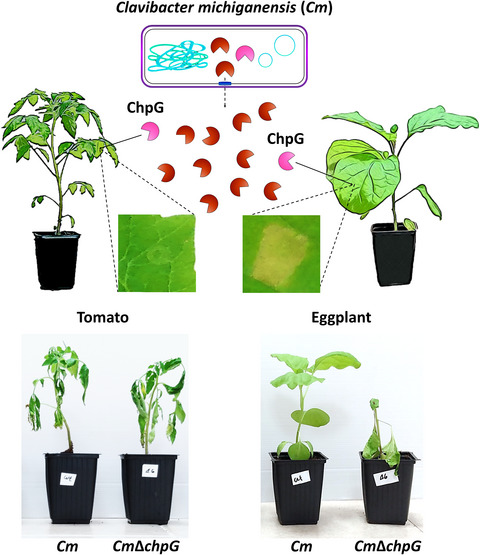
Bacterial avirulence gene encodes for a secreted protease and restricts host range (Mol Plant Path)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant pathogenic bacteria of the genus Clavibacter tend to have a narrow host range, but different species affect many important crops. Clavibacter michiganensis (Cm) causes bacterial wilt and canker in tomato, pepper and a few varieties of eggplant. There are no Cm-resistant tomato varieties but many…
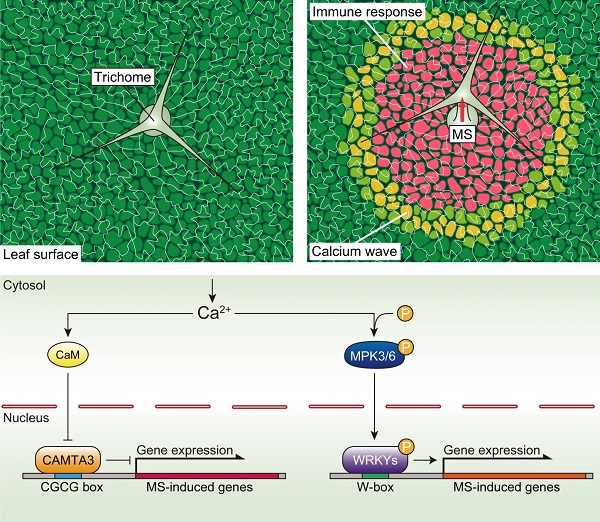
Always prepared: priming of the defense response by trichomes (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRain contributes to plant disease. Rain can contain high concentrations of pathogens (like Pseudomonas, Xanthomonas, Alternaria, Fusarium sp., etc.), and high humidity associated with rain antagonizes stomatal closure, leaving open entry points for some pathogens. Matsumura and colleagues have demonstrated…
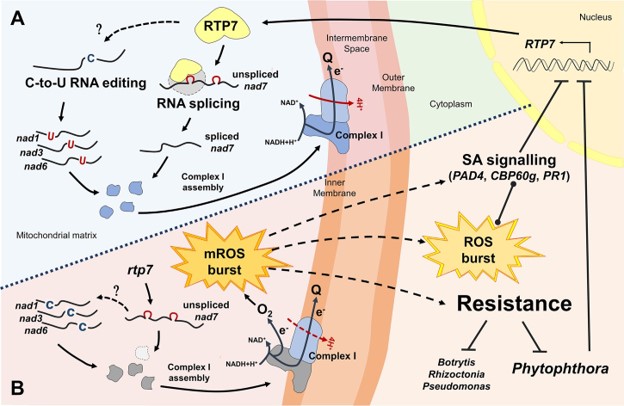
A mitochondrial RNA processing protein mediates plant immunity to a broad spectrum of pathogens by modulating the mitochondrial oxidative burst (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytophthora are a group of oomycete pathogens that infect a wide range of plants and cause disease in many important crop species. Large scale mutant screens have previously been used to identify Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with enhanced resistance to P. parasitica. Here, Yang and colleagues investigate…
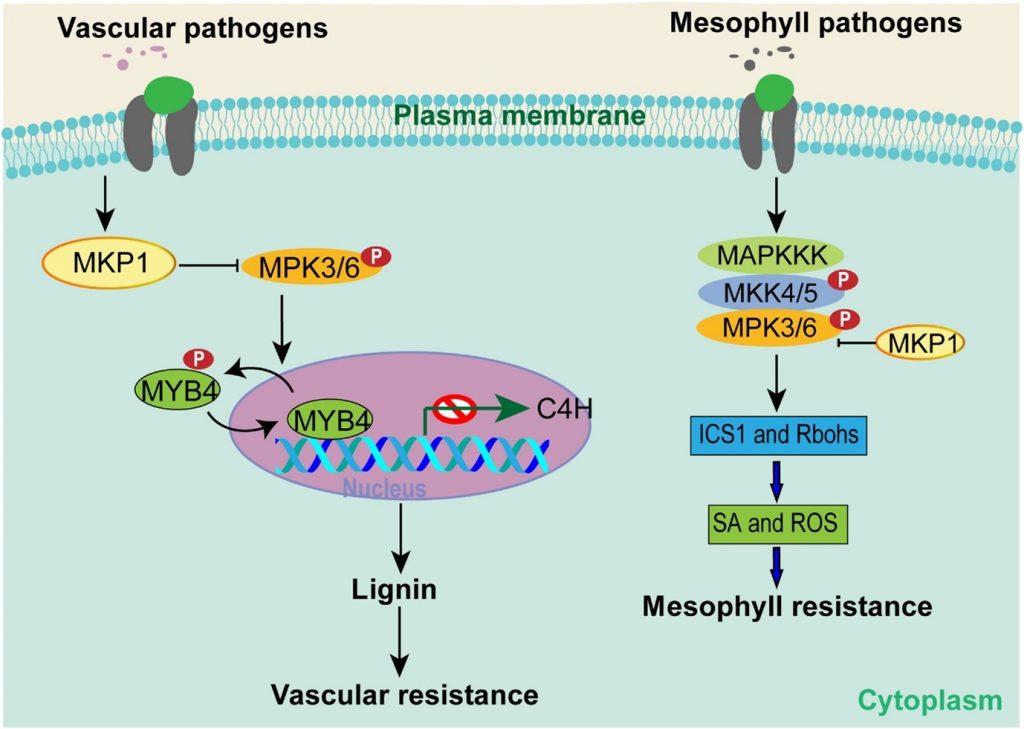
MAP kinase cascade acts as a hub to decide the ways to fight infection (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of our understanding of plant immunity comes from studies of pathogens that infect mesophyll tissues, (e.g., Pseudomonas syringae). However, there are many pathogens that specifically invade vascular tissues (e.g., Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; Xoo), which causes rice bacterial blight. In a recent…
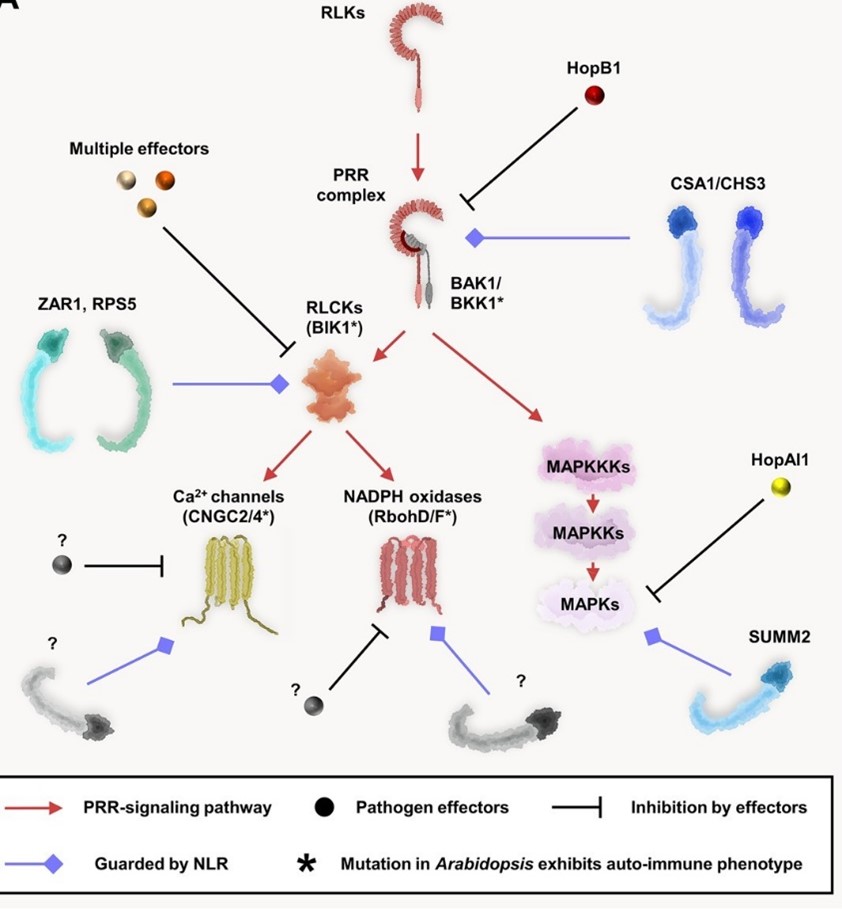
Review. The complex zigzagging in the plant immune system (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyI remember when I joined my PhD lab, the first article I was recommanded was a review by Jones and Dangl (2006) titled “The plant immune system”. Even today it remains the first article given to newbies in the lab. But the field has progressed way ahead in the more than fifteen years since that article…
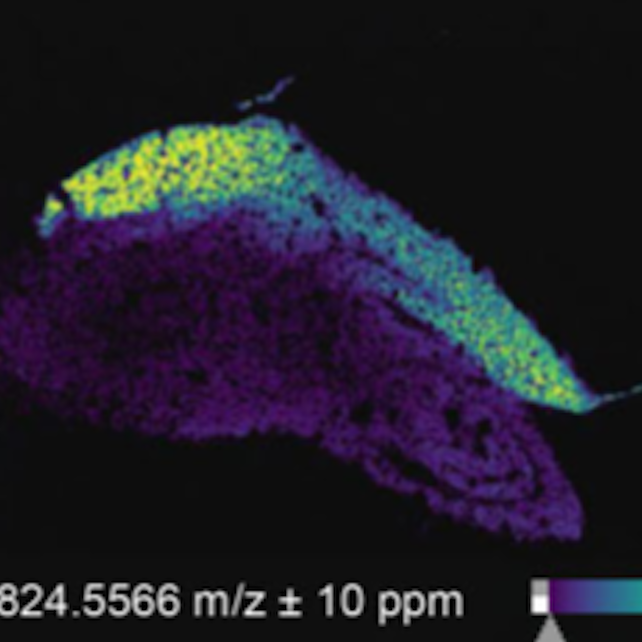
Shielding the oil reserves: the scutellum as a source of chemical defenses (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIf you work with grasses, you are probably familiar with the scutellum –the shield-like cotyledon typical of seeds from these plants. This structure has a renowned role in transferring nutrients to the growing embryo. However, Murphy and colleagues show us that not only does this structure look like…

Coordinated evolution of plant immune receptor repertoires (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants, immune signalling and the corresponding defence responses are initiated by direct or indirect recognition of pathogen molecules via immune receptors. In the plasma membrane, pattern-recognition-receptors (PRRs) recognize signs of invasion and pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) is initiated.…
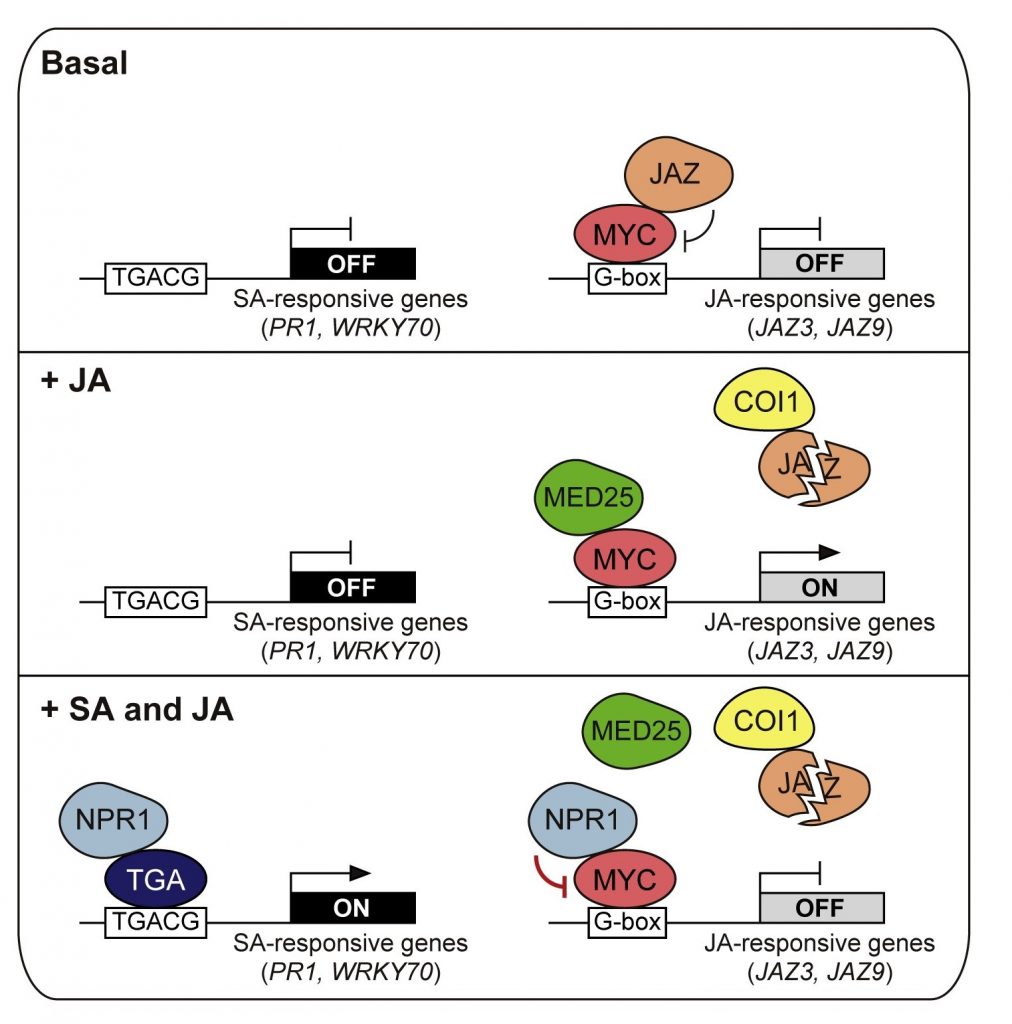
Suppression of MYC transcription activators by the immune cofactor NPR1 fine-tunes plant immune responses (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Arabidopsis, NONEXPRESSOR OF PR GENES 1 (NPR1) plays an important role in the antagonistic crosstalk of salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) signalling. It activates SA-induced genes that protect against biotrophic pathogens and suppresses JA-induced genes that protect against necrotrophic pathogens.…

CPK28 is targeted by the ubiquitin ligases ATL31 and ATL6 for proteasome-mediated degradation to fine-tune immune signaling
Plant Science Research Weekly‘Fine tuning’ is a very significant process that takes place in the cell to correctly modulate plant responses. BOTRYTIS-INDUCED KINASE 1 (BIK1) is an important hub protein that is at the center of the signaling hub that controls defense responses. Hence, plants fine tune this important protein through…

