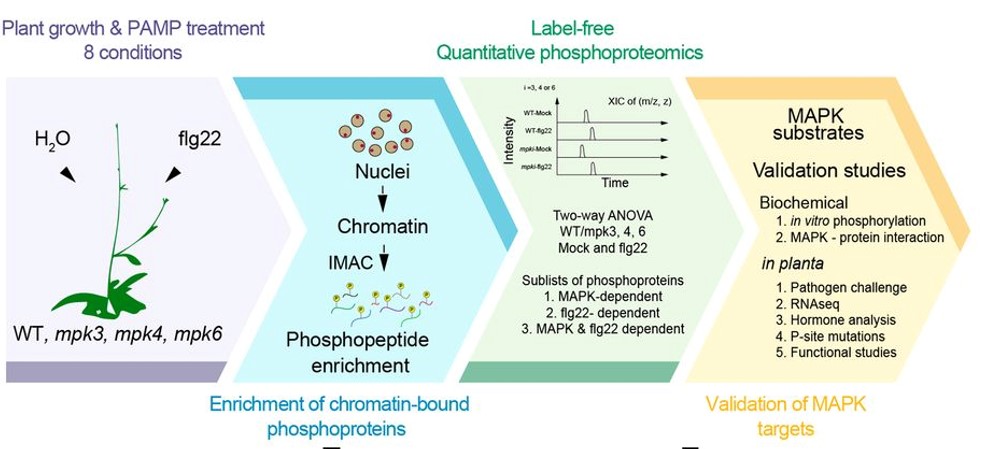
Chromatin phosphoproteomics identifies an AT-hook motif protein involved in PAMP-triggered immunity (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are conserved protein kinases in eukaryotes that participate in signaling from cytoplasmic to chromatin events to allow transcription reprogramming. MAPKs play prominent roles at the chromatin level. Rayapuram et al. report a chromatin-associated phosphoproteome…
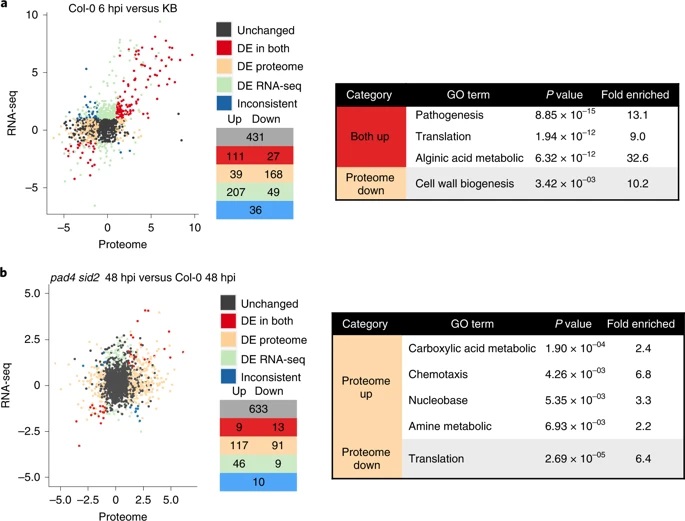
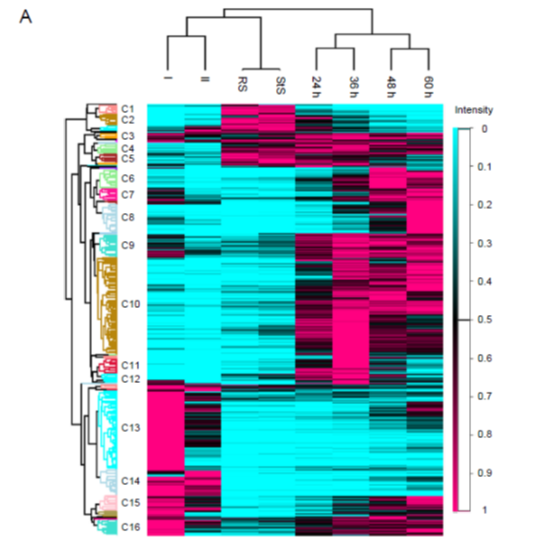
Multidimensional gene regulatory landscape of a bacterial pathogen in plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe outcome of a plant-bacteria interaction is determined by the bacterial virulence and plant immune systems. Individually, these systems, and to an extent their interactions, have been well studied. However, certain aspects of their interactions remain elusive, particularly how plant immunity affects…
A New Plant Component of the Conserved Machinery for Cellular Trafficking
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellGarcia et al. discover a plant-specific component of TRAPP membrane trafficking complexes with important roles in plant development. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00044.
By Veder Garcia and Zhi-Yong Wang
Department of Plant Biology, Carnegie Institution for Science, Stanford, CA
Background:…

Tissue-resolved multi-omics atlas of Arabidopsis (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArabidopsis as a model system has been intensively studied over the past twenty years, but the proteome of Arabidopsis has been less well characterized. Here, Mergner et al. report the first 30-tissue-type integrated proteome, phosphoproteome and transcriptome atlas of Arabidopsis. The data cover the…
Identification of low-abundant lipid droplet proteins in seeds and seedlings (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability of seeds to pack nutrients into dense stable capsules transformed plants’ and animals’ ability to thrive on land (imagine getting through your day without eating any foods derived from seeds or animals that eat seeds). Within many seeds, nutrients are packaged in lipid droplets, with…
Part of the Stack; How Does a Protein Know its Place?
Research, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellParsons et al. successfully separate early to late Golgi cisternae to reveal the sequential localization of resident proteins and the sequence features that guide transmembrane proteins within the Golgi stack. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00081
By Harriet T. Parsons (University of Cambridge)…
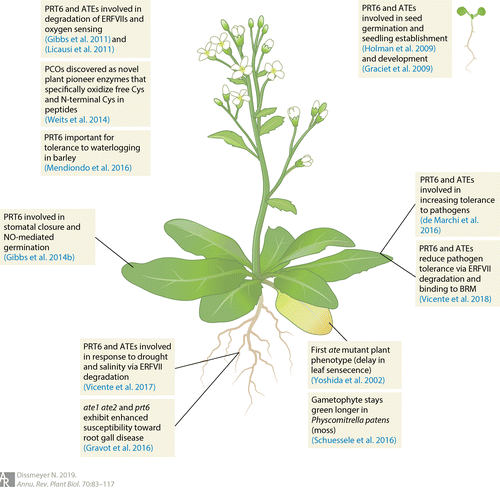
Review: N-degron pathway-mediated proteostasis in stress physiology (Annu Rev Plant Biol)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The rate of most biological processes is ultimately determined by protein activity levels, which of course are determined by rate of degradation or inactivation as well as production. Dissmeyer reviews the Cys/Arg branch of the N-degron pathway (previously called the N-end rule pathway) that contributes…

MapMan4: A refined protein classification and annotation framework applicable to multi-omics data analysis (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRevolutions in omics technologies have rapidly increased the number of plant genomes, transcriptomes and proteomes available. However, protein sequences need to be assigned a biological function to provide useful insights for comparative genomics and transcriptomics. Here, Schwacke et al present MapMan4,…

Updates on Resources, Software Tools, and Databases for Plant Proteomics in 2016–2017 ($) (Electrophoresis)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProteomics, like metabolomics research, depends on the mass-spectrometry tools. Data processing, protein annotation, statistical and data analysis, as well as visualization are often the hurdles in obtaining meaningful biological insights from high throughput datasets. To this end, the author has summarized…

