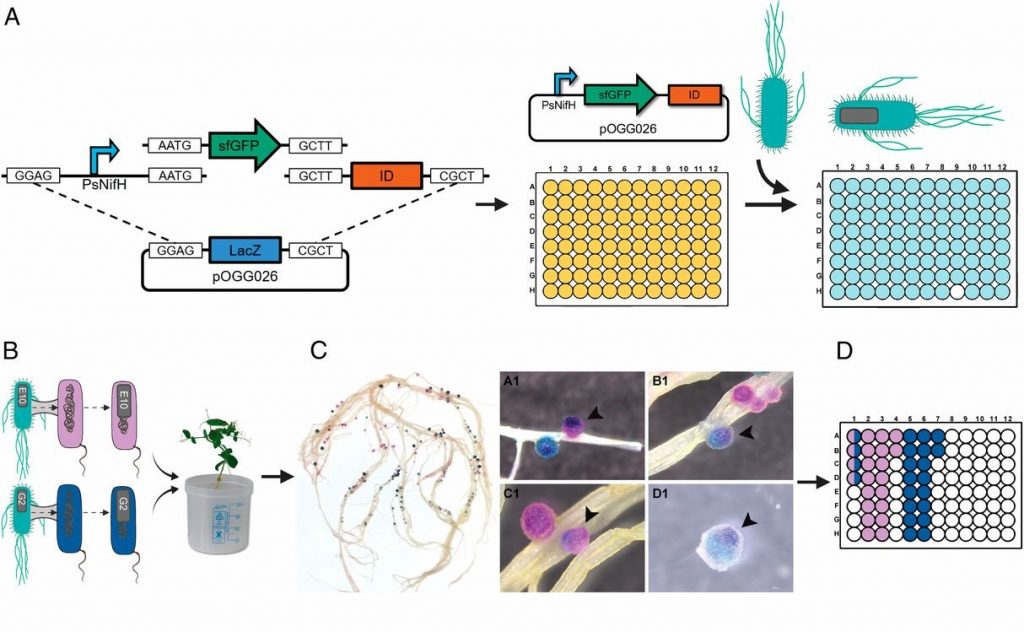
A molecular toolkit for screening elite rhizobia (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyN2-fixing rhizobia bacteria are able to establish symbiotic interactions with legumes in specialized organs called root nodules. Identifying elite rhizobia that are both competitive for nodule occupancy and effective in N2 fixation in agricultural environments is crucial for maximizing the yield of legumes.…
A regulatory module for survival on low potassium (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPotassium ions (K+) play a variety of important roles in plant physiology and are maintained at a high concentration in the cytosol relative to the available K+ in the environment. Potassium may accumulate to an even higher concentration in the vacuole, where it helps to regulate turgor pressure. During…
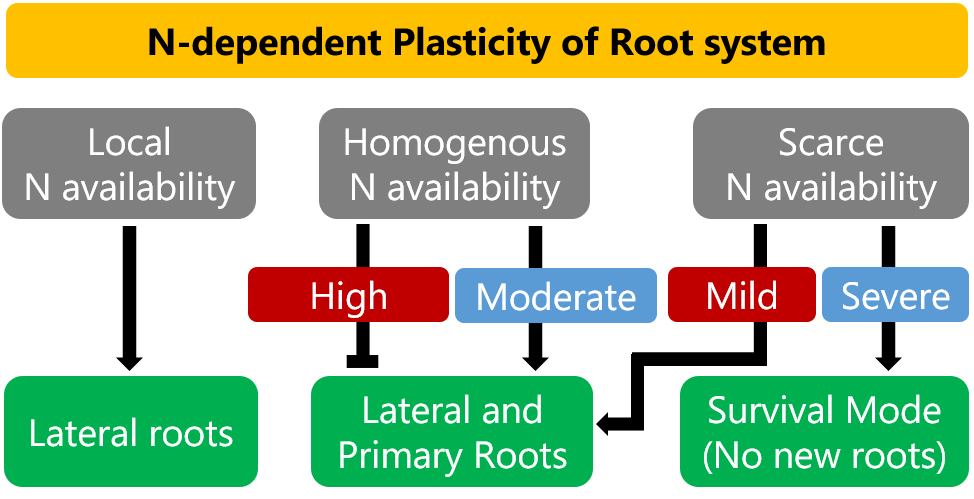
Review. Signalling pathways underlying nitrogen-dependent changes in root system architecture: from model to crop species (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen (N) is one of the seventeen essential nutrients for a plant to complete its life cycle and is one of the most important determinants of productivity of various crops globally. Nitrate (NO3‑) and ammonium (NH4+) are the major plant-available forms of N. The spatiotemporal heterogeneity of N…
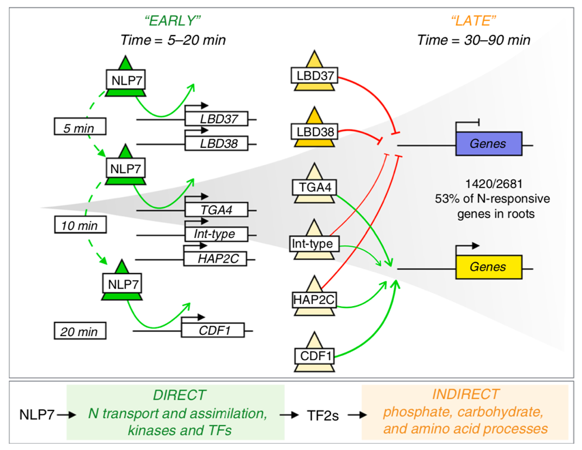
Transient genome-wide interactions of the master transcription factor NLP7 initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTranscription factors (TFs) and their genome-wide targets form gene regulatory networks that allow organisms to respond to stimuli. However, conventional biochemical assays only identify a subset of the TF-target interactions. In this paper, Alvarez et al. elucidate the genetic network of NIN-LIKE PROTEIN…
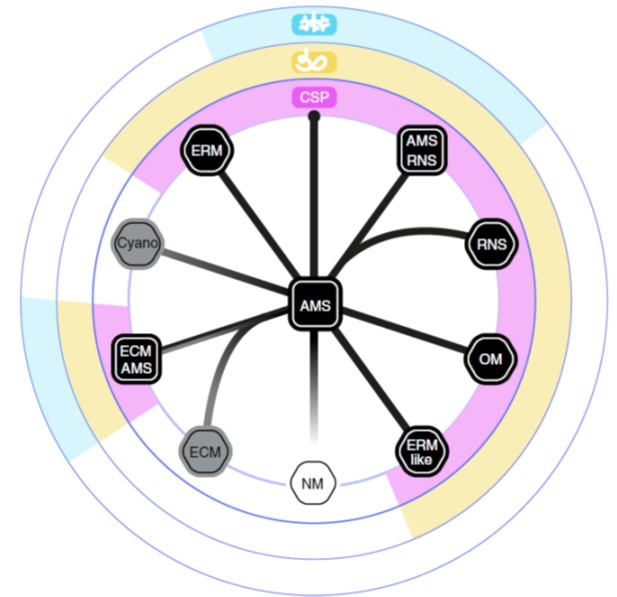
An ancestral signalling pathway is conserved in intracellular symbioses-forming plant lineages ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s widely thought that plants acquired the ability to live on land thanks to a little help from their friends, specifically arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Even now, most land plants form mutually beneficial associations with fungi or bacteria, and these often involve the plant cells acting as hosts…

Review: How mycorrhizal associations drive plant population and community biology ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGreat strides have been made in discovering the molecular players that allow plants and mycorrhizal fungi to establish their symbiosis. Here, Tedersoo et al. look beyond the single plant and address how these associations affect plant communities. Notably, they review the functions of the four evolutionarily…
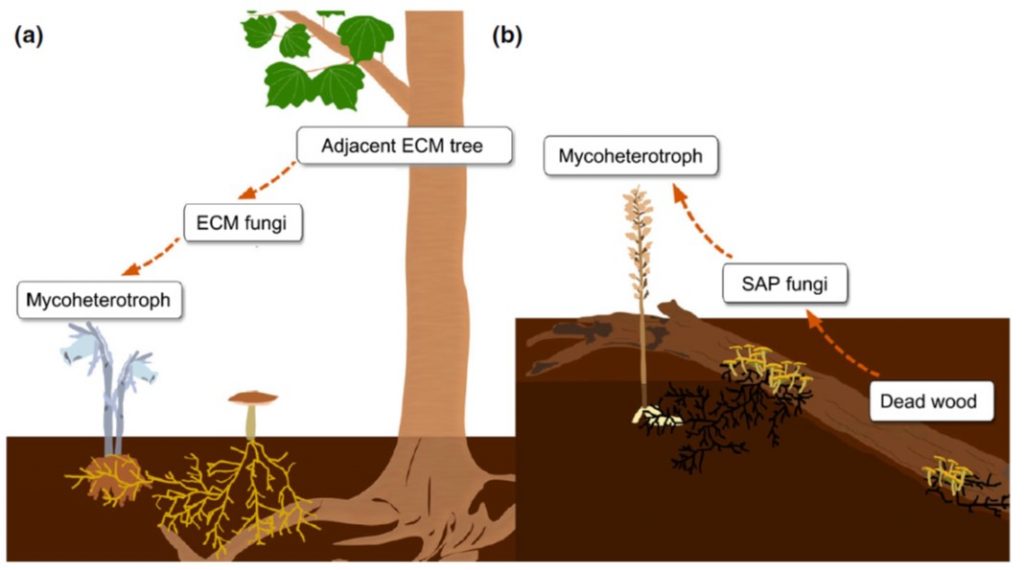
Some mycoheterotrophic orchids depend on carbon from deadwood: novel evidence from a radiocarbon approach (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA mycoheterotrophic ("fungal-other-eating") plant takes carbon nutrients from a fungus, but as fungi are not themselves photosynthetic, the (ectomycorrhizal) fungus must get its carbon from somewhere, usually a plant. Thus the typical flow of carbon goes from autotrophic photosynthesizing plant to fungus…
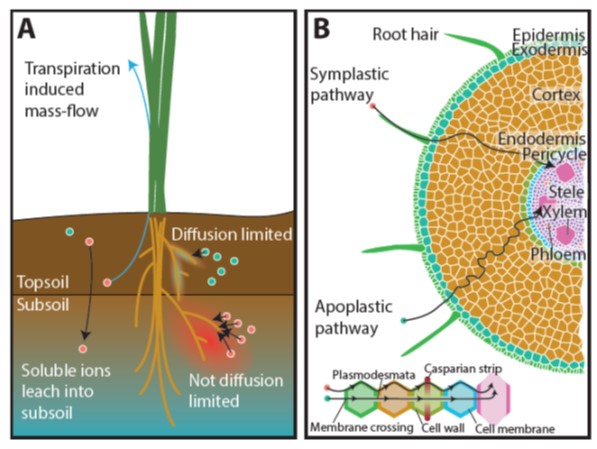
Review: Targeting root ion uptake kinetics to increase plant productivity and nutrient use efficiency (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots anchor plants and take up water, but one of their most important and complex functions is to bring a large number of different essential nutrients into the plant. Root architecture affects and is affected by nutrient uptake, but ultimately uptake is largely controlled by membrane-bound ion transporters.…

Review: Methods to visualize elements in plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plant Science Research Weekly: February 14
February 14, 2020/in Blog, WWR Full Post /by Mary Williams
Review: Deep learning for plant genomics and crop improvement
One of the goals of plant science is to use the molecular phenotype (genome, transcriptome, proteome) to predict the…

