
Coordination between microbiota and root endodermis supports plant mineral nutrient homeostasis (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots have been described as the gut of the plant, as they are the main interface for nutrient and water intake from their surrounding environment. This interface is remarkably complex. Not only must the root allow for the proper diffusion of substances into the plant, but by virtue of being constantly…
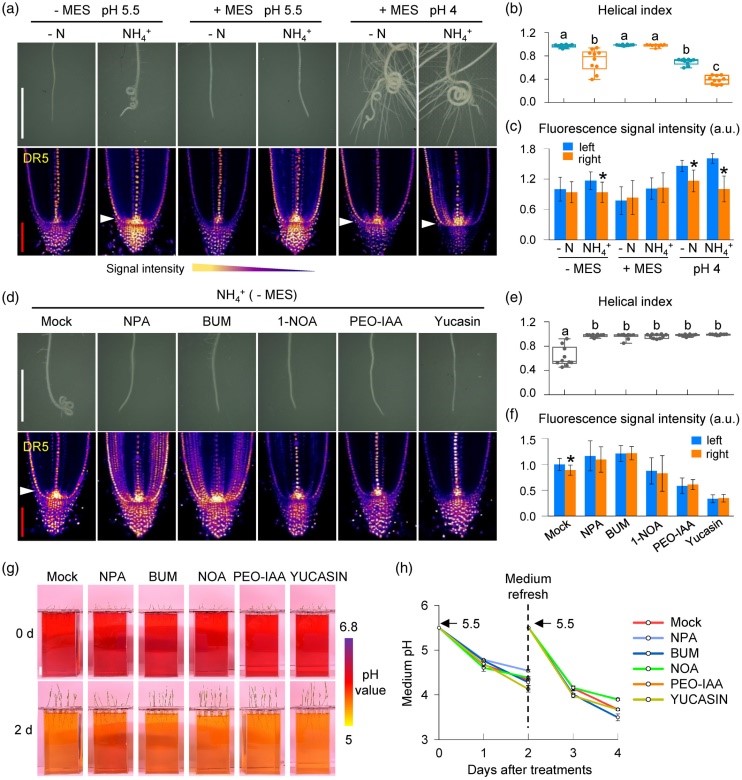
Spiral down: Rice plants adopt helical root growth under ammonium stress (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhile ammonium ions (NH4+) serve as important sources of nitrogen nutrition, higher concentrations are toxic and inhibit plant growth and development. In an attempt to understand how roots of rice plant adapt to high concentrations of NH4+, Jia and colleagues found the roots coil and adopt a helical…
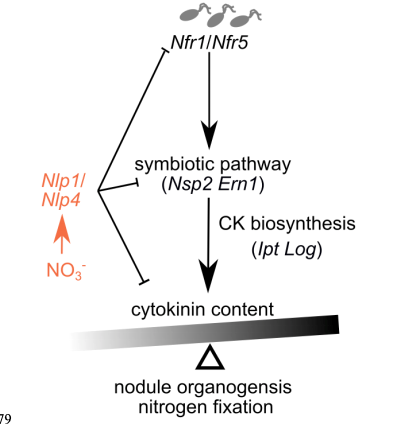
Nitrate inhibits nodule organogenesis through inhibition of cytokinin biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe symbiotic association between legumes and nitrogen-fixing rhizobia leads to the formation of nodules in roots, which supply nitrogen to the plant in low soil nitrate condition. In contrast, the presence of high nitrate reduces nodule formation. Cytokinin (CK) biosynthesis plays a major role in nodule…

Identification of a unique ZIP transporter involved in zinc uptake via the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal pathway (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLast week, PSRW presented two review papers regarding host plant interactions with microbial populations, particularly for plant nutrient intake. Watt-Williams et al. utilize such knowledge for their paper, performing an RNA-seq dataset to identify a novel zinc transporter in Medicago truncatula. Zinc…
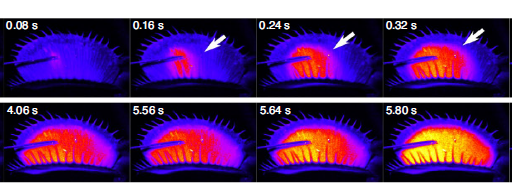
Calcium dynamics during trap closure visualized in transgenic Venus flytrap (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research Weekly
For centuries, carnivorous plants and the mechanisms they use to capture prey have been enigmas. While some clarity regarding the molecular mechanisms is beginning to emerge, Suda and colleagues have uncovered a vital role for calcium (Ca2+) signals in trap closure in Venus flytrap. The researchers…

Vascular transcription factors guide plant epidermal responses to limiting phosphate conditions (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants produce more root hairs (epidermal projections) in response to low soil phosphate and the detailed mechanism of this developmental response remains elusive. TARGET OF MONOPTEROS 5 (TMO5) and LONESOME HIGHWAY (LHW) are vascular specific bHLH proteins that work as a heterodimer to activate the rate…
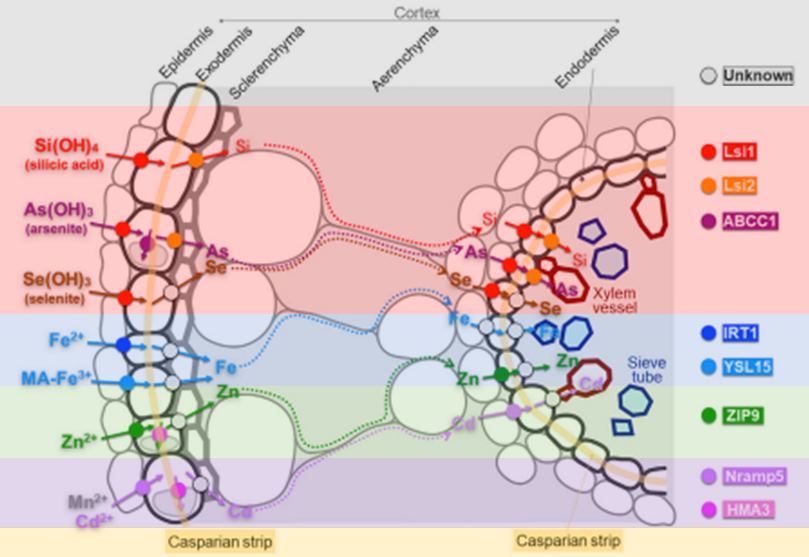
Review. Plant nutrition for human nutrition: Hints from rice research and future perspectives
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmong all the mineral elements transported from the soil to the plant, cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As)- are toxic for all organisms whereas 13 micronutrients, including iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn), are beneficial for both human and plant nutrition. Ideally, food crops should accumulate fewer soil contaminants…
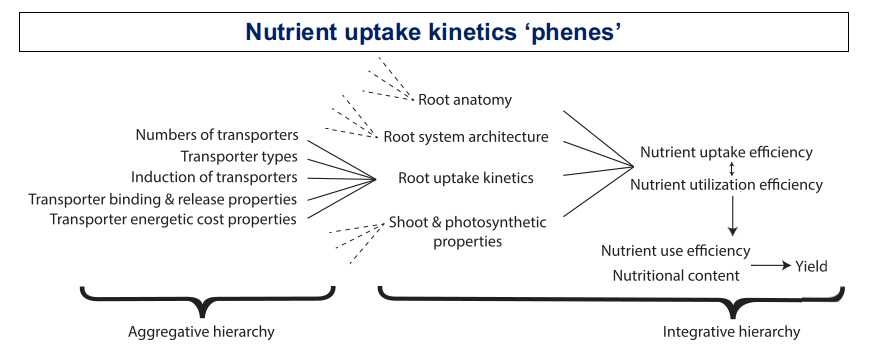
Review: Targeting root ion uptake kinetics to increase plant productivity and nutrient use efficiency (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyContinuous agricultural production is required to feed the growing population, and fertilizers are important factors determining the productivity of today’s high-input agriculture. Fertilizers increase the cost of production, some are produced from finite sources, and some create environmental concern,…

Nutrient dose-responsive transcriptome changes driven by Michaelis–Menten kinetics underlie plant growth rates (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can increase their growth and biomass proportionately to an increase in nutrient dose and, conversely, their growth is limited by limiting nutrients. In this study, Swift et al. explored the molecular underpinnings of the nutrient dose-response phenomenon. The authors first show that nitrogen-dose…

