
COP1 can be hijacked by photoreceptors via their VP motifs (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant development is characterized by a high degree of plasticity in response to light. Light‐activated plant photoreceptors bind and inhibit the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1, thus protecting downstream transcription factors from degradation. However, the detailed mechanisms of how COP1 can function between…
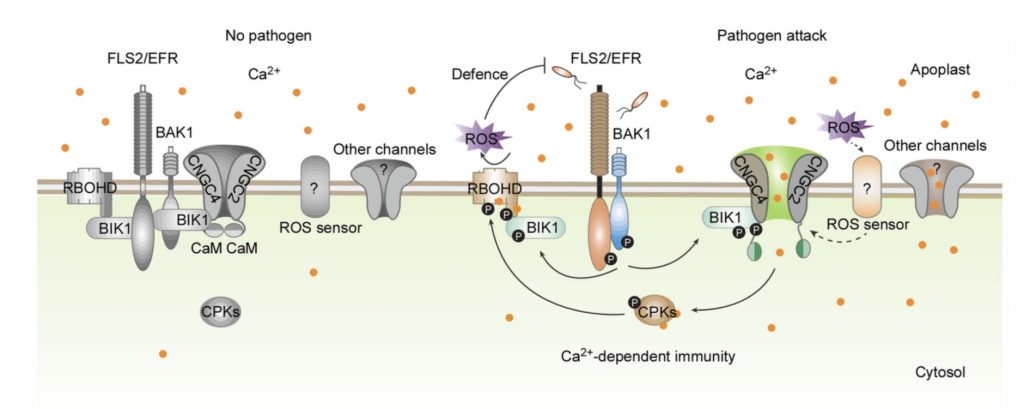
A calmodulin-gated calcium channel links pathogen patterns to plant immunity ($) (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium ions mediate calcium-based defense responses in pattern triggered immunity (PTI) upon detection of pathogen patterns by plant surface receptors. A new study by Tian et al. has elucidated the molecular events that activate the calcium response. The authors show that adequeate calcium nutrient…
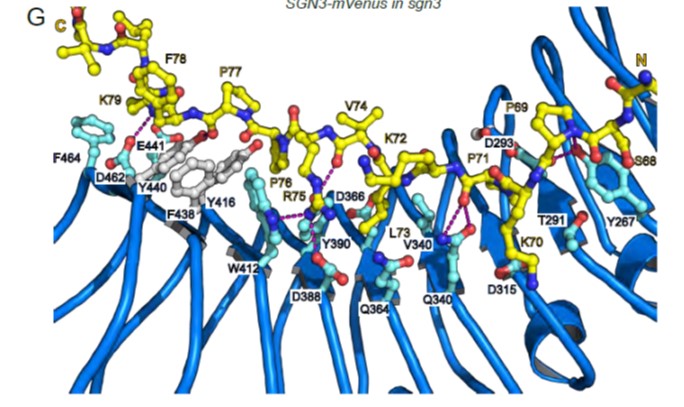
Recognition of sequence-divergent CIF peptides by the plant receptor kinases GSO1/SGN3 and GSO2 (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklySCHENGEN 3 [SGN3, also known as GASSHO1 (GSO1)] is a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase (LRR-RK) previously shown to interact with CIF peptides (CASPARIAN STRIP INTEGRITY FACTORS) to regulate the development of the Casparian strip boundary in roots. Here, Okuda et al. characterize the CIF/LRR-RK interaction.…
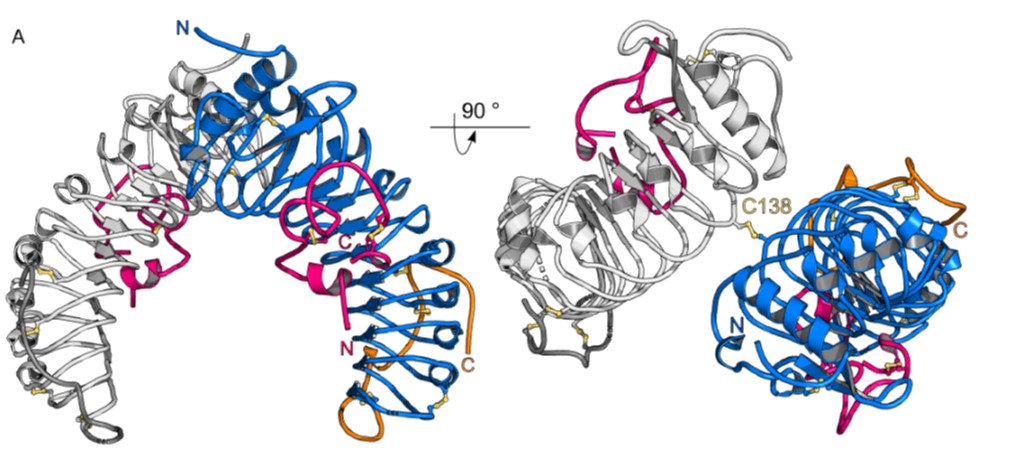
Structural basis for recognition of RALF peptides by LRX proteins during pollen tube growth (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRALFs (Rapid Alkalinization Factors, based on historical observations that they induce alkalization of the extracellular space) are signaling peptides with diverse roles. RALF4 is required for pollen tube growth and guidance through its interactions with CrRLK1Ls and leucine-rich extension (LRX) proteins.…
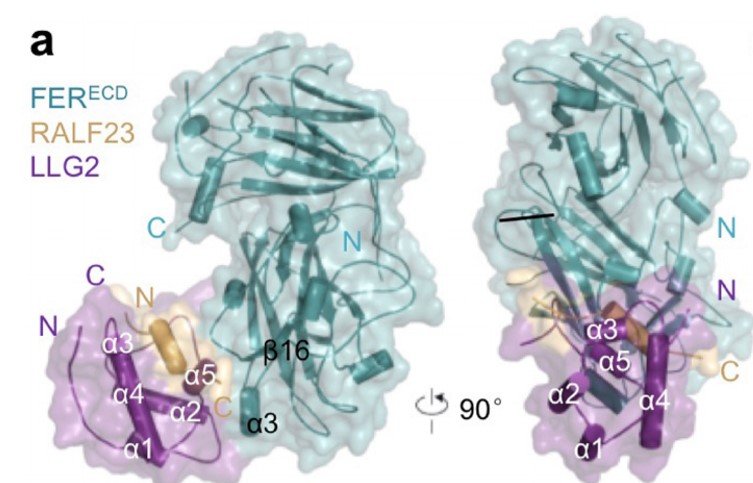
Mechanisms of RALF peptide perception by a heterotypic receptor complex (Nature) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRALFs (Rapid Alkalinization Factors, based on historical observations that they induce alkalization of the extracellular space) are signaling peptides with diverse roles. RALFs have previously been shown to bind to the extracellular domain of (among others) FERONIA (FER), a member of the Catharanthus…
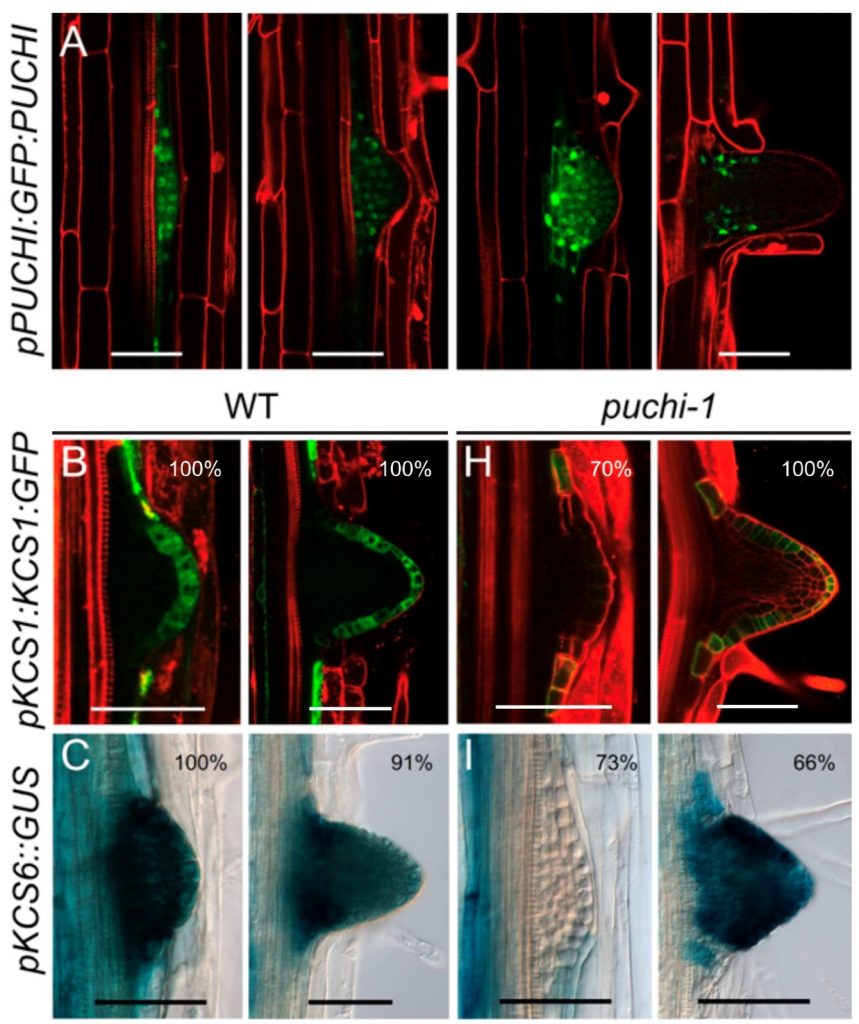
Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are involved in lateral root formation (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot branching determines the spatial organization of the root and its interaction with the soil. The emergence of lateral roots (LR) is controlled by a complex regulatory network, involving genetic, hormonal and mechanical factors. In this study, Trinh et al. got new insights about PUCHI, a transcription…

Pipecolic contributes to systemic acquired resistance in barley ($) (MPMI)
Plant Science Research WeeklySystemic acquired resistance (SAR) is a robust long-distance immune response mediated by a diverse contingent of candidate phloem-mobile signals that prime distal uninfected tissues for enhanced resistance to future infections. The lysine-derived catabolite pipecolic acid (Pip) has emerged as a key mediator…
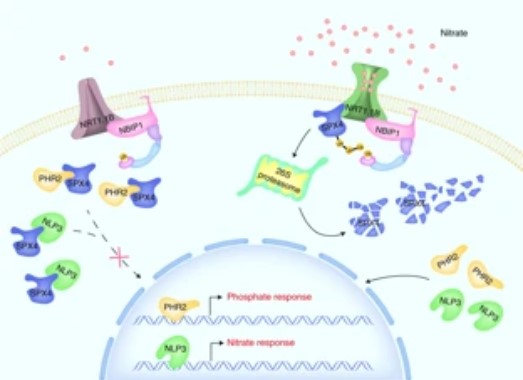
Nitrate–NRT1.1B–SPX4 cascade integrates N and P signaling networks (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need several mineral nutrients for their optimal growth and development. This is contingent on a proper nutrient balance particularly between the two most required essential elements, nitrogen (N) and phosphorus. Even though considerable success has been achieved in understanding the molecular…

