
Plastid stress signaling alters cell cycle progression (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The chloroplast is in constant communication with the nucleus via so-called retrograde signaling. This signaling, which can take many molecular forms, is important for maintaining chloroplast function. In this paper by Duan et al. we learn that interfering with plastid DNA replication, either through…
Synthetic conversion of leaf chloroplasts into carotenoid-rich plastids reveals mechanistic basis of natural chromoplast development (PNAS) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiofortification aims at increasing the content of health-promoting nutrients in edible parts of the plant. As an example, enhancing the production of carotenoids - natural pigments that provide the yellow to red color – in crops could prevent vitamin A deficiency in humans. In nature, carotenoids…

How to transfer lipids from one membrane to another during thylakoid biogenesis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe thylakoid membranes are located in the stroma of chloroplasts and house the machinery for the photosynthetic light reactions. They emerge largely de novo during the transition from pro-plastids into mature, photosynthesizing chloroplasts. Generating new thylakoid membranes requires a supply of lipids,…
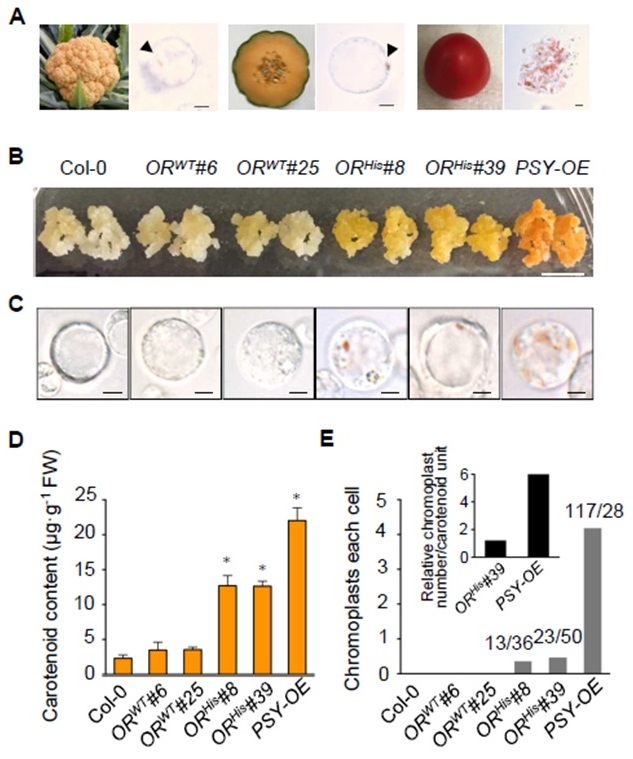
A natural variant of ORANGE interacts with plastid division factor ARC3 to regulate chromoplast number and carotenoid accumulation (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome “superfoods” have high nutritional value due to the presence of carotenoids, which prevent degenerative diseases like cancer. In plants, these pigments are biosynthesized and stored by plastid organelles called chromoplasts. Chromoplast number and size define total carotenoid accumulation. ORHis,…
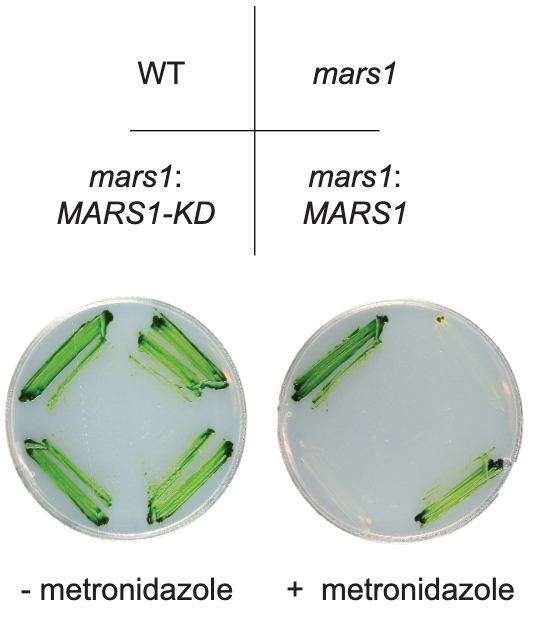
Mars1 kinase signaling in the chloroplast unfolded protein response (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn stressful situations, such as high light and nutrient scarcity, the chloroplast may experience increased proteotoxicity due to a surge in damaging reactive oxygen species. In response, a signal is sent to the nucleus to increase production of many proteins, including proteases and chaperones to help…

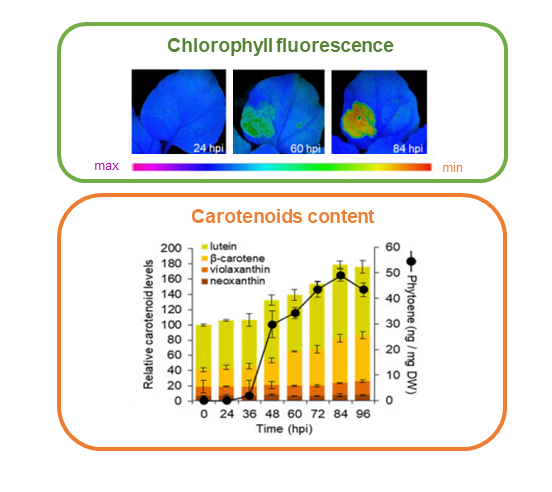
Synthetic biogenesis of chromoplasts from leaf chloroplasts (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChromoplasts are a type of plastid, usually found in fruits and flowers, that can accumulate large amounts of carotenoids including beta-carotene (pro-vitamin A). It has been proposed that increasing chromoplast formation could be a way to enhance human consumption of vitamin A. In a new report, Llorente…

