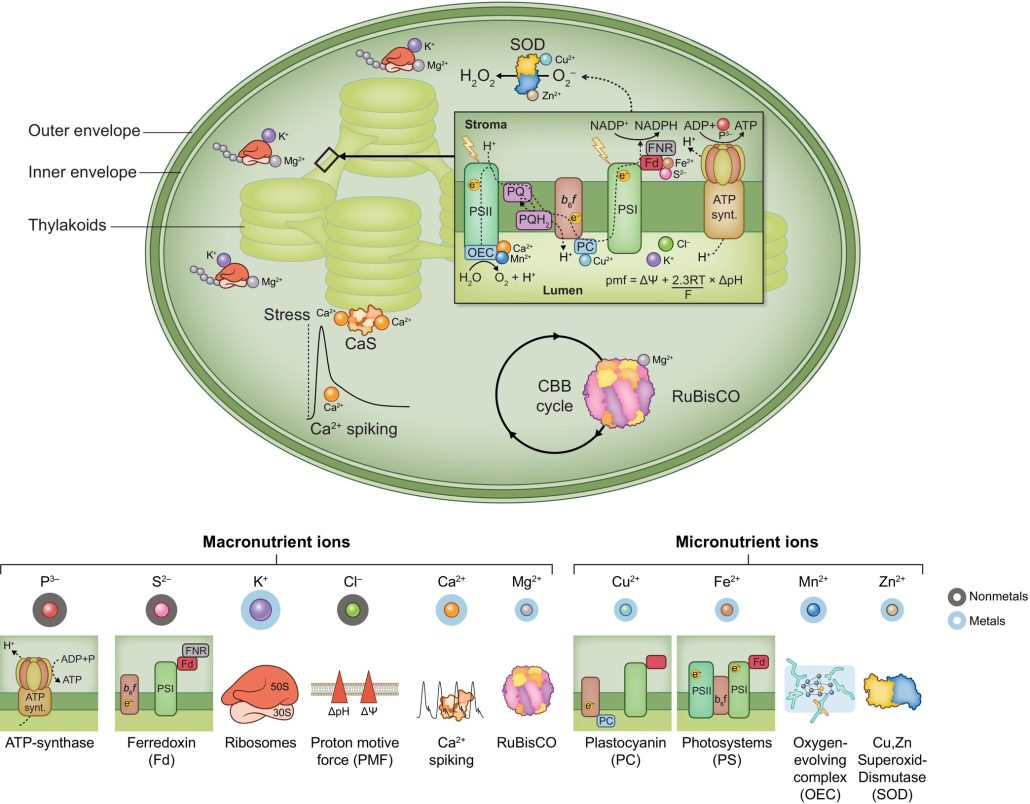
Review: Chloroplast ion homeostasis
Plant Science Research WeeklyHealthy plants require access to several mineral nutrients, which are usually taken up in ionic form. The details of nutrient uptake, distribution, and function have been painstakingly revealed over several decades. In this excellent new Tansley Review, Kunz et al. provide an overview of ion homeostasis…
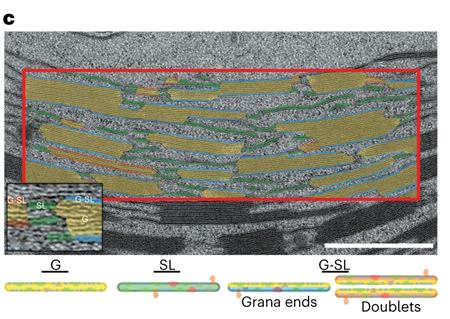
Thylakoid membrane remodelling during the dark-to-light transition
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the dark, plants modify thylakoid stacking to alter electron transport and reduce photodamage. More photosystem II (PSII) is located in thylakoids within stacked grana, which promotes cyclic electron transport. Upon light exposure, there is granal unstacking, which increases the amount of linear electron…
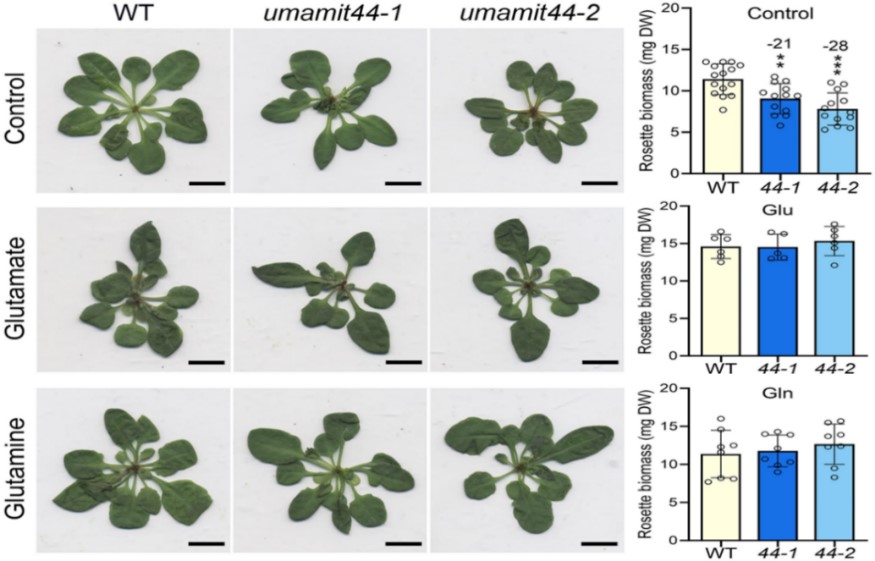

UMAMIT44 exports plastidial glutamate and is essential for plant growth
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmino acids (AA) are fundamental components of peptides, proteins, and enzymes that play a critical role in plant growth, cellular metabolism, and stress response. Plants synthesize most AA within chloroplasts and require membrane transporters to transfer them from stroma to cytosol. Cytosolic AA are…

Altering chloroplast biogenesis leads to increased yields in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyTranscription of chloroplast genes is carried out by the plastid encoded polymerase (PEP) with help from PAPs (PEP-associated proteins). PAP3 is important for chloroplast development in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana, however its role in crops has not been fully elucidated. Here Seo et…
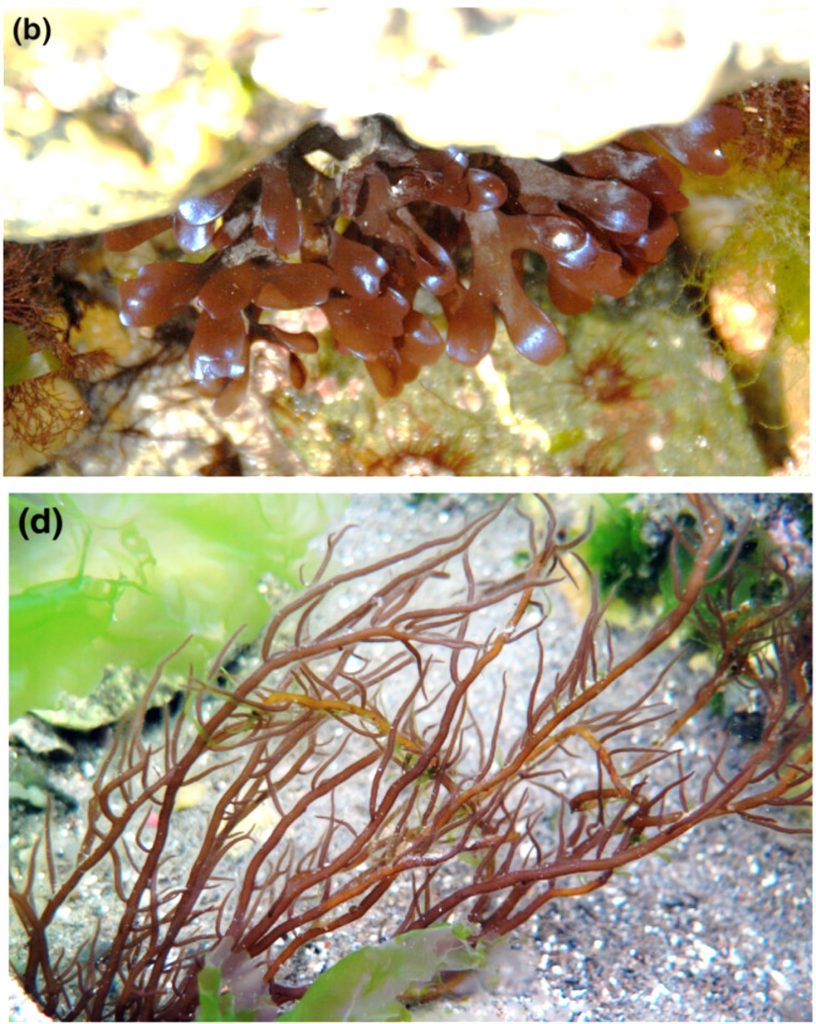

Review: Red macroalgae in the genomic era
Plant Science Research WeeklyI highly recommend this excellent and accessible article by Borg et al. that provides an overview of the red macroalgae, which “may have been the first eukaryotic lineage to have evolved complex multicellularity”. It’s full of fascinating information: although 97% of red algal species are marine,…
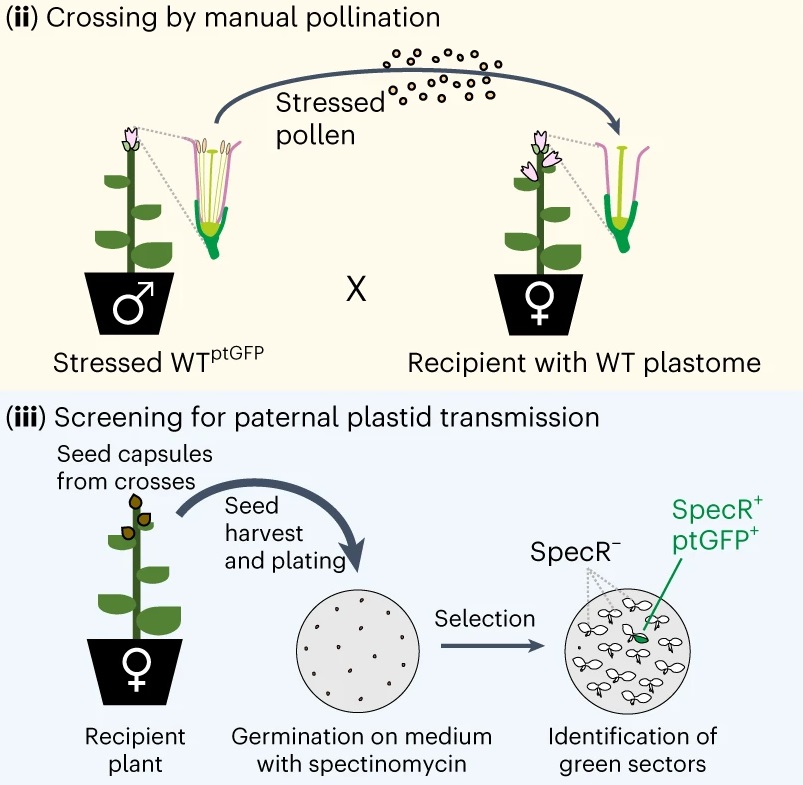
A paternal perspective on maternal inheritance
Plant Science Research WeeklyNuclear DNA is inherited from both parents during sexual reproduction, but organellar DNA is (usually) exclusively received from the mother. However, stable biparental inheritance of organellar DNA has also been reported in plants and animals but its molecular mechanism is unknown. Using quantitative…
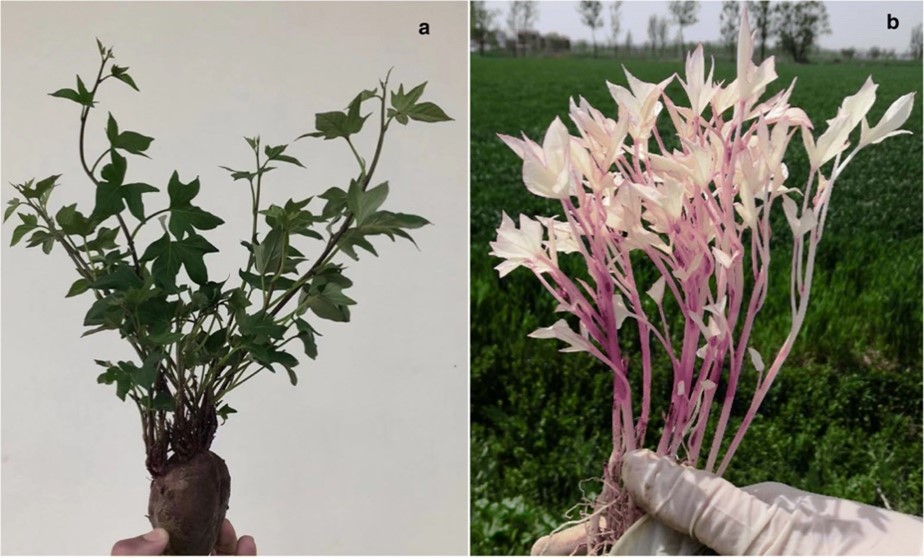

Transcriptome sequencing of a novel albino mutant of hexaploid sweetpotato (Plant Mol Biol Rep)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlbino plants lack chlorophyll, which means that they cannot photosynthesize. These kinds of plant are unique and can offer information as to the molecular mechanism of chlorophyll degradation and photosynthesis in plants. Here, Arisha et al. explored the differences in gene expression patterns of seedling…
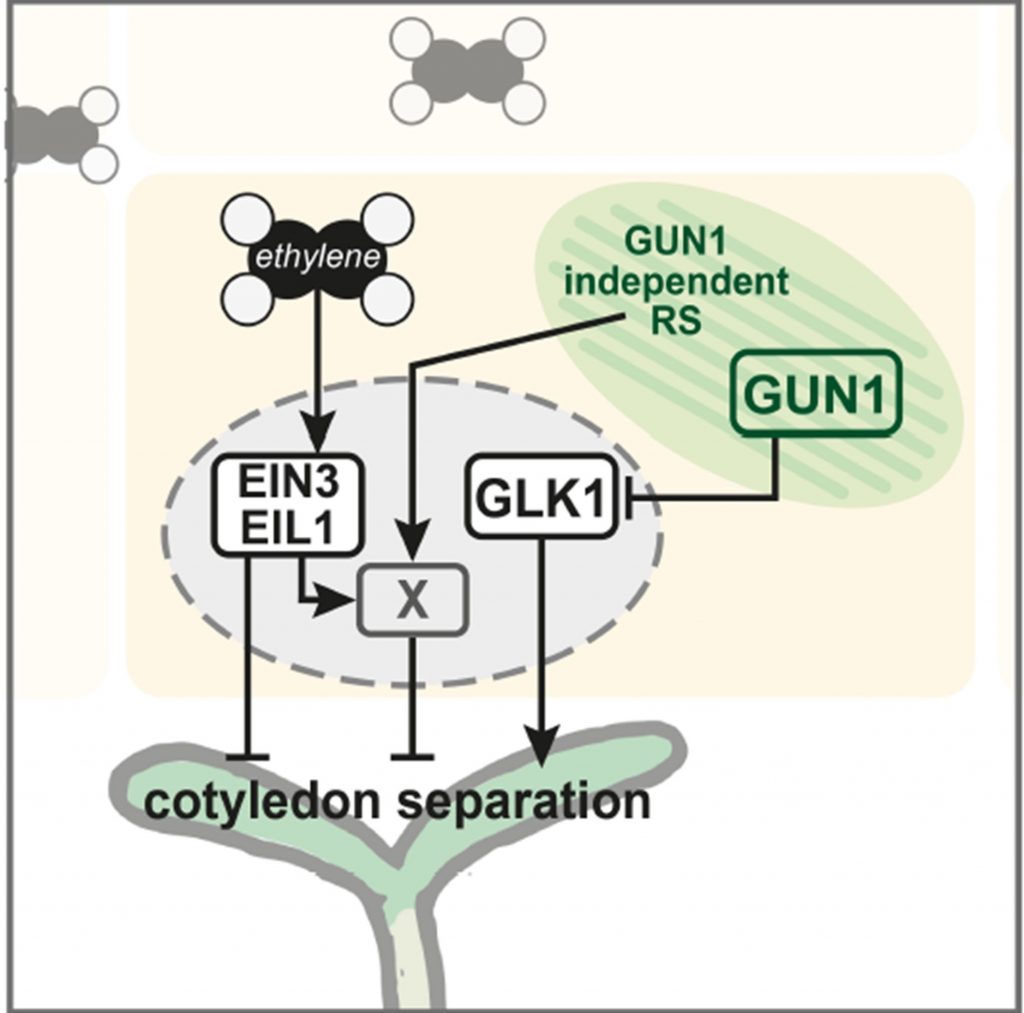
A novel GUN1-independent retrograde signaling pathway represses photomorphogenesis (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeedlings emerging in light undergo photomorphogenic development, forming short hypocotyls and green, fully opened cotyledons. Disruption of chloroplast development by drugs such as lincomycin induces retrograde signals (RS) that inhibit photomorphogenesis. The retrograde signaling pathway has been known…
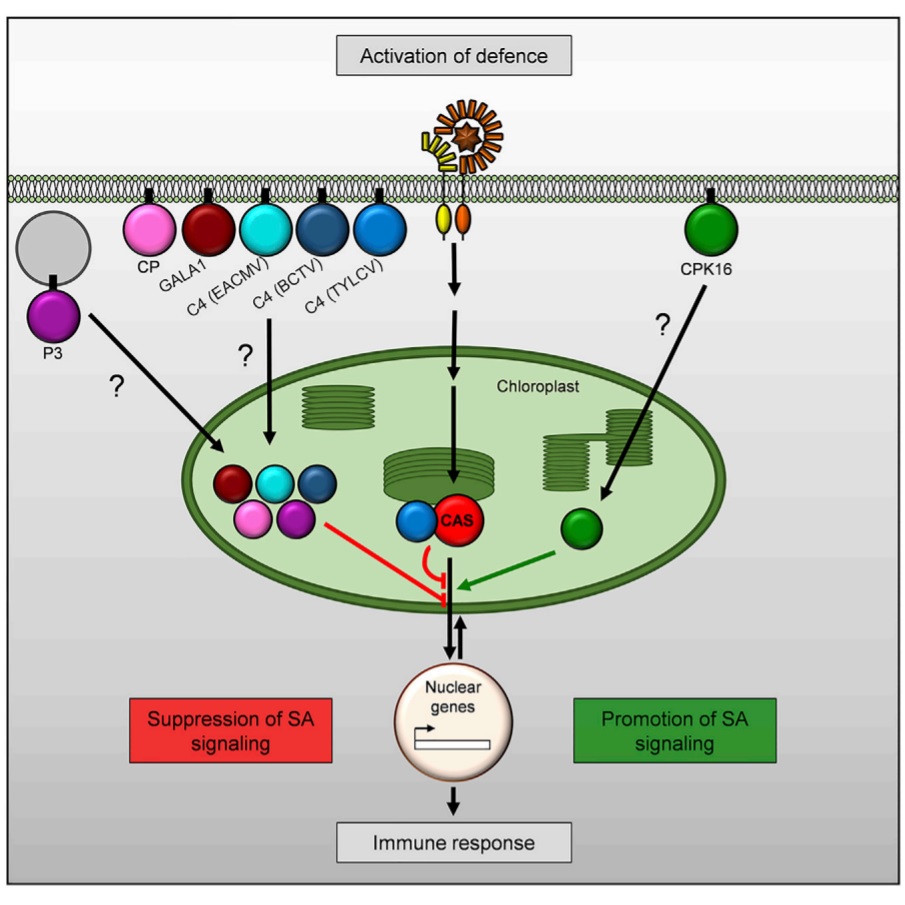
More than photosynthesis: The chloroplast’s role in plant cell defense pathways ($) (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChloroplasts are involved in various plant cell functions outside of photosynthesis including defense activation. How is the chloroplast able to do so? In this study, Medina-Puche et al. characterized the molecular function and cellular localization of the Tomato yellow leaf curl virus-derived C4 protein.…

