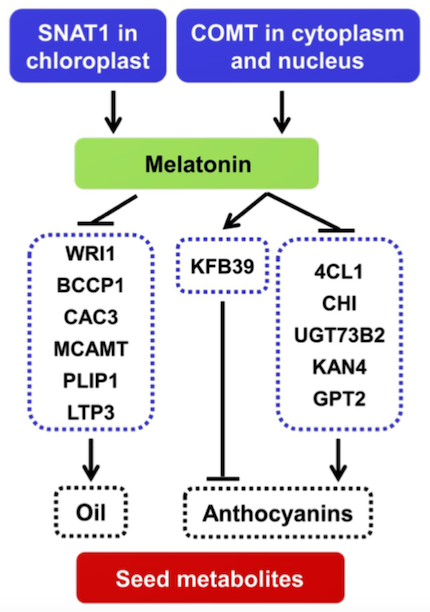
Melatonin represses oil and anthocyanin accumulation in seeds (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed oils and anthocyanins play several roles in plant physiology and are promising substances for crop engineering given their benefits for human health. Recent studies proposed that melatonin –a potent antioxidant present in all plant species– regulates the deposition of these metabolites in seeds,…

MYB30 negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by interacting with PIFs and phytochromes in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotomorphogenesis is the growth and development of plants in response to light. The phytochrome family of photoreceptors absorbs red and far-red light, and in Arabidopsis the most abundant phytochromes are phyA and phyB. PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) repress photomorphogenesis, and under red…

