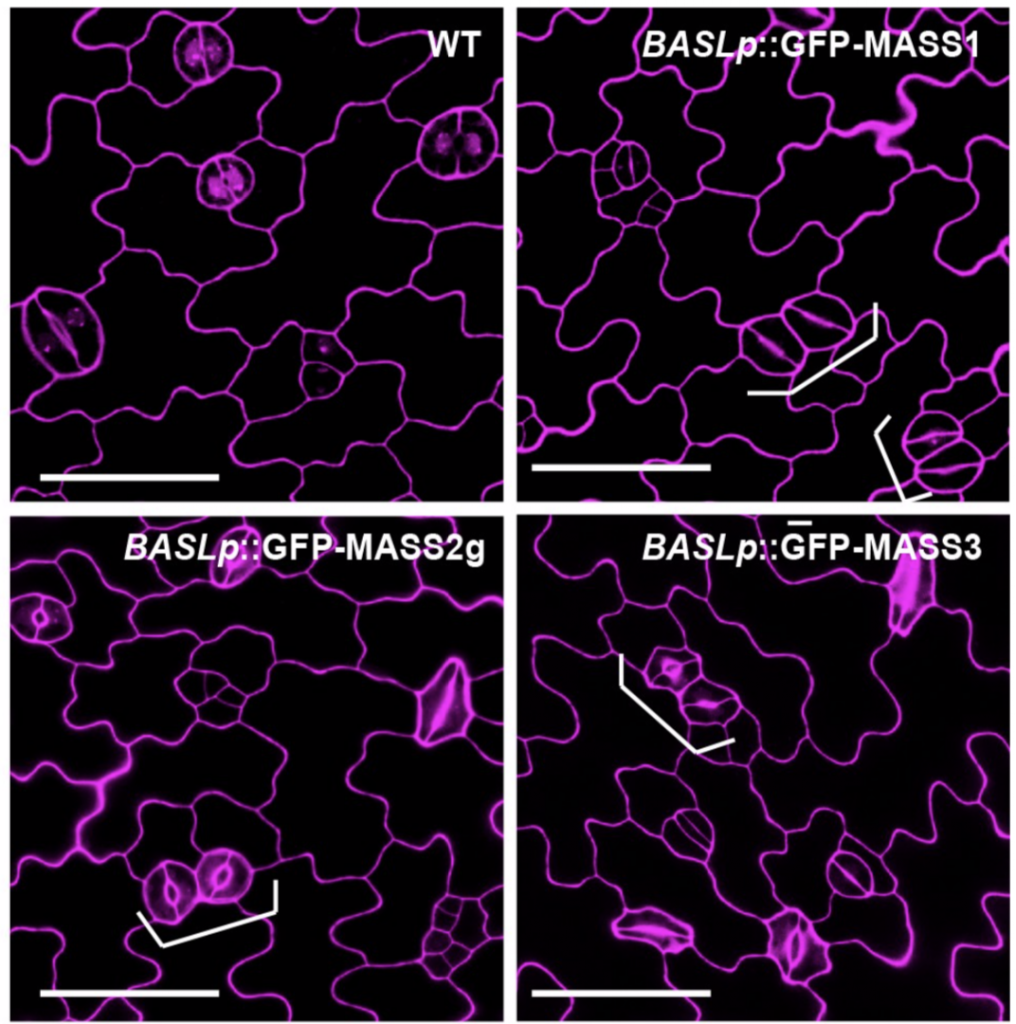
MASS proteins and stomatal development in Arabidopsis (PLOS Genetics)
Stomata are the pores surrounded by a pair of guard cells on the plant epidermis that help in gaseous exchange. The number and spacing of stomata are regulated by a series of phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation events of key transcription factors through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)…

Interplay between phosphorylation and ubiquitination is key for regulating reactive oxygen species during plant immunity (Nature Comms)
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential secondary messengers for rapid transmission of local and long-distance signalling in plants. Respiratory oxidase homologs (RBOHs) are the family of enzymes in plants that produce extracellular ROS, with RBOHD being the primary oxidase in Arabidopsis for ROS…
A regulatory module for survival on low potassium (Nature Plants)
Potassium ions (K+) play a variety of important roles in plant physiology and are maintained at a high concentration in the cytosol relative to the available K+ in the environment. Potassium may accumulate to an even higher concentration in the vacuole, where it helps to regulate turgor pressure. During…
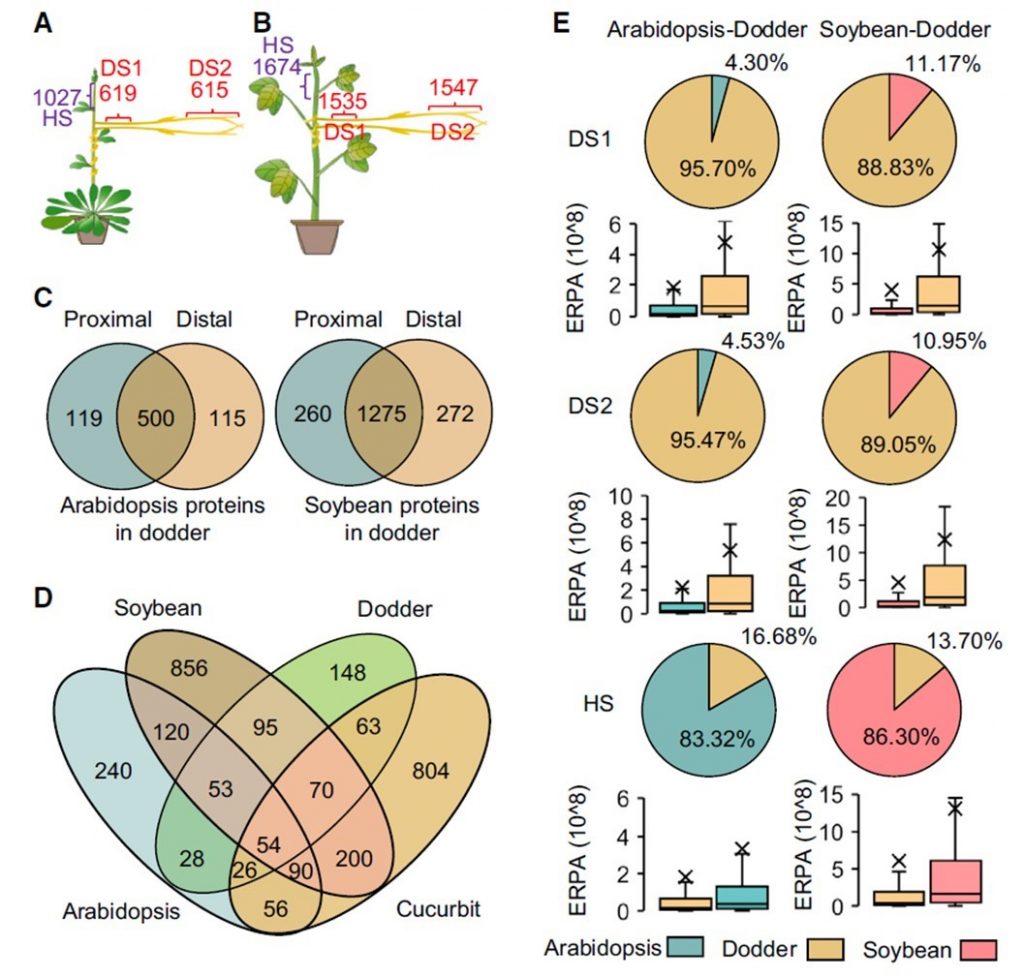
Extensive inter-plant protein transfer between Cuscuta parasites and their host plants (Mol. Plant)
Cuscuta (dodders) are parasites that survive on other host plants.Liu et al. found more than 1500 proteins are transferred between Cucuta and host plants forming a sort of interplant chemical communication. Furthermore, proteins could move between two hosts that are connected by dodder bridges, and retain…

miRNA-mediated lateral inhibition controls rhizoid cell patterning in Marchantia polymorpha (Curr. Biol.)
In multicellular organisms, the patterning of different cell types in spatial arrays is regulated through several mechanisms, one of which is lateral inhibition, a process well characterized in metazoans. In this process, an individual cell transmits signals to neighboring cells to instruct a different…
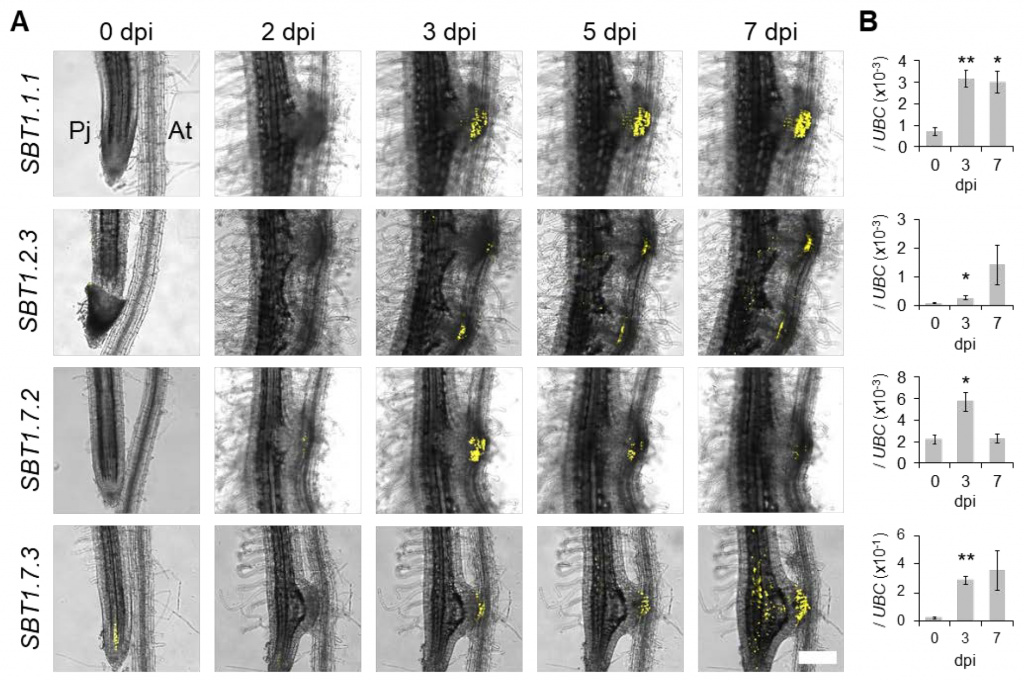
Subtilase activity in intrusive cells mediates haustorium maturation in parasitic plants (bioRxiv)
Parasitic plants develop unique structures called haustoria that penetrate into the host plant vasculature, from which they take nutrients. During this process, haustorial epidermal cells differentiate into specialized cells called intrusive cells, which eventually re-differentiate into a xylem bridge…

Review. Twenty years of CBL-CIPKs: The knowns and the unknowns (Trends Plant Sci)
What are the chances that homologs of a vital animal protein could be found in plants, and how much structural and functional similarity would they share? These questions led to the discovery of Calcineurin B-like (CBL) and CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK) protein families in plants. In this review,…
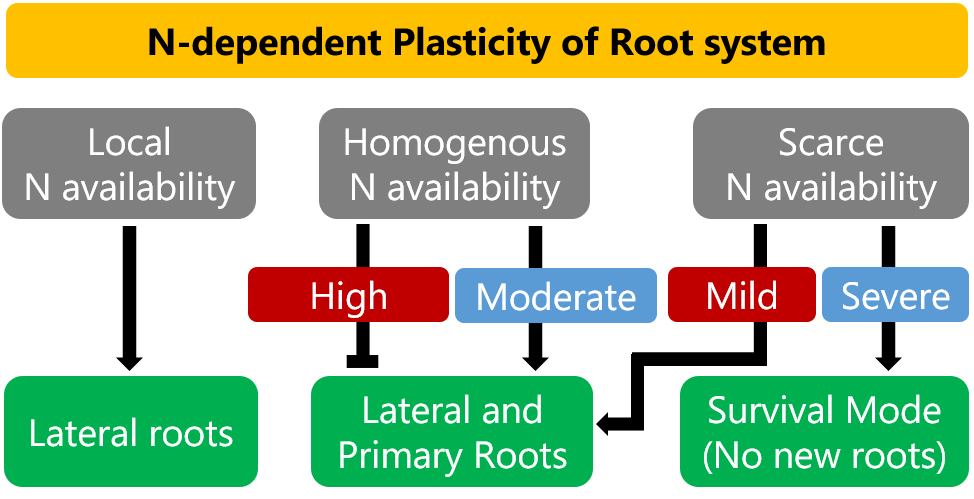
Review. Signalling pathways underlying nitrogen-dependent changes in root system architecture: from model to crop species (J. Exp. Bot.)
Nitrogen (N) is one of the seventeen essential nutrients for a plant to complete its life cycle and is one of the most important determinants of productivity of various crops globally. Nitrate (NO3‑) and ammonium (NH4+) are the major plant-available forms of N. The spatiotemporal heterogeneity of N…
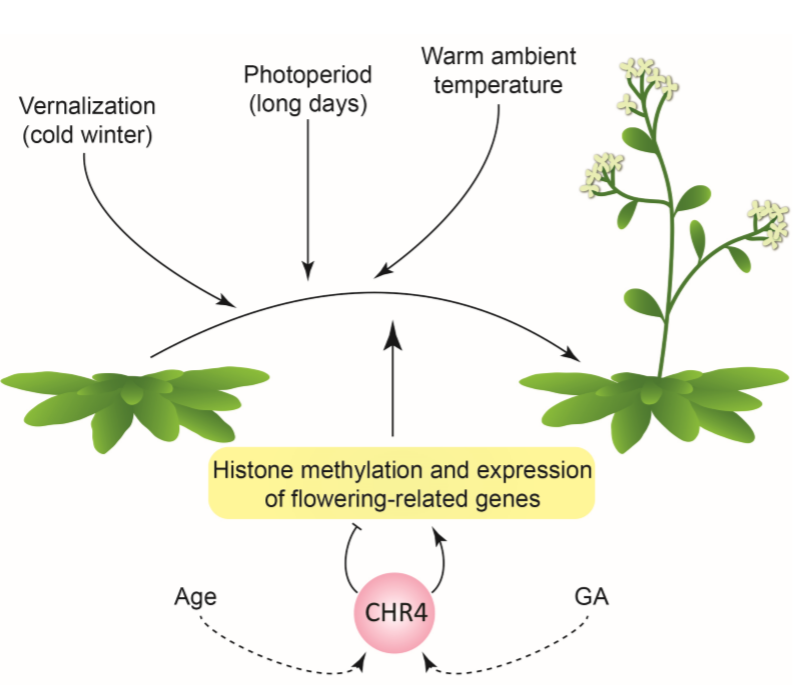
Roles for CHROMATIN REMODELING 4 in Arabidopsis floral transition (Plant Cell)
The time at which flowers appear is critical for plant reproductive success. As such, the vegetative to reproductive growth transition is governed by several cues: environmental (photoperiod, temperature) and endogenous (gibberellins, age). Here, Sang et al. used an elegant forward-genetics approach…

